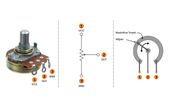
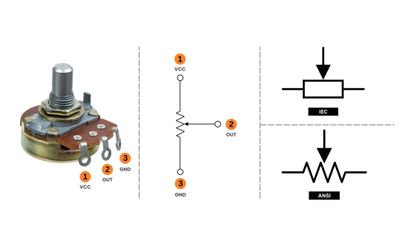
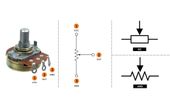
Source Transformation: Theory, Methods, and Practical Implementations for Modern Electronics and Digital Design
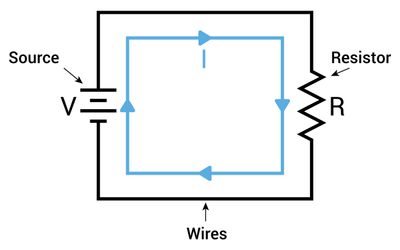
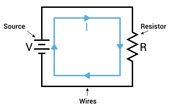
Source transformation is the method of converting a voltage source with series resistance into an equivalent current source with parallel resistance (and vice versa). This guide explains the theory, math, circuit examples, and practical applications for modern digital and hardware engineers.