UWB in the Enterprise Hospital - Enabling Precision-Aware Patient Care
Ultra wideband enables centimetre-accurate location radar sensing and secure RTLS in hospitals, improving patient safety, staff efficiency, asset tracking, and navigation.
Hospitals want more efficient and personalized care, but traditional technologies ( e.g., BLE, Wi-Fi, RFID) often lack the precision and reliability necessary to deliver it. To support a new generation of precision-aware patient care, many designers are turning toward ultra-wideband (UWB) technology as a new solution.
UWB is highly sought after due to its unique ability to provide high-ranging and angular accuracy, robust security, and advanced sensing capabilities that surpass those of existing systems. Rather than simply offering precision, UWB excels at accurately estimating both the distance and direction between devices, which is simply unmatched by other short-range wireless technologies
For these reasons, major enterprise vendors like Cisco and Juniper are already embedding UWB radios directly into next-generation Wi-Fi access points, enabling hospitals to deploy precision location services without standalone infrastructure. With these capabilities, UWB can enhance hospital operations with a multitude of new features and functionalities.
Why Hospitals Need Precision-Aware Infrastructure?
Time is of the essence in hospital care, as even a few minutes or seconds in care delivery can significantly impact a patient's health. Yet modern hospitals are also uniquely dynamic and high-density environments. Crowded wards, staff shortages, and equipment bottlenecks often create inefficiencies that can hinder care delivery.
To organize and orchestrate, hospitals have long relied on location systems that track the movement of patients, staff, and equipment across facilities. These systems, often referred to as Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), feed data into dashboards that help administrators manage patient flow, locate equipment, and monitor staff activity for both efficiency and safety.
Current RTLS deployments typically operate using Wi-Fi triangulation, RFID tags, or BLE beacons. While useful, these methods usually provide accuracy only within a few meters. In tangible terms, hospital workers might be able to identify that an infusion pump is on a particular floor, but not which storage closet it occupies. Or they could confirm that a patient is in the right wing, but not which room. With limited granularity, location data is ineffective, causing delays, equipment misplacement, and potential safety risks.
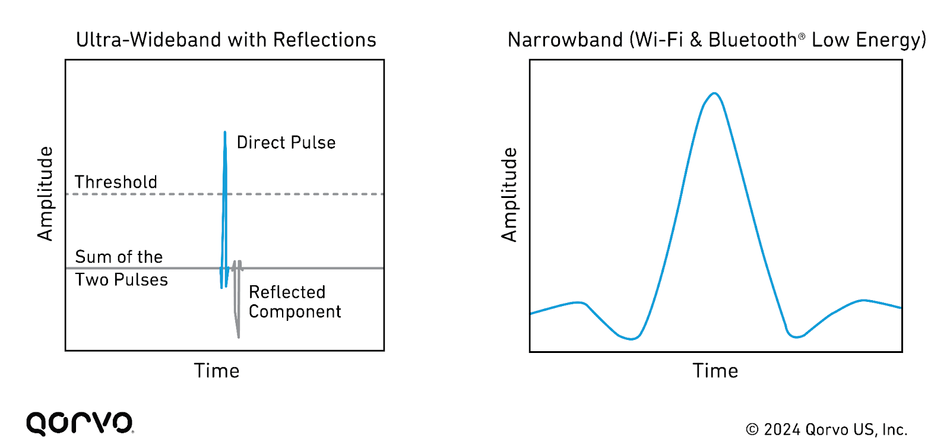
UWB technology resolves these issues with its design specifically for high-precision positioning and sensing. Where Wi-Fi, BLE, or RFID are designed for other applications and are retrofitted for location tracking, UWB was engineered from the start to measure distance and position with extreme accuracy. By transmitting ultra-short pulses across a wide spectrum, UWB calculates the time of flight between anchors and tags, thereby determining both range and angle with centimeter-level accuracy. This gives it the unique ability to provide fine-grained location data even in crowded, interference-heavy hospital environments. UWB also maintains accuracy in non-line-of-sight conditions, penetrating walls and equipment clutter that can confound other systems.
Real-Time Patient & Staff Location Tracking
The ability to locate patients and staff with room-level granularity is not enough for modern healthcare. With its improved performance, UWB unlocks continuous, precise tracking that can distinguish between individuals in crowded spaces and provide exact location data within a few centimeters.
Such a level of precise tracking direct impacts patient safety. In a dementia ward, for instance, badges equipped with UWB can issue alerts the moment a patient tries to exit a secure area. During an emergency code, the same system can identify the closest staff member and direct them straight to the patient’s location. Beyond safety, the technology also supports efficiency by allowing hospitals to allocate tasks in real time based on where staff members are and who is available.
A useful parallel comes from professional sports. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the European League of Football used UWB micro-location to track player proximity in real time and identify exposure chains. Hospitals can adapt the same tag-and-anchor model to monitor patient movement and run contact tracing during outbreaks.
Ultimately, UWB-enhanced location precision translates into better patient outcomes. Faster response times, improved safety protocols, and optimized staff workflows simultaneously reduce risk and improve overall quality of care.
Vital Signs Monitoring with UWB Radar Sensing
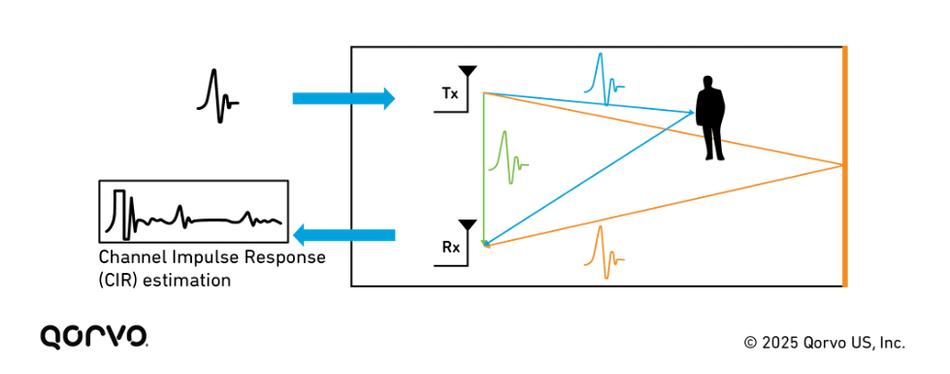
Beyond tracking, UWB also functions as a radar sensing technology with medical applications. By transmitting ultra-short pulses and analyzing their reflections, UWB radar algorithms can detect the subtle chest movements caused by breathing or the micro-motions associated with a beating heart. As a result, UWB-based radar can measure respiration, heart rate, and movement without wearable devices.
UWB broadens how hospitals monitor patients. Conventional systems use contact sensors such as pulse oximeters or chest straps that can irritate skin and restrict movement. UWB radar senses respiration and micro-motion through bedding and clothing, meaning patients can stay covered in isolation rooms and during post-operative recovery. Typical radar modes draw less than 10 mW, so engineers can easily integrate UWB into enterprise access points or compact bedside monitors.
Applications include post-operative monitoring for apnea, where continuous observation without tethered devices improves patient comfort. In isolation wards, UWB reduces the need for repeated staff contact and minimizes exposure risks. And in neonatal and elderly care, fragile patients can be monitored without harm from adhesive-based monitors.
UWB radar benefits are augmented when integrated with AI-driven analytics platforms, where predictive models can detect anomalies such as irregular breathing or early signs of distress. By combining continuous, contactless monitoring with predictive intelligence, hospitals can embrace more proactive care strategies.
Asset & Equipment Visibility
For hospitals, accurate and real-time inventory is tantamount to patient safety and operational efficiency. For example, in the case of a patient emergency, mission-critical devices such as ventilators and defibrillators must be located within seconds. In general, hospitals lose significant time and resources each year due to misplaced or unavailable equipment.
UWB’s ranging and angular accuracy solves this challenge. Devices tagged with UWB can be tracked across multiple floors and through structural barriers, giving staff immediate visibility into their exact location via centralized dashboards. The primary and most obvious benefit is improved patient outcomes due to faster emergency response times. Beyond patient health, however, hospitals also benefit from avoiding unnecessary over-purchasing. Where hospitals often purchase excess equipment to compensate for losses, UWB improves the utilization of existing assets and reduces redundant costs.
UWB also supports compliance and auditing by maintaining historical records of the movement of sensitive equipment and pharmaceuticals. Just as factories use UWB-enabled digital twins to model workflows and optimize logistics, hospitals can construct real-time digital models of their assets and equipment. Improved visibility ensures that resources are present and correctly deployed, resulting in higher operational efficiency and readiness.
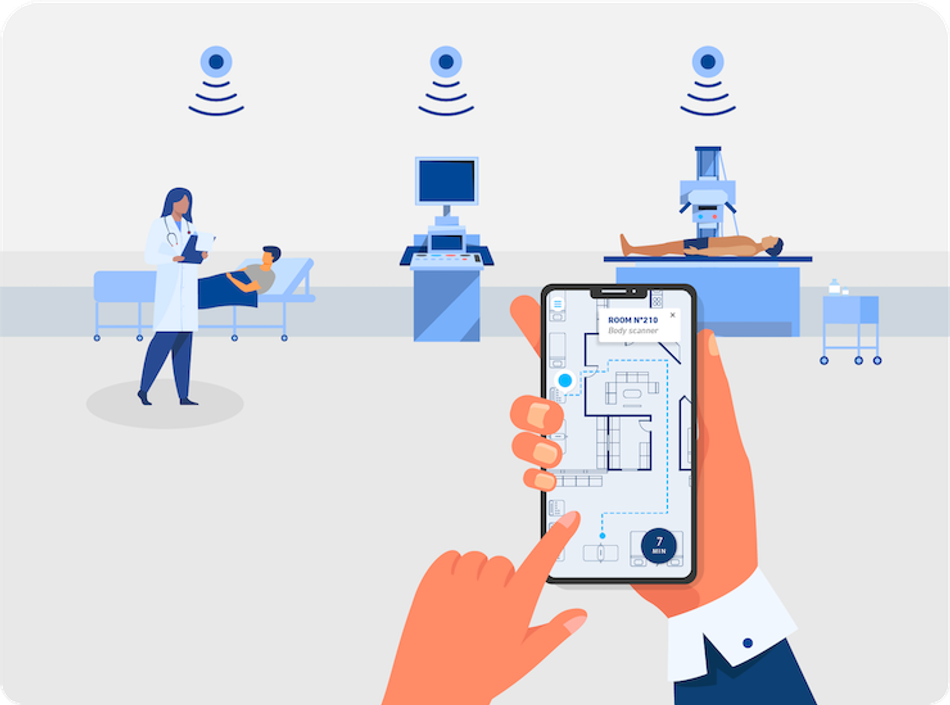
Indoor Navigation for Patients & Visitors
Navigating large hospitals is often compared to navigating airports. Long hallways, multiple wings, and complex layouts can leave patients and visitors disoriented. Missed appointments and late arrivals are common consequences.
UWB-enabled navigation systems can change this experience by providing turn-by-turn indoor directions with accuracy down to the room level. Where Wi-Fi triangulation only provides approximate locations, UWB can directly guide a patient to the correct department or waiting area. Visitors can locate ICU rooms, labs, or pharmacies without confusion, and staff can optimize routes for transporting patients or retrieving equipment. Hospitals are also beginning to deploy autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for the delivery of medications, lines, and supplies, and UWB can be used to enhance the navigation accuracy. This reduces human workload and guarantees timely deliveries in complex facilities.
If device compatibility is a concern, operators can combine Wi-Fi and UWB within the same ecosystem rather than choosing one or the other. In a hybrid approach, Wi-Fi handles broad coverage and basic connectivity, and UWB supplies the fine-grained positioning layer. A patient’s phone, for example, might use Wi-Fi to connect to the hospital’s digital navigation app. But once indoors, UWB anchors can refine that position to the exact hallway or room. Staff tablets could similarly rely on Wi-Fi for communications but tap into UWB data for precise equipment retrieval or patient handoff.
By layering the two technologies, hospitals marry the universal reach of Wi-Fi with the centimeter-level precision of UWB. The result is fewer missed appointments, smoother patient navigation, and higher throughput across operations.
Infrastructure & Ecosystem Readiness
For hospitals considering adoption, one of the biggest enablers is that UWB is no longer a standalone technology requiring a separate network. Cisco’s Wi-Fi 7 Catalyst access points and Juniper’s Mist ecosystem are early examples of this integration, where UWB radios are co-located with Wi-Fi radios to deliver precision location capabilities at the infrastructure level. This level of broad adoption removes deployment barriers by allowing hospitals to extend precision location services on top of their existing wireless networks. It also means that hospitals can adopt UWB without the prohibitive costs and barriers typically associated with integrating new enterprise technologies into existing IT and OT.
The broader ecosystem also already supports UWB adoption, as smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices are already shipping with embedded UWB chips, such as Apple’s U2 and equivalent Android platforms. As the technology is more widely adopted by hardware giants, costs will decrease, and adoption will be more feasible.
One last reason to adopt UWB is the enhanced security levels it uniquely offers. Specifically, UWB incorporates encrypted timestamp sequences (STS) and AES-based cryptography to protect against spoofing and relay attacks. These built-in features make UWB compliant with tight healthcare security requirements and give hospitals confidence in deploying the technology at scale.
Conclusion
Legacy RTLS and monitoring systems are no longer sufficient for the accuracy and responsiveness demanded by modern healthcare. UWB is a ready-to-deploy technology that fills this gap with centimeter-level location ranging accuracy, radar-based vital sign monitoring, and secure, scalable infrastructure.
As UWB integrates into enterprise Wi-Fi access points, hospitals can create more precision-aware environments that can anticipate needs, minimize risks, and deliver safer, faster, and more personalized outcomes.
The next-generation of patient care will depend on precision. With UWB, hospitals are finally equipped to deliver it.