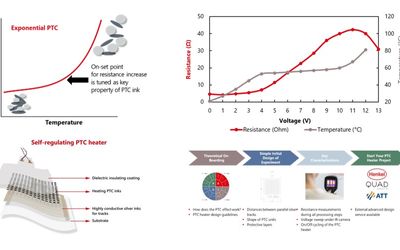
Thermal imaging for remote patient monitoring: Winners of the OKdo Engineering Challenge Wevolver Community Vote
In response to the OKDo Engineering Challenge, Marcel Ochsendorf and Sebastian Kindorf developed a medical device that uses thermal imaging for remote patient monitoring. Their innovative project won the Wevolver Community Vote.