Be the first to know.
Get our Semiconductors weekly email digest.
Semiconductors
PCB Trace Width Calculator
Glossary of Semiconductors Terms
Engineers Wiki. Most Asked Questions.
Comprehensive Guide
Semiconductors are the building blocks of modern electronics, powering everything from smartphones to satellites. This in-depth guide provides a comprehensive understanding of semiconductors' engineering principles and applications, delving into their fundamental concepts, materials, devices, manufacturing processes, and their impact on today's technology landscape.
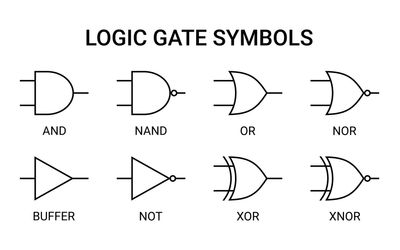
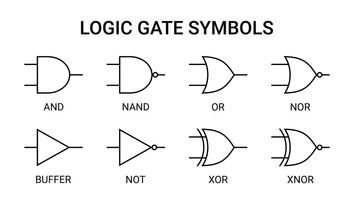
Understanding Logic Gate Symbols: Comprehensive Guide for Engineers
By Umar Waseem.
15 minutes read.
Transistor Circuit Design – Theory and Practice for Modern Engineers
By Muhammad Sufyan.
14 minutes read.
UART Protocol: Understanding Serial Communication for Engineers
By Ramsha Jawaid.
18 minutes read.
Arduino UNO Pinout: Comprehensive Guide for Engineers and Students
By Umar Waseem.
16 minutes read.
How to Read Resistor Color Code: Theory, Practice and Design
By Umar Waseem.
13 minutes read.
Transistor Circuits: Theory, Types, and Practical Applications
By Ramsha Jawaid.
23 minutes read.
View more
ORGANIZATIONS. SHAPING THE INDUSTRY.
Nordic Semiconductor
Semiconductors
Nordic Semiconductor is a fabless semiconductor company specializing in wireless technology that powers the IoT.
181 Posts
View more