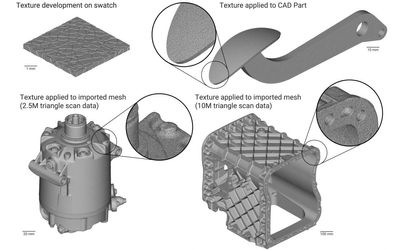
Podcast: How to Turn Gum into Shoes, Reducing CO2 in Construction by 40 percent, High-Speed Flying Boats
In this episode, we talk about a company that is upcycling chewed and unwanted gum to create polymer based products, a software solution to reduce embodied carbon in construction projects, and a Boston based startup that is planning to change the way consumers think about coastal transportation.