Tagged with
additive manufacturing
ORGANIZATIONS. SHAPING THE INDUSTRY.
polySpectra
Additive Manufacturing
We help innovative engineers 3D print end-use components they can trust usi...
12 Posts
FACTUREE – The Online Manufacturer
Manufacturing | Procurement
The digital all-in-one solution for effortless procurement of custom parts
12 Posts
Latest Posts
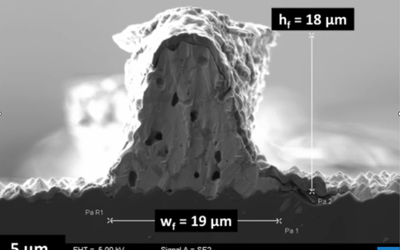
Combining SLA 3D printing and soft lithography for fast, versatile, and accessible high-resolution fabrication of customised multiscale cell culture devices with complex designs
Taking advantage of low-cost, high-resolution desktop resin 3D printers combined with PDMS soft-lithography we have developed an optimised microfabrication pipeline capable of generating a wide variety of customisable devices for cell culture and tissue engineering in an easy, fast reproducible way
Meet Keiron Printing Technologies: the startup building the next generation microfabrication machine
A young team with a new technology are currently creating a revolution in the world of printed electronics. In their modern, brand-new lab at the High Tech Plaza, they will be developing a device that can deposit any material on any substrate at a very rapid pace.