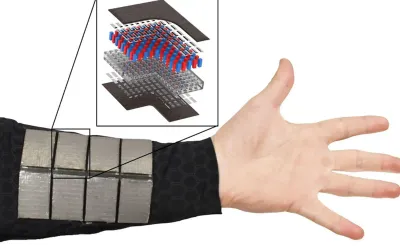
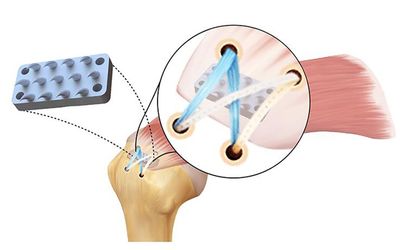
healthcare
In this episode, we explore the groundbreaking invisible mask developed by a University of Michigan spin-off that is equipped with a wearable air curtain capable of killing viruses and blocking 99.8% of aerosols.
Engineers Wiki. Most Asked Questions.
The applications of 3D printing span many industries, from aircraft fuel nozzles to dental aligners. Here we look at some of the most important uses of the technology.
Capacitors in Parallel: Theory, Design, and Practical Implementation
14 minutes read.
Understanding AMR Robots: A Comprehensive Guide
15 minutes read.
Applications of TinyML in healthcare for a safer future
6 minutes read.
ORGANIZATIONS. SHAPING THE INDUSTRY.
The Next Byte
Entertainment
The Next Byte Podcast is hosted by two young engineers - Daniel and Farbod - who select the most interesting tech/engineering cont...
165 Posts
High Tech Campus Eindhoven
High Tech
High Tech Campus Eindhoven is Europe's smartest square km and has the ultim...
49 Posts
ETH Zurich
University for science and technology
Freedom and individual responsibility, entrepreneurial spirit and open-min...
43 Posts
Harvard University
University
At the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (...
42 Posts
View more