2023 Edge AI Technology Report. Chapter VIII: Case Studies
Inspiring Examples of Edge AI in Action.

2023 Edge AI Technology Report. Chapter VIII: Case Studies
Edge AI, empowered by the recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence, is driving significant shifts in today's technology landscape. By enabling computation near the data source, Edge AI enhances responsiveness, boosts security and privacy, promotes scalability, enables distributed computing, and improves cost efficiency.
Wevolver has partnered with industry experts, researchers, and tech providers to create a detailed report on the current state of Edge AI. This document covers its technical aspects, applications, challenges, and future trends. It merges practical and technical insights from industry professionals, helping readers understand and navigate the evolving Edge AI landscape.

Learning from applications
Edge AI is making its way into various industries, leading to some surprising innovations. With enhanced data processing capabilities and relatively lightweight integration into existing systems, Edge AI is emerging as an optimal solution for gathering precise, accurate, and insightful information. In this chapter, we compiled several case studies that demonstrate some of the extraordinary innovations in Edge AI, but first asked industry experts at semiconductor company ST about their approach to Edge AI. Here’s what they had to say:
Interview: A Glimpse into Edge AI From ST’s Perspective
How would you describe Edge AI?
There are many definitions in the market for what Edge AI is, but for us, it is very simple, the Edge is where a signal becomes data. This means that the Edge is literally within the machine or the sensors; this is why we also speak about embedded AI, meaning Machine Learning that runs in a microcontroller (MCU) or microprocessor (MPU).
What is the adoption trajectory for machine learning at the Edge?
Machine Learning at the Edge is a rapidly growing segment of the market. There are about ten billion connected devices, of which a very small number have embedded intelligence. However, according to several analysts, 25% to 40% of them will have embedded algorithms in production within four years, which means that billions of devices will rapidly become embedded-AI smart. We observe this trend now, with hundreds of clients either already in production or testing prototypes for deployment in 2024. We believe that thanks to our 10-year investment in Edge AI, a very large number of these deployments will be on ST’s platforms.
What are the benefits of Edge AI versus more traditional Cloud-based AI approaches?
Edge AI brings a set of advantages compared to the first generation of so-called smart devices, which were just connected to a Cloud and relied on the Cloud’s intelligence.
An embedded device will not constantly stream data to the Cloud, which in itself brings a number of benefits, including smaller bandwidth requirements, lower cost of connection, and of course, improved security as you don’t send raw data to the Cloud. Additionally, for battery-operated devices, the energy cost of constantly streaming data far exceeds the cost of inferring within the device and simply sending a report at a pre-set duration or when an anomaly occurs.
The total cost of operation will be way lower as there is simply no additional cost to inferring onto the device while running inferences in a Cloud can be costly, especially for vision-related use cases. This is why with the emergence of Edge AI, many solutions that simply were not affordable for the vendors as they required an expensive Cloud Service connection are now becoming affordable.
The total cost of energy of an Edge AI solution is significantly lower than a combo “Smart Device/Cloud AI” approach, like Milliwatts vs. kilowatts, which, when multiplied by thousands of devices, creates a very important difference and something that we and many of our clients are now very sensitive to.
What is ST’s machine learning at the edge’s mission?
Our mission is to enable Edge AI by facilitating the creation, implementation, and operation of Edge AI solutions by providing a set of software, examples, and hardware that will create and run the embedded ML models.
What are the main design and implementation challenges that developers face, especially newcomers? And how do ST platforms address these challenges?
We are engaged with hundreds of customers implementing their projects and have observed a number of patterns:
First, data collection is very often hard to do for them, especially when they need to create abnormal data for predictive maintenance solutions. Secondly, they are often constrained by MCU size and RAM and flash limitations. Thirdly, they are not always sure of how to handle their approach or build their models.
Our solutions precisely address these issues. Cube.AI allows optimizing models so that they run smoothly on MCU platforms, and NanoEdge AI Studio has a fully integrated data capture and data preparation tool that allows for easy data input for model creation and an optimized search engine that will select the best model for our client’s hardware constraints. And finally, with our model zoo, clients can have access to a wide range of examples that can inspire their own model creation.
What application segments is ST targeting with machine learning at the edge?
We think that Edge AI is a perfect fit for all kinds of needs where clients want a good level of service at an affordable price. Today, the two largest segments that our clients are deploying are predictive maintenance solutions and vision-related applications, where, in both cases, the availability of an edge solution is authorizing new deployments that clients had previously deselected because of the cost of ML Cloud processing.
Edge AI Case Studies
Sensory Inc. - Revolutionizing User Experience with Voice-Activated AI Technologies
One of the most profound changes in computing came years ago in the then-unheralded world of human-machine interface (HMI) design. Innovators figured out how to marry the right hardware with the right software to create voice-activated applications. In the nearly three decades since this application caught fire, it’s revolutionized everything from homes to personal assistants, computer programs, and automobiles. And leaders in the industry are just getting started.
Sensory Inc. has been developing software AI technologies for speech, sound, and vision out of Santa Clara, California, for the past 30 years. It has collaborated widely with industry leaders, including Arm and STMicroelectronics, to enhance the integration of its AI technologies and provide optimal solutions to customers. For example, Sensory has leveraged its long-standing partnership with Arm to support numerous chip partners using Arm Cortex-M4 microcontrollers with its Truly Hands-Free software, which enables devices with an extremely intelligent natural language user interface.
Two years ago, Sensory partnered with STMicroelectronics and their Arm Cortex-M7-based STM32H7 family. Sensory’s TrulyNatural technology typically runs on an application process found in appliances, like microwave ovens, and enterprise types of products, like Zoom. It can provide natural language processing with more than 50,000 unique phrases that it recognizes. By leveraging the Cortex-M7-based STM32H7 family and integrating it with VoiceHub, Sensory’s online portal enables developers to quickly create wake word models and voice control command sets for prototyping and proof-of-concept purposes.
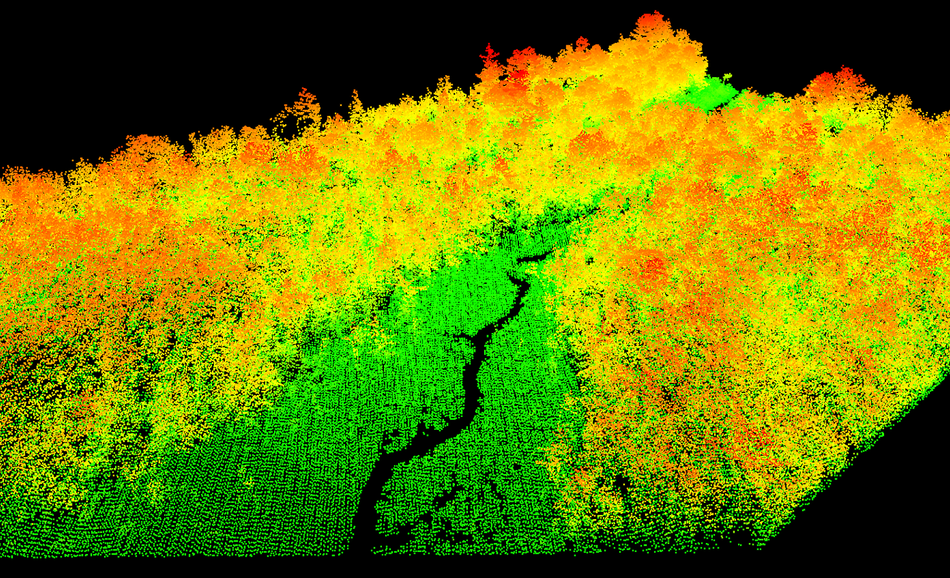
Pachama - Predicting carbon capture in forests
Pachama is a San Francisco-based company with a mission to build market confidence in carbon credits with the help of Edge AI. The company uses remote sensing, including data from lidar, satellites, drones, and field plots, to estimate carbon captured by forests around the world and predict carbon storage in the future. Pachama has developed machine learning models using AI to process data captured by devices at the edge of a network.
Pachma relies on these sensors to monitor ‘carbon sequestration,’ the mechanism trees and other plants use to remove and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Carbon sequestration is essential in mitigating greenhouse gasses that contribute to climate change. You can view global projects curated by Pachama in the Pachama Marketplace, a carbon credit marketplace built to assure companies and individuals that their carbon credit purchases are effective.
Activ Surgical - Real-time surgical visualizations
Activ Surgical is a medical startup developing surgical tools with Edge AI. The company aims to reduce complications during surgery and improve patient results. Activ Surgical’s ActivSight Intelligent Light technology provides surgeons with real-time augmented imaging that enhances existing surgical techniques. With ActivSight, surgeons can view systems and functions humans can’t normally see, like blood flow to anatomical structures.
ActivSight relies on the company’s ActivEdge platform, a surgical imaging and guidance system that uses Edge AI. ActivEdge integrates with existing tools for surgical visualization, including human-operated scopes and surgical robotics. This integration benefits medical institutions because surgeons can perform operations with enhanced accuracy using standard equipment and techniques.
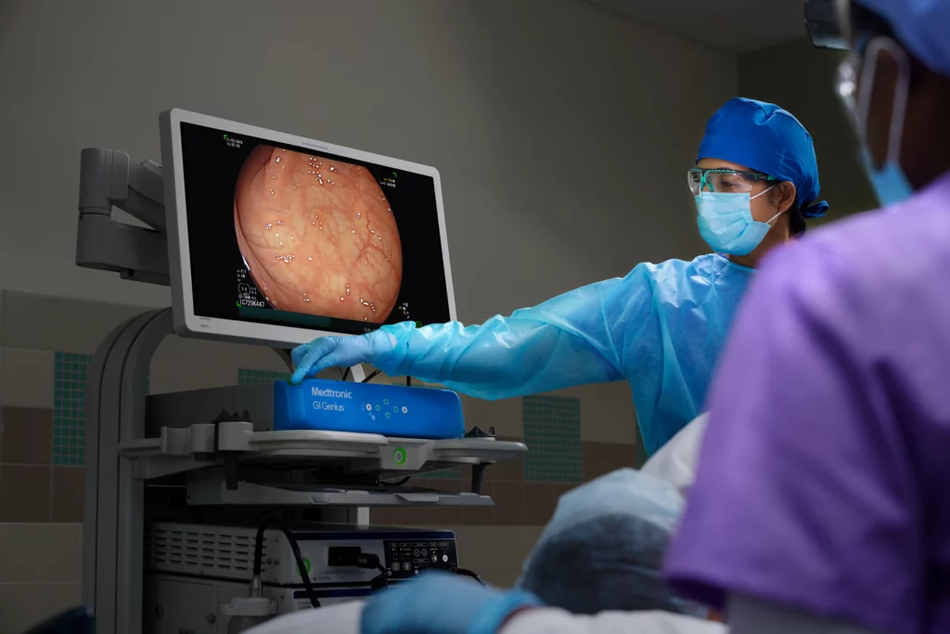
Medtronic - AI-Powered Endoscopy, Glucose Monitoring, and Cardiology
Medtronic is another company using Edge AI in medical applications. Medtronic has recently partnered with NVIDIA to implement the NVIDIA Holoscan platform in AI systems for medical devices. In particular, the Holoscan platform is integrated into Medtronic’s GIGenius, an AI-assisted endoscopy module. With the help of this Edge AI technology, physicians can detect early signs of colorectal cancer.
Medtronic also develops other medical applications with edge AI. Its continuous glucose monitoring system measures glucose levels through a sensor inserted under the skin and uses AI to improve and personalize diabetes management. Medtronic’s pacemaker uses sensing algorithms to detect and alert patients to cardiac arrhythmia. The company integrates edge AI into medical sensors to provide highly personalized medical care and detection.
Fero Labs - Reducing Carbon Emissions with IoT
Fero Labs develops advanced software that optimizes industrial processes with Edge AI. Their process improvements have been shown to improve product quality, lower costs, and reduce manufacturing waste, with an average 35% reduction in CO2 emissions.
The company develops machine learning models designed to run on edge devices that are already present in factories. The software connects with standard industrial databases and processes data in its native format. With Fero Labs’ software solutions, manufacturing plants can use existing equipment to predict product quality, identify problems with equipment, avoid flawed products, and improve process stability.
NoTraffic - Traffic Management for Smart Cities
NoTraffic is an AI-based platform that manages traffic in real-time. NoTraffic’s technology is another system built on NVIDIA technology, combining sensors and software to process and quickly respond to traffic conditions. NoTraffic’s Edge AI technology detects, identifies, and tracks road users, including their speed and direction as they approach an intersection, and adjusts the traffic signal accordingly.
NoTraffic has gained worldwide attention and has partnerships with US state transportation departments in California and Arizona. The platform has been shown to reduce traffic wait times by as much as 50%, which may also contribute to reduced vehicle emissions. An added benefit of NoTraffic’s technology is that smart cities with traffic systems built on Edge AI can quickly implement policies and analyze data from traffic flow.
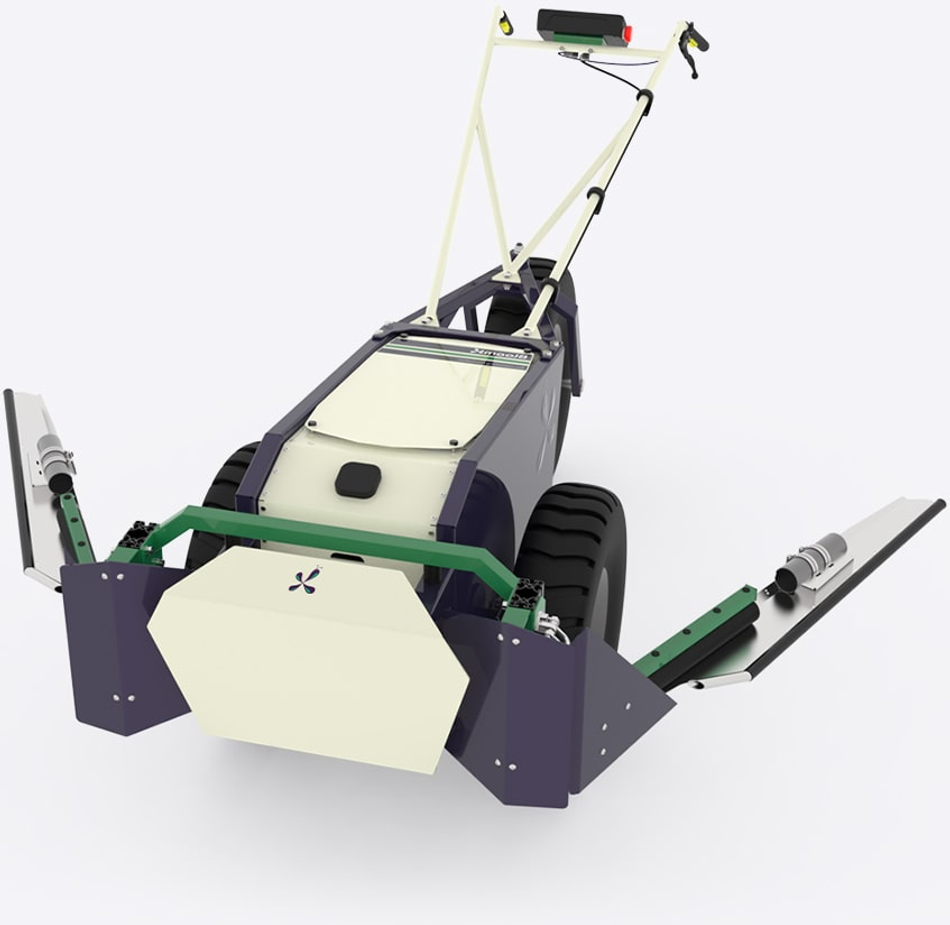
BloomX - Pollination with Robot Biomimicry
BloomX has developed a surprising application for Edge AI by mimicking the work of natural plant pollinators using predictive algorithms and purpose-built robotics. BloomX’s line of EV pollinators includes the Robee robot, which uses mechanical arms that have undergone years of testing and refinement to mimic the vibration that the bumblebee provides. In the natural world, this vibration is a mechanism that releases pollen from flowering plants. To maximize crop growth, pollinator robots rely on Edge AI to pinpoint the precise window for pollination, with onboard equipment that uses GPS-tracking and environmental sensors, giving growers real-time tracking data and controls.
BloomX indicates that their technology may result in up to a 30% increase in crop yield. The company’s clients include growers around the world, particularly blueberry and avocado growers in Latin America, South America, Africa, and the US. The company recently secured $8 million in funding from global organizations and manufacturers interested in developing this technology.
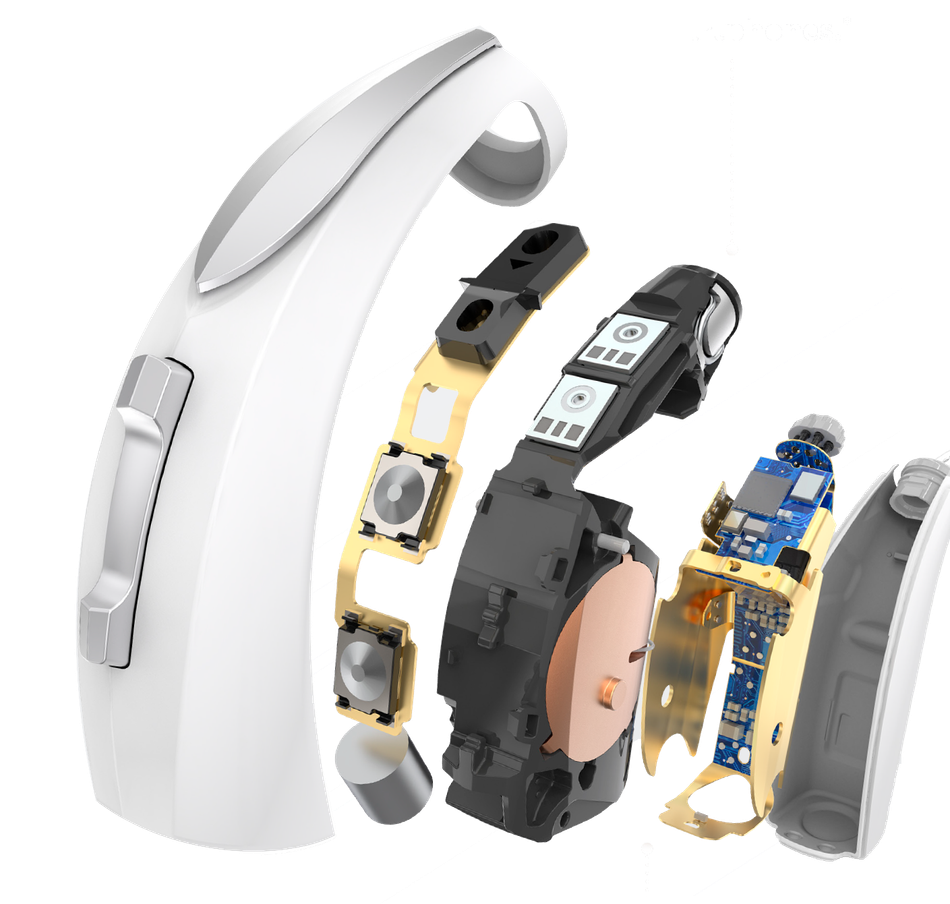
Starkey - Advanced Performance for Hearing Aids
Starkey is another company using Edge AI to bring innovation to the medical industry. The company’s hearing aid products, the Livio Edge AI and Evolv AI, feature Starkey’s Edge Mode technology, which can sense and respond to the wearer’s sound environment. Edge Mode uses machine learning algorithms to conduct real-time analysis of the listening environment and make adjustments to gain, noise management, and speech audibility.
Starkey’s hearing aids are a consumer-ready edge AI product available on the market today. However, Starkey’s most advanced hearing aids with Edge Mode may cost USD 4,200 or more, depending on features. Their Edge Mode hearing aids are rechargeable and offer fall detection, user-friendly control, customization via a smartphone app, and other features. According to a review in Forbes Health, these devices may mitigate the issues associated with hearing loss, such as isolation and depression, that result when users have difficulty adjusting to traditional hearing aids.
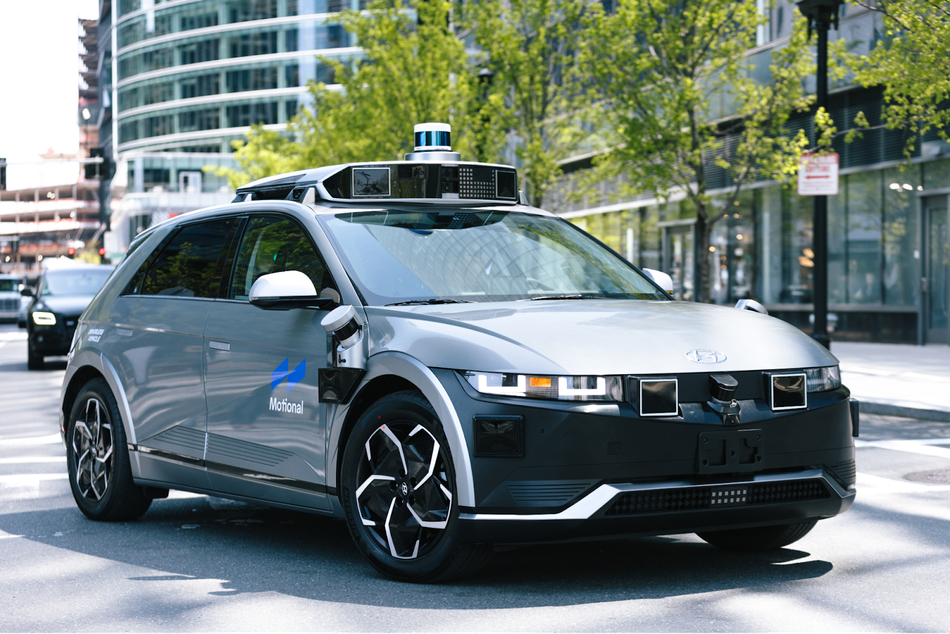
Motional - Autonomous Robotaxis
A report on Edge AI use cases would be incomplete without a nod to autonomous vehicles, an industry taking a major role in AI and hardware innovations. Motional is one such company in this sector that is implementing Edge AI in autonomous vehicles. The company is building autonomous robotaxis that use over 30 sensors with 360-degree vision and onboard AI computing. Motional aims to develop AI-controlled vehicles that adhere to the highest safety standards and integrate easily into existing ridesharing networks. Motional’s flagship, the IONIQ 5, was designed with an AI-first approach, meaning that its systems are fully engineered for driverless operation.
Motional is a joint venture between the automotive tech company Aptiv and the automotive manufacturer Hyundai. Recently, Motional partnered with Uber to launch an autonomous ride-hailing service in Las Vegas. Currently, the project employs human operators, but the companies aim for completely driverless vehicles in 2023. In Santa Monica, Motional partnered with Uber Eats to make autonomous food deliveries using Motional vehicles. The company also conducts testing in Boston, Pittsburgh, and Singapore, gathering data from diverse environments for improved onboard algorithms.
Edge AI is a versatile technology with diverse applications. It is a scalable and adaptable tool that has the potential to transform every industry. The ability to use existing equipment is a common goal among companies implementing Edge AI—a factor that lowers the barrier to adopting this beneficial technology. Another common feature of Edge AI technology is that it offers real-time insight, meaning that data can be immediately applied in critical situations, which could be anything from a surgical procedure to monitoring factory equipment or to a quick response to changing traffic conditions. Edge AI complements, enhances, and brings innovation to data processing capabilities.
Gain a broader perspective on Edge AI by revisiting our comprehensive guide.
The 2023 Edge AI Technology Report
The guide to understanding the state of the art in hardware & software in Edge AI.
Click through to read each of the report's chapters.
Report Introduction
Chapter I: Overview of Industries and Application Use Cases
Chapter II: Advantages of Edge AI
Chapter III: Edge AI Platforms
Chapter IV: Hardware and Software Selection
Chapter V: Tiny ML
Chapter VI: Edge AI Algorithms
Chapter VII: Sensing Modalities
Chapter VIII: Case Studies
Chapter IX: Challenges of Edge AI
Chapter X: The Future of Edge AI and Conclusion
The report sponsors