AI-Driven AR in Manufacturing: From Data to Actionable Insights
Article #5 of Transforming Industrial Manufacturing with Industry 4.0 Series: The next evolution of AR in manufacturing comes by pairing it with AI, allowing for seamless information access and tracking of specific surfaces/points of interest in real-time.
This is the fifth article in a 7-part series featuring articles on Transforming Industrial Manufacturing with Industry 4.0. The series looks at technological developments and emerging trends in the manufacturing industry that drive growth and innovation. This series is sponsored by Mouser Electronics. Through their sponsorship, Mouser Electronics shares its passion and support for engineering advancements that enable a smarter, cleaner, safer manufacturing future.
As manufacturing processes become increasingly complex and data-driven, companies are seeking innovative ways to streamline operations and increase efficiency. One promising solution is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR), which can offer real-time data visualization, analytics capabilities, and much more.
By leveraging AI’s analytics, and recommendations, AR devices can be upgraded to let manufacturers gain better insights into their production processes, identify potential issues before they become major problems, and make informed decisions about optimizing performance and safety. In this article, we will explore how AI-driven AR is transforming the manufacturing industry and how it is helping companies stay ahead of the competition in an increasingly data-driven world.
Introduction
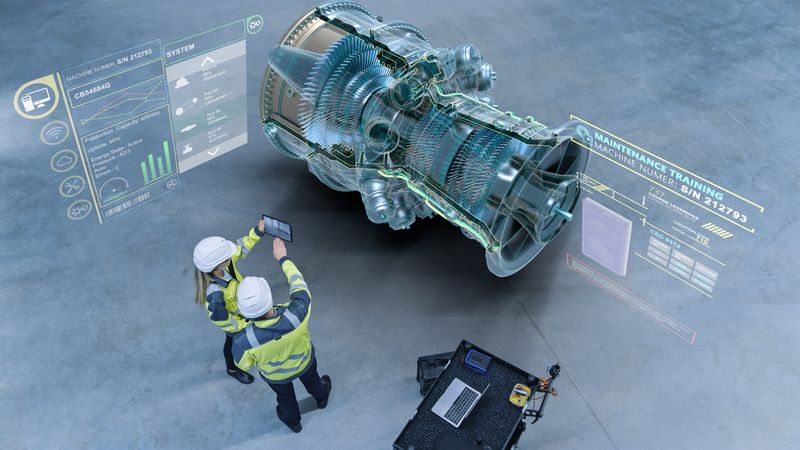
AR is a software–hardware fusion that enables creators to display information and 3D models digitally in the real world, giving users the sense that they are actually there. AR is not new, but the hardware and powerful software needed to use it conveniently are becoming more common now. With this level of accessibility, AR is finding its use in manufacturing environments to solve many information access challenges.
The next evolution of AR includes pairing it with AI. This combination establishes a relationship between real and digital objects by locating and tracking specific surfaces and points of interest. Thus, not only can AI-driven AR display information and models, but it can now also aid in discovering new objects, reading text, and making decisions based on what is happening in the environment. Rather than AR only being an aid for humans, it has the potential to serve as a raw data collection stream for AI and machine learning. This technology has begun to change the ecosystems of video games and the sale of online products, but AI-driven AR has the potential to provide even better information accessibility and solutions in industrial manufacturing environments.
The global immersive technologies in manufacturing market is expected to reach a valuation of $72.4 billion by 2031 growing at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.8%.[1]
Challenges in Accessing Information
Manufacturing requires speed, precision, consistency, quality, and traceability of raw materials, individual components, and finished goods. At any given time, information flows in every direction and constantly changes. Unfortunately, the data is not always available where workers need it the most.
In-process controls —for example, standard work instructions ensure that users perform tasks the same way every time. Often, these process documents live in a binder or are posted on a wall near the work area. Even when tablets are used for digital instructions, users must hold the tablet, lift parts, walk around, and complete tasks at the same time. With these constraints, work instructions are instead used as training documents or as an after-the-fact reference following an incident rather than for task-oriented work.
In logistics, inventory control poses many challenges, especially when the organization must manage thousands of parts coming and going. It is not uncommon for the expected inventory and actual inventory to vary. To combat this potential for the discrepancy, companies conduct periodic inventories, which is a valid but tedious, time-consuming, and costly process.
Effective communication channels are also important, but they are hampered by large, noisy, often-separate areas. Email is not necessarily instant, nor does it present a solution for workers who do not have corporate email addresses or access to technology. Cell phones are an option, but in some industrial spaces, they can present a safety hazard —not to mention that cell phone use is a sore subject for many businesses, which view the devices as a distraction.
AR is already helping solve these challenges with the help of cell phones, tablets, and laptops. AR works by using a visual sensor or camera, a display device, and software that presents information and 3D models—all of which can be found in most modern mobile devices. The processing power of some of the current smartphones can outperform laptops, which means that every person with a cell phone has access to this emerging technology.
The Potential of AI-Driven AR to Solve Problems
The combination of AR with AI could provide even greater results. Consider that without AI, the information displayed would be superimposed over an arbitrary real-world view from the device’s camera —the equivalent of subtitles overlayed onto a movie. The text can be there, with or without the video, because the two have no direct interaction or connection.
Here is a video showcasing how AR can be used to create intuitive learning experiences in the manufacturing industry:
While AR content needs to be created manually, AI-driven AR does not depend on human input to acquire new and accurate information about the environment. Such systems could recognize surfaces and establish anchor points for digital text and objects to reference and interact with. Whereas AR places a chair on the floor of a room, AI locates the surface of the floor by using a camera and sensors. After identifying the surface, it places the object and tracks its position as the user moves to other areas. The system can see for itself and display the real-time background as the user moves through space.
Within manufacturing environments, this means that the background environment and the information displayed for users would be in sync and in real time. That’s significant because the AI-driven AR system could:
Display expected inventory values at each location in real-time and verify whenever someone accesses the location.
Help a robotic vision system count inventory, forwarding an image to a human if the robot detects a discrepancy or needs secondary verification.
Monitor repetitive tasks and inform workers if they do not complete tasks correctly.
Enable a system to track and verify inventory digitally to validate a part's dimension and critical features.
Identify discrepancies and discover the root cause of those issues.
The Future of Manufacturing with AI-Driven AR
The integration of AI and AR has the potential to address numerous challenges associated with the human-machine interface by providing a more intuitive and immersive way to interact with machines and systems, enabling real-time insights and recommendations based on complex data analysis. The way information is displayed and communicated could be instant and prioritized by urgency rather than proximity to a human’s location or line of sight. This type of interaction would create the perfect human–machine symbiosis. Further, AI-driven AR will likely be a key technology in driving manufacturing businesses into Industry 5.0, which focuses on product customization and human–machine collaboration.
Companies that recognize technology as an extension of human capability will have to understand that harmonious communication and decision-making are paramount. An industrial environment in which information is in real-time and part of users' field of vision is within arm’s reach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR) in the manufacturing industry has the potential to revolutionize the way companies operate. With the ability to provide real-time data visualization and analytics capabilities, AI-driven AR can help companies optimize their performance and safety. The challenges of accessing information in a manufacturing environment can be solved through the combination of AI-driven AR.
The technology does not solely depend on human input to acquire new and accurate information about the environment. It can recognize surfaces and establish anchor points for digital text and objects to reference and interact with, making the background environment and the information displayed for users in sync and in real-time. With the help of AI-driven AR, the manufacturing industry can streamline operations, and drive growth and innovation..
This article is based on: AI-Driven AR Melds Manufacturing and Data, a blog by Mouser Electronics. It has been substantially edited by the Wevolver team and Electrical Engineer Ravi Y Rao. It's the fifth article from the Transforming Industrial Manufacturing with Industry 4.0 Series. Future articles will introduce readers to some more trends and technologies transforming industrial automation.
The introductory article presented the different topics covered in the Transforming Industrial Manufacturing with Industry 4.0 Series.
The first article discusses Sensor Fusion, PLCs, Low-Power Components, and Vision Systems and their impact on the progression of Manufacturing 4.0.
The second article examines the expanding and evolving roles of systems, process, and design engineers within the design chain of bringing new industrial automation products to fruition.
The third article takes a look at the development of smart factories, their characteristics, benefits, and challenges that need to be addressed for a successful digital transformation.
The fourth article focuses on technologies like Robot Operating Systems, edge computing, and new software solutions that are improving robotics in industrial and commercial environments.
The fifth article explores some challenges in accessing information in the manufacturing sector and how AI-driven AR has the potential to overcome them.
The sixth article explains how digital twins are helping bridge the gap between design and manufacturing.
The seventh article how manufacturing environments are adapting to the evolving customer needs and expectations.
About the sponsor: Mouser Electronics
Mouser Electronics is a worldwide leading authorized distributor of semiconductors and electronic components for over 1,200 manufacturer brands. They specialize in the rapid introduction of new products and technologies for design engineers and buyers. Their extensive product offering includes semiconductors, interconnects, passives, and electromechanical components.