How CO2 sensors can improve energy efficiency in buildings
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor can help increase air quality and reduce HVAC costs in buildings

Human health, safety, and building energy efficiency depend on regulating and monitoring indoor carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. Lack of adequate air circulation can significantly impact CO2 concentrations, resulting in poor indoor air quality and reduced productivity.
Every building requires a constant flow of fresh, conditioned air to provide a comfortable and safe environment indoors. However, many buildings do not comply with green building standards, such as LEED, WELL, or Passive Hause, which makes them expensive to heat and cool.
In order to achieve higher levels of energy efficiency and improved air quality in buildings, CO2 sensors can be used to monitor the CO2 levels indoors. This data can be sent to HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) controllers to regulate the air flow inside the building.
This article explores how the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor from Infineon can benefit ventilation design and air quality monitoring to make buildings more energy efficient by regulating and monitoring indoor CO2 levels.
CO2 sensors for IoT-based enhanced ventilation
CO2 sensors allow IoT systems to monitor the carbon dioxide concentration in the air.The ventilation system can be automatically controlled by analyzing the CO2 sensor data to provide the required airflow based on the number of people in the building. When there is more people indoors, the ventilation system can operate at a higher power to ensure adequate air circulation. Conversely, it can consume less power when the number of people inside is lower.. This approach is called Demand Control Ventilation (DCV) .
In DCV, the HVAC system receives the CO2 data output from the CO2 sensor in order to control how much outside air is blown into the building. This approach is well established and defined in existing standards (e.g., ASHRAE 62-1) or enforced legislation (e.g., California Building Code Title 24).
DCV vs Conventional ventilation
Compared to conventional ventilation strategies, DCV offers several advantages. ,. DVC ensures the optimal indoor air quality in each room and increas the operating efficiency of HVAC systems. Reports indicate that DCV can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, resulting in higher energy efficiency and lower costs.This increase in energy efficiency helps buildings comply with with green building certification systems, such as LEED and WELL and with indoor air quality standards.Furthermore, DCV systems with the integration of a CO2 sensors have lower maintenance costs and longer life cycles. [1] [2]
Conventional CO2 sensor types
There are different types of CO2 sensors, which have different operation principles. The most commonly used types are:
- Electrochemical (EC): EC sensors consist of an anode, a cathode, a gas-permeable membrane, and an electrolyte. They allow charged molecules to pass through a thin electrolyte layer, and the chemical reaction produces an electrical signal proportional to the gas concentration. These sensors are cheap and simple to use. However, they have a limited measurement range and relatively short life service.
- Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR): an NDIR sensor is composed of a detector and a heater, which emits infrared light towards the detector. CO2 molecules absorb this energy, increasing their temperature and radiating more infrared light to the detector. NDIR sensors are accurate, easy to use, and require no calibration. However, these sensors are more expensive than other types and require regular maintenance.
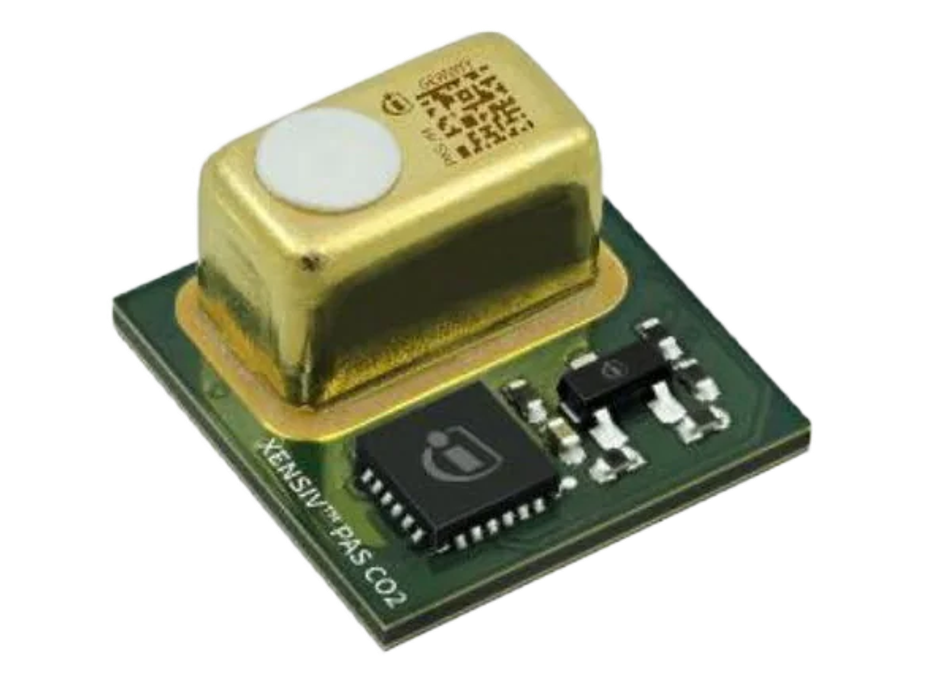
- Photo-acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS): a PAS sensor uses infrared pulses to measure how much CO2 is in the air. They are popular for air quality monitoring because they require no calibration and have an accurate reading. In addition, PAS sensors have low power consumption. A strong example of this sensor type is the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 from Infineon.
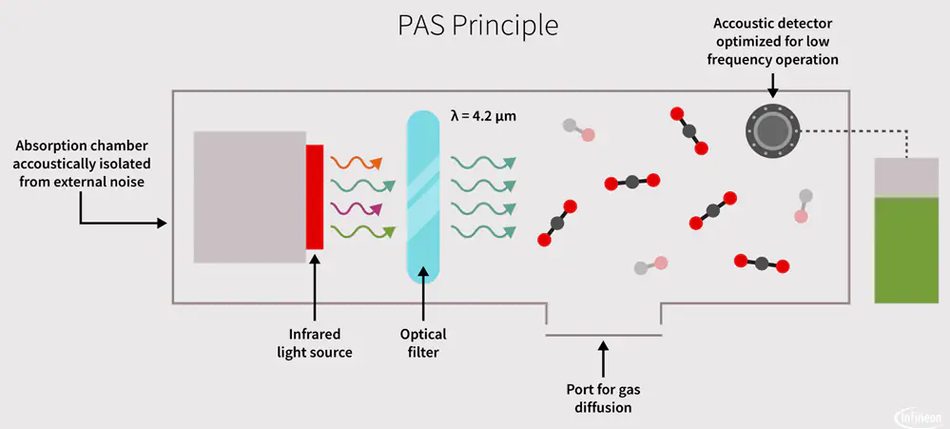
PASCO2 contributes toward earning points needed for WELL & LEED certifications. The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor is a solution for real CO2 monitoring that can be integrated in a monitoring system to improve health, productivity, and overall well-being within buildings. It is based on the principle of photo-acoustic spectroscopy (PAS), in which pulses of light from an infrared source pass through an optical filter explicitly tuned to the CO2 absorption wavelength (λ = 4.2 μm). The CO2 molecules inside the measurement chamber absorb the filtered light, causing the molecules to vibrate and generate a pressure wave with each pulse. The XENSIV™ PAS includes a MEMS acoustic sensor with a high signal-to-noise ratio that converts the acoustic output into CO2 readings in ppm.
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor integrates in a small form factor module: a PAS transducer (MEMS acoustic detector, infrared source and optical filter); a microcontroller for signal processing and algorithms; and a MOSFET chip to drive the infrared source. The integrated microcontroller performs ppm calculations as well as advanced compensation and self-calibration algorithms.
The exceptional sensitivity of the acoustic detector enables best-in class accuracy, while its miniaturized size (14 mm x 13.8 mm x 7.5 mm3) reduces space requirements by more than 75 percent compared to other commercially available real CO2 sensors. As a result, the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor outperforms state-of-the-art NDIR sensors in terms of size and cost, without compromising on performance.
- Operating range: 0 ppm to 32000 ppm
- Accuracy: ± (30 ppm +3%) of reading between 400 ppm and 5000 ppm
- Lifetime: 10 years
- Operating temperature: 0-50°C
- Operating relative humidity: 0% to 85%
- Interface: I2C, UART, and PWM
- Average power consumption: typically, 30 mW at 1 measurement/minute.
In addition, the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor was designed specifically for air quality monitoring and ventilation applications, making it an optimal and cost-effective solution for buildings that pursue green building certifications such as WELL and LEED.[3]
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor fulfills the performance requirements defined by the international green building certification systems WELL and LEED.
WELL Building Standard™ is a rating system that aims for a positive impact on human comfort, health, and well-being in buildings and their interiors. WELL establishes performance requirements by looking at ten factors: air, water, food, light, movement, thermal comfort, sound, materials, mind, and community.
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor contributes to 5 WELL features as illustrated in the table below.
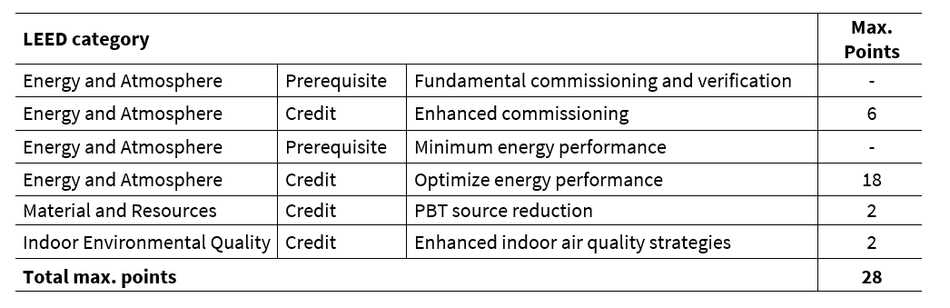
The U.S. Green Building Council LEED® is the world’s most widely used green building rating system and was created as a leadership standard defining best practices for healthy, high-performing green buildings.
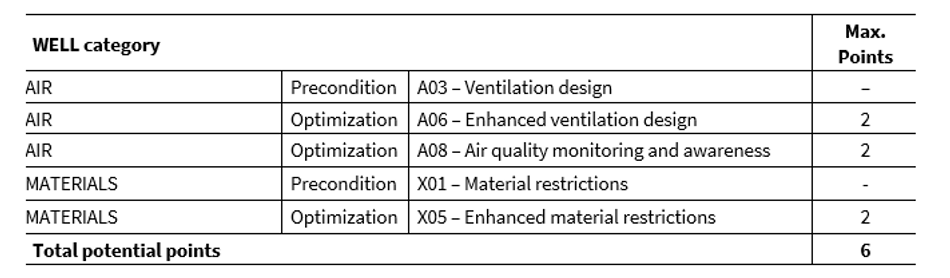
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor contributes to 6 LEED credits as shown in the table below.
The overall value that the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor brings by meeting WELL & LEED performance criteria includes:
- Higher real estate value of residential and commercial buildings
- Higher levels of wellbeing, comfort and productivity to occupants
- Increased energy efficiency and lower energy costs through Demand Controlled Ventilation
- Significant reduction in CO2 emissions thanks to a higher operating efficiency
- No human exposure to hazardous chemical substances such as mercury & lead
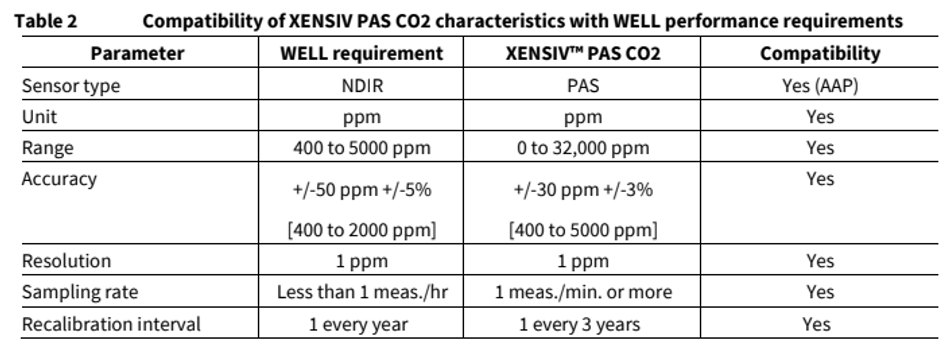
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 officially meets the sensor technology requirements approved by WELL So far NDIR has been considered by WELL the state-of-the-art technology for CO2 sensors. The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 has now provided evidence that the Photo-Acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS) principle officially meets the sensor technology requirements approved by WELL. In other words, the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 equals the performance of high-end NDIR sensors in a 4-times smaller size .
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 provides a digital ppm measurement. The operational concentration range is specified as 0 to 32,000 ppm. Also, the CO2 accuracy is specified as ± 30 ppm ± 3%, and the operational concentration range of the sensor is 1 ppm. Therefore, these specifications are compatible with those required by WELL.
WELL requires measurement intervals to be no larger than 15 minutes for CO2. XENSIV™ PAS CO2 has a programmable sampling rate of 1 measurement/5 s up to 1 measurement/hour.
In addition, WELL requires that all sensors that measure air quality parameters be recalibrated or replaced annually. Infineon's CO2 sensor fulfills this requirement since it has been designed to operate for 10 years and the sensor has an annual drift of maximum 1% for a year, with an automatic baseline offset correction function activated. [3] [4]
HVAC systems using CO2 sensors
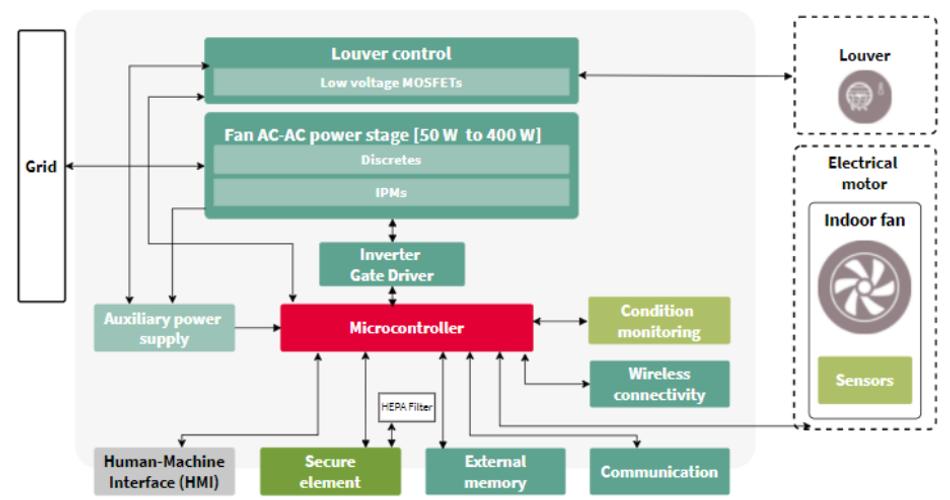
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor is useful for applications that aim to ensure optimal indoor air quality levels,. Intelligent HVAC systems are controlled by microcontrollers using sensors' data. Based on the CO2 levels measured, the microcontroller can regulate the ventilation via an indoor fan.
The diagram below illustrates an example of an indoor HVAC unit using a CO2 sensor. Infineon's XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor is ideal for this application due to its high accuracy in CO2 measurements, ensuring better ventilation control.
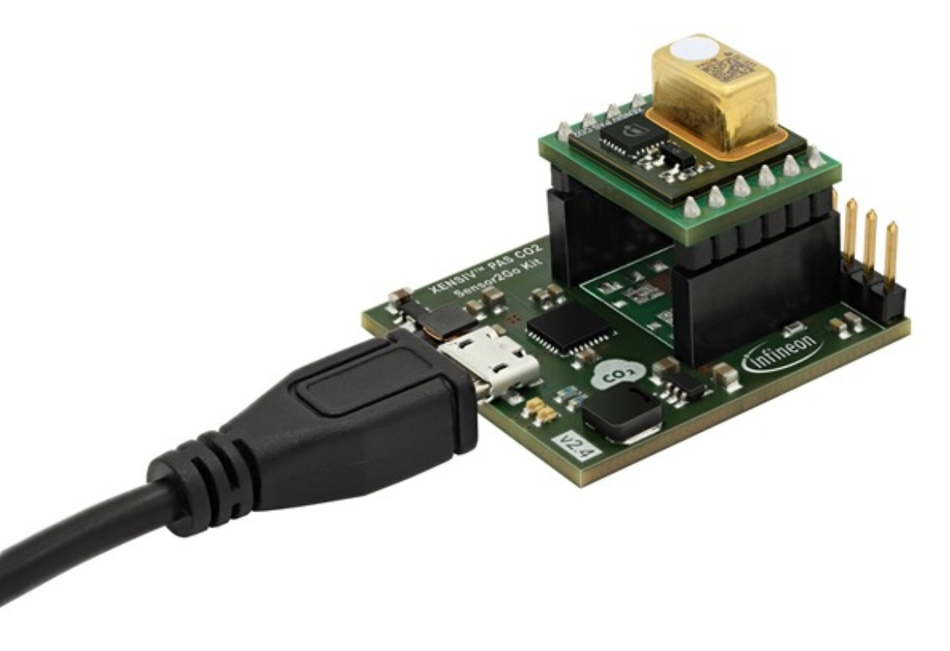
Simplifying CO2 monitoring with XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor2Go
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor2Go is a solution to make it easier and faster to start your project. It comes with features such as plug-and-play, logging of sensor history and the option to access it using USB or via I2C. In addition, Infineon also provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and software via Infineon toolbox. A case study of office air quality monitoring using the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor2G was presented in [5].
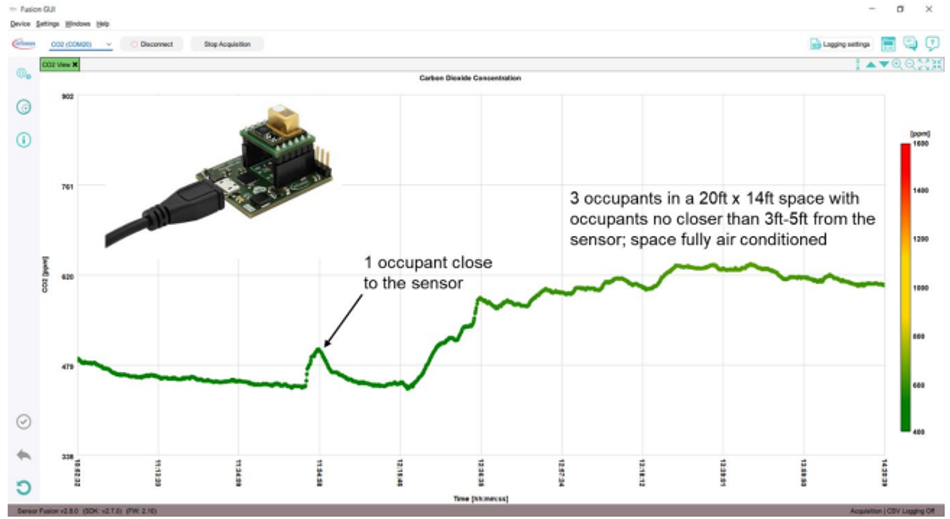
In order to show the monitoring behavior of the XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor2Go Evaluation Kit, the figure below illustrates the monitoring of CO2 concentration in an office with three occupants (masked and talking). The room is 20 ft x 14 ft and is fully air-conditioned. Initially, when there is just one occupant close to the sensor, the air quality is in the green range, which is good. However, when more people occupy the room, there is an increase in the CO2 level, indicating that the HVAC system should adjust the airflow to reduce the CO2 level.
The system could be expanded from local data measuring using IoT solutions, such as the CSK_PASCO2, which provides wireless connectivity and uses the XENSIV™ PAS CO2. This approach would enable data collection from multiple spots to improve the ventilation system.
Conclusion
Ensuring proper CO2 measurements and dispersion in buildings is crucial for human health, safety, and energy efficiency. An effective ventilation system utilizing CO2 sensors and DCV is essential to achieve these goals.
The XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor is a highlyaccurate, and long-life sensor for CO2 monitoring applications. Its robust perfromance and compact size make it ideal for indoor air quality monitoring solutions. In addition, this sensor fulfills the performance requirements defined by the international green building certification systems WELL and LEED and contributes to buildings that pursue these certifications.

References
[1] CO2 METER. DEMAND CONTROLLED VENTILATION. Available from: https://www.co2meter.com/collections/demand-controlled-ventilation
[2] PDHonline Course M251. HVAC – Guide to Demand Control Ventilation. Available from: https://pdhonline.com/courses/m251/m251content.pdf
[3] Infineon Technologies. XENSIV™ PAS CO2: its contribution to the implementation of the WELL Building Standard™ and of the LEED rating system, 03-2023.
[4] Infineon Technologies. XENSIV™ PAS CO2 sensor - PASCO2V01. Available from: https://www.infineon.com/cms/en/product/sensor/co2-sensors/pasco2v01/
[5] Infineon Technologies. Meeting stringent CO2 building code requirements with Infineon’s XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor. Available from: https://www.mouser.com/pdfDocs/Infineon-PAS_CO2_sensor_Whitepaper-Whitepaper-v01_00-EN.pdf
[6] Infineon Technologies. XENSIV™ PAS CO2 Sensor2Go Evaluation Kit. Available from: https://www.infineon.com/cms/en/product/evaluation-boards/eval_pasco2_sensor2go/