Exploring the Emerging Uses of Radar Technology
From its beginnings as a military technology, radar has found its way into many of the world’s most important industries.
Introduction
Radar technology, initially developed in the early 20th century for military navigation and detection, has experienced a remarkable evolution over the years [1]. What began as a means to locate aircraft and ships has transformed into a versatile tool that permeates various aspects of modern life. Beyond its foundational use in aviation and maritime navigation, radar now finds applications in fields as diverse as automotive safety, healthcare, industrial operations, and even smart home technology. This article explores the cutting-edge uses of radar technology in areas not commonly associated with it.
Inside Cabin Monitoring
While radar is used in automotive as a means for achieving greater levels of vehicle autonomy, it has also found major uses inside the cabin. Specifically, radar sensors have carved a niche within the automotive industry in enhancing in-cabin monitoring systems.
In the context of inside cabin monitoring, radar sensors utilize electromagnetic waves to detect objects and movements inside the vehicle, providing real-time data about the cabin's interior environment. Combined with sophisticated software and mapping algorithms, this technology is adept at identifying the position and movement of passengers, for the purposes of occupant monitoring and safety. For example, inside-cabin monitoring can be used to ensure that airbags deploy appropriately in the event of a collision to minimize injuries. Furthermore, radar-based systems can monitor driver alertness, detecting signs of drowsiness or distraction by observing head position and movement, thereby prompting alerts to reduce the risk of accidents[2].
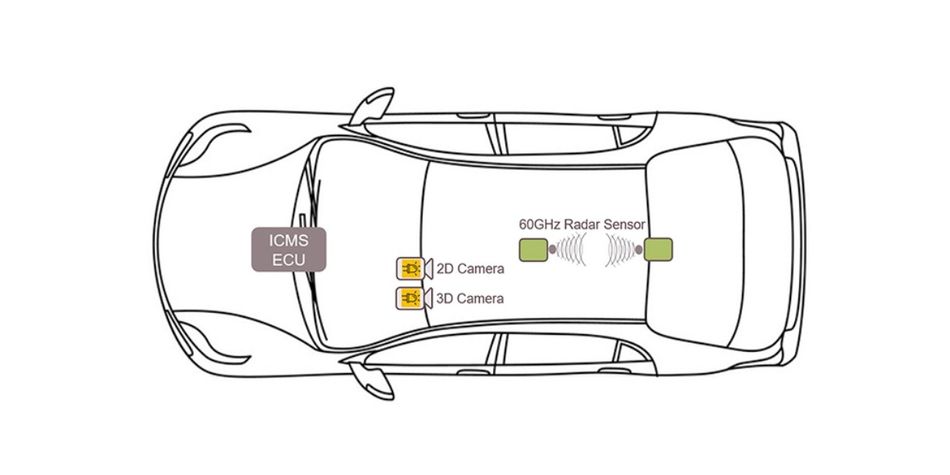
Radar is used for in-cabin monitoring applications in modern vehicles. Image credit: Infineon.
One notable application of in-cabin radar is the child presence detection system. This system alerts drivers if a child is inadvertently left behind in a vehicle, thereby preventing heat-related injuries or fatalities.
The benefits of in-cabin radar technology also extend beyond safety. Comfort is significantly enhanced through features like automatic adjustment of climate control systems based on the occupancy and positioning of passengers. This might include optimal temperature settings across different zones within the vehicle, improving the overall driving experience.
Contactless Health Monitoring
In the health sector, radar technology offers a groundbreaking approach to monitoring vital signs without any physical contact.
This approach uses electromagnetic waves to detect the minute movements of the chest as the heart beats and lungs expand and contract, converting these movements into digital signals that can be analyzed to monitor health metrics continuously. Unlike traditional methods that require physical contact with the body, radar-based health monitoring is non-intrusive, offering a significant advantage in various settings, from hospitals to homes.[3]
There are many benefits of contactless monitoring in today's health-conscious world. For patients in critical care, it minimizes the risk of infection and discomfort associated with frequent physical check-ups. In home settings, it allows for the continuous observation of elderly or chronically ill patients without intruding on their comfort or privacy.
One of the most noteworthy advancements in this area is the development of radar-based sleep monitors. These devices can accurately measure sleep quality, breathing rate, and even detect sleep apnea without the need for uncomfortable wearables. This technology is particularly useful for monitoring sleep patterns and detecting early signs of respiratory or cardiac conditions, enabling timely medical intervention.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, radar technology has become a critical tool for enhancing both safety and efficiency. Here, radar’s ability to provide accurate, real-time data in challenging environments—where dust, smoke, or extreme temperatures may impair other types of sensors—makes it extremely valuable for a wide range of applications.
One of the key benefits of radar in industrial settings is its contribution to workplace safety. For instance, radar sensors can create invisible safety zones around dangerous machinery. When these zones are breached by an unexpected object or person, the system can automatically shut down the equipment, preventing potential injuries. In manufacturing facilities and construction sites where the interaction between heavy machinery and workers is a constant concern, these safety zones can be a huge step toward worker safety. [4]
Furthermore, radar technology is instrumental in improving operational efficiency. In large warehouses or ports, radar-based systems can track the movement of goods and vehicles, optimizing logistics and reducing the time it takes to load and unload cargo. This helps to speed up operations as well as minimize the risk of accidents by providing operators with better awareness of their surroundings.
Smart Home and IoT Applications
The integration of radar technology into smart home devices and the broader Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is ushering in a new era of enhanced functionality and intuitive user experiences. Radar sensors, with their ability to detect motion, presence, and even the breathing patterns of individuals, are becoming key components in making smart homes more responsive and personalized.
One of the primary advantages of radar in smart homes is its precision and reliability. Unlike traditional motion sensors that might be triggered by irrelevant movements, radar can discern between different types of motion, distinguishing between a person walking into a room and minor movements like curtains fluttering. This capability allows for smarter automation of lighting, heating, cooling, and security systems, ensuring they operate more efficiently and only when needed. [5]
For instance, smart thermostats equipped with radar can adjust the temperature based on the number of people in a room and their level of activity, optimizing comfort and energy use. Similarly, security systems can use radar to monitor the surroundings of a property without the need for cameras, offering peace of mind without the intrusion of visual surveillance.
Products equipped with radar are already on the market. Google's second-generation Nest Hub uses radar for sleep tracking, allowing users to monitor their sleep patterns without wearing any devices.[6] As radar technology continues to evolve, its integration into smart home devices and IoT ecosystems is expected to grow, offering even more sophisticated and user-friendly solutions.
Conclusion
From its inception as a military tool in the 1930s, radar has undergone a significant transformation in the past century. As radar technology and related software algorithms become more advanced, various industries—from automotive safety and healthcare to industrial operations and smart homes—are now adopting the technology to adopt it. Whether it's in developing safer vehicles, supporting health monitoring, optimizing industrial processes, or enriching smart home experiences, it's clear that radar technology is poised a significant contributor to many of the world’s most important industries.
References
https://sickconnect.com/safety-technology-radar-2d-lidar-3d-tof-use/
https://www.innosent.de/en/sector/building-automation-smart-home/
https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/10357288?hl=en&co=GENIE.Platform%3DAndroid

