DARwIn OP
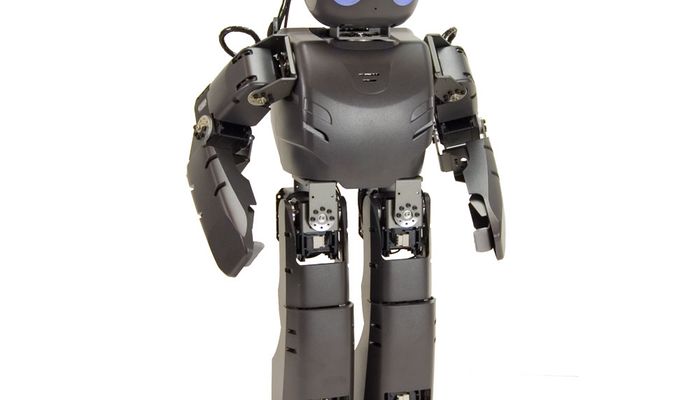
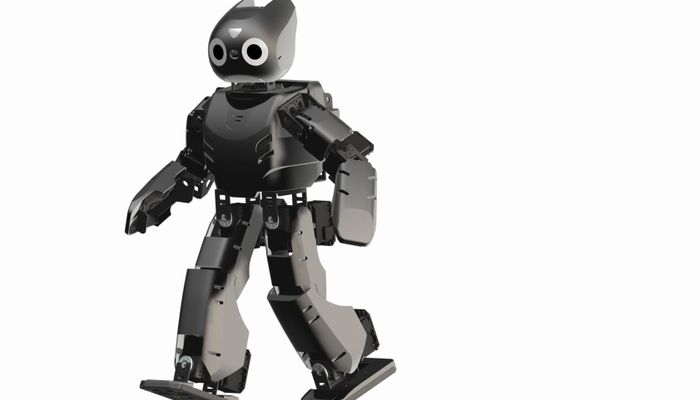
A miniature-humanoid-robot platform with advanced computational power, sophisticated sensors, high payload capacity, and dynamic motion ability. DARwIn-OP has 20° of freedom, and the center of mass is located at the center of its pelvis, which is optimal for proper balancing and proper of inertia during walking. The robot has hollow frames which allows the robot to maintain a low overall weight. The frames are designed so that the user can include additional sensors to the robot, including wiring. The hollow design maintains the scope of a network-based modular structure and facilitates periodic robot maintenance.
Technical Specifications
| Built-in PC | |
| Camera | 2 |
| Actuator | 3 |
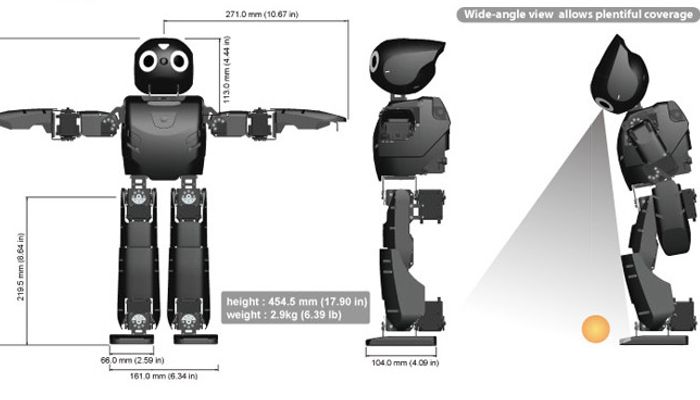
| Height | 45.5 |
| Default walking speed | |
| Weight | 2.9 |
| Degrees of freedom | 20 |
| 2 | |
| 2x3 | |
| 2x6 | |
| Main controller | CPU |
| RAM | |
| Disk | |
| Network | |
| USB port | 2 |
| Sensor | Gyroscope |
| Accelerometer | |
| Pressure-meter |
Overview
DARwIn-OP has 20° of freedom, and the center of mass is located at the center of its pelvis, which is optimal for proper balancing and proper of inertia during walking.
The robot has hollow frames which allows the robot to maintain a low overall weight. The frames are designed so that the user can include additional sensors to the robot, including wiring. The hollow design maintains the scope of a network-based modular structure and facilitates periodic robot maintenance.
System overview
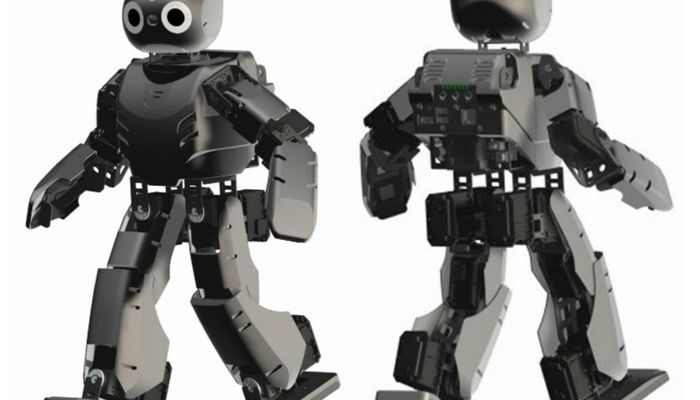
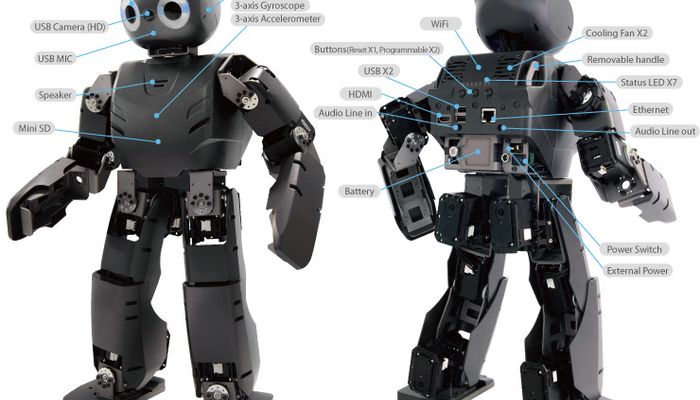
DARwIn-OP has a network-based modular structure and a standard PC architecture. Actuators, sensors, LEDs, buttons, and external I/Os, are connected to the sub-controller by a serial bus network which fully supports DYNAMIXEL protocol. Each device has a memory-mapped operation structure with designated ID. The main controller is an Intel ATOM Z530 CPU.
Actuators
DARwIn-OP has an improved MX-28 actuator which has a higher resolution, faster communication speed, and a more sophisticated controller compared to the previous RX-28 actuator. The MX-28 has a contactless magnetic potentiometer; its contactless aspect of the encoder virtually eliminates any limited operation angle of the actuator. The MX-28 also has increased 12-bit resolution for more precise position control, and all over 360° without any gaps or stops. The MX-28 supports PID controller for position andspeed control. The user can adjust not only position andspeed profile but as well as PID gain parameter in realtime.
Sensors
The sasic sensors on the DARwIn-OP are a three-axis gyro-scope and a three-axis accelerometer for posture estimation and balancing are mounted in the upper body. DARwIn-OP uses the three-axis accelerometer and gyroscope for balancing and posture estimation without compromising walking performance. A USB-based camera for image processing, and a total of three microphones are located in the head. The camera is a high-definition camera that interfaces with the robot via USB. The high-definition camera provides detailed information and helps maintain a simple robot configuration, eliminating the need for a dedicated camera actuator.
The microphone enables voice commands. An API can be installed in DARwIn-OP for voice recognition followed by any programmed sequential behavior from the voice command. Two other microphones are also placed inside the head for the purposes of sound localization.
Display and Interfaces
The robot comes with full-color range RGB LED’s in the eyes and forehead, which can be programmed to specific colors for each LED.
DARwIn-OP is equipped with external ports like HDMI, USB, a flash memory port, and Ethernet port. This enables interfacing, communications, data storage, and software implementation with the robot.
Software
The software for DARwIn-OP is built with a hierarchical framework enabling modularity and independency. It consists of a device communication module, motion module, walking module,sensing module, behavior module, vision module, anddiagnostics module. The framework is developed with C++ programming language where the code is operating system independent.
References
Describes the design method for the humanoid platform, the system overview, actuators, sensors, software architecture, application tools, and the conclusion of the research.