A Platform for Smarter Robots: How TDK's Sensor Ecosystem Powers Next-Gen Robotics
This article is part 4 of a 4-part article series on TDK's advanced robotics.
Introduction
Service robotics is a fast-growing field, with intelligent, adaptive, and autonomous systems becoming increasingly prevalent across industries. As these robots become more sophisticated, engineers face more complex challenges when it comes to achieving real-time perception, precise motion control, and environmental awareness. TDK Corporation, a leading Japanese electronics company, has developed a comprehensive sensor ecosystem to address these challenges. The result is a modular and scalable platform for next-generation robots.
TDK’s sensor ecosystem is integrated with the ROS 1 and ROS 2 framework, and is a unified solution for robotic developers. Drawing inspiration from the sensory capabilities often imagined in anime and manga, this technology brings us closer to creating robots that are highly perceptive and responsive. By combining cutting-edge sensor technologies and flexible algorithms, TDK is leading the way for a new era of intelligent robotics that can interact with humans and their environment.
The TDK Sensor Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Robotics Solution
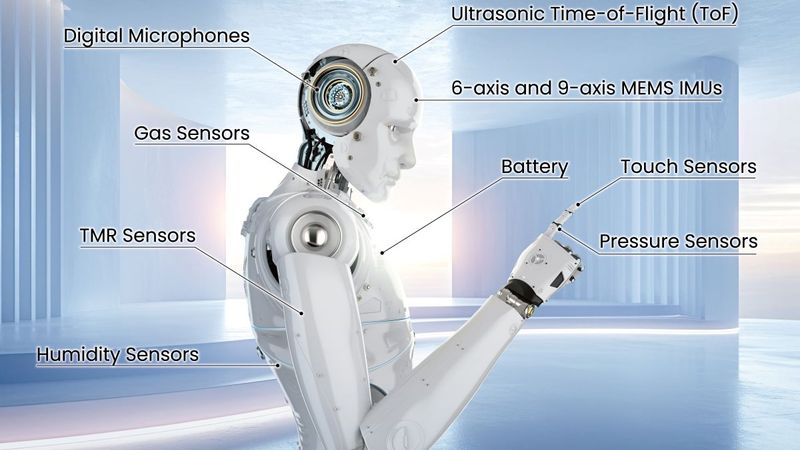
The core of TDK’s ecosystem is a collection of modular sensors. Each sensor is engineered to perform a specific function, yet they are designed to work together to improve robot performance.
Motion sensing is handled by 6-axis and 9-axis MEMS-based Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), like the ICM-42688P. These units provide the high-precision tracking necessary for balance, navigation, and posture correction. Environmental factors are monitored through gas, humidity, and barometric pressure sensors. For example, the IPC-10111 capacitive barometric pressure sensor detects changes in air quality and altitude, which is particularly valuable in industrial contexts.
Robots also gain a sense of touch and proximity through capacitive and piezoelectric touch sensors. These components allow machines to detect objects and interact safely with humans by responding with tactile feedback that makes interactions more intuitive. Additionally, a layer of acoustic and spatial awareness is provided by digital microphones (like the ICS-43434) and ultrasonic Time-of-Flight sensors (including CH101 and CH201). These components enable functions like obstacle avoidance and voice interaction.1
This comprehensive sensor suite enables flexible hardware configurations, which allows developers to customize robots for specific tasks. The plug-and-play integration with ROS also reduces development time and improves cross-compatibility between components. TDK's multi-sensor fusion techniques merge data from different types of sensors to give robots a holistic perception of their environment, like the multi-sensory awareness often portrayed in the futuristic robots of pop culture.
Motion Sensing and Adaptive Locomotion
TDK’s IMUs play a very important role in robotic motion control by enabling precise movement and posture management. These sensors allow robots to move smoothly, maintain balance, and even prevent falls, particularly in humanoid designs.
When IMUs are integrated with other sensing technology, like LiDAR and vision-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), it improves robotic positioning and mapping. This sensor fusion approach allows robots to navigate complex environments with greater accuracy and adaptability.
Robotic systems benefit from advanced algorithms like Kalman filtering, which compensates for sensor drift and ensures fluid transitions between movements. In AI-enhanced applications, IMUs also support predictive trajectory planning, so that robots can adapt to chaning environments in real time. These capabilities are demonstrated in robots like ANYmal, developed by ANYbotics (a TDK Ventures portfolio company), which uses TDK sensor tech to operate autonomously in industrial settings and cluttered environments.2
These capabilities are especially apparent in robots like ANYmal, developed by ANYbotics, a company backed by TDK Ventures. ANYmal demonstrates advanced locomotion and navigation in industrial environments and is a real-world application for TDK’s sensor technologies.
Environmental Awareness: Enhancing Robot Sensing Capabilities
TDK’s environmental sensors also have real-world applications. These sensors significantly enhance robots’ ability to detect and interact with their surroundings and operate safely around humans. TDK’s environmental sensors support this by providing real-time data on air quality, humidity and atmospheric pressure:
Gas Sensors — The TCE-11101 MEMS-based CO2 gas sensor detects harmful substances with high accuracy, which is important in industrial and healthcare environments.
Humidity Sensors — TDK's humidity sensors, featuring ±5% RH accuracy, enable adaptive climate control in smart homes and workplaces.
Pressure Sensors — The ICP-10111 capacitive barometric pressure sensor, integrated into TDK's RoboKit1, allows for altitude detection and atmospheric pressure monitoring.
Beyond atmospheric sensing, TDK sensors enhance object detection and give robots a reliable, non-contact method for navigation and interaction:
Object Detection — TDK's SmartSonic ultrasonic Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors, such as the ICU-20201, provide non-contact object detection and navigation up to 5 meters in any lighting condition.
Voice Detection — The ICS-43434 digital I²S microphones enhance spatial awareness in voice-activated robots.3
With these advanced sensing capabilities, robots can better adapt to their environment and interact with humans in a more intuitive way.
Intelligent Human-Robot Interaction with TDK’s Sensor Fusion
Human-machine interaction is more engaging with sensors that understand gestures, proximity, and touch. TDK’s sensor fusion technology also facilitates more natural and intuitive robot-human interactions. Touch and proximity sensing is especially relevant for consumer-facing robotics, where intuitive feedback helps build using trust:
Haptic Touch Sensors — TDK's piezoelectric actuators provide high-definition haptic feedback for enhanced touch interactions in robotic applications.
Gesture-Based Control — The CH101-00ABR ultrasonic ToF sensor enables gesture-based control and user input recognition with a configurable 180° field of view.
Through TDK’s RobotKit 1 development platform, integrated with ROS and TDK’s adaptive learning models, robots can tailor their responses over time, learning from repeated interactions. This personalized behavior improves functionality and provides more dynamic human-machine interaction:
Holistic Awareness — The ICM-42688-P 6-axis IMU, combined with other sensors in the RoboKit1, provides real-time situational awareness.
Adaptive Learning — TDK's RoboKit software, integrated with ROS, enables personalized interactions using adaptive learning models.
Social Applications — The combination of IMUs, microphones, and ToF sensors in the RoboKit1 platform enhances social robotics applications.
These advancements bring us closer to the kind of seamless human-robot interactions often portrayed in science fiction, where robots can understand gestures, emotions, and intentions with remarkable accuracy.
ROS 1 and ROS 2: The Software Framework Unifying TDK’s Sensor Ecosystem
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a critical standardized platform for robotic perception, planning, and control. TDK’s ROS 1 and ROS 2 extension includes pre-configured sensor libraries and real-time data synchronization, streamlining development and performance.
This software foundation supports critical functions like real-time sensor processing, AI-enhanced decision-making, and cross-platform compatibility. Developers can use the same ecosystem to build robots for very different applications, from smart retail kiosks to autonomous healthcare aides, without having to reinvent the platform for each use case.
Real-World Applications of TDK’s Robotics Sensor Platform
As highlighted throughout this series, TDK’s sensor platform is already making a big impact in the real world. Its technologies are used in robotics systems for healthcare, retail, personal assistance, and more. The investment by TDK Ventures in companies like ANYbotics further underlines the company’s commitment to driving innovation in robotics.
By enabling smarter, safer, and more adaptable machines, TDK is solving today’s engineering problems and laying the groundwork for human-robot coexistence.
Conclusion
TDK's sensor ecosystem is more than just a set of components—it's a modular, scalable, and AI-driven solution that is already shaping real-world robotics. As innovation continues and ethical considerations evolve, we are closer than ever to a future where intelligent, responsive robots integrate seamlessly into our daily lives—much like the imagined robotic companions of anime and manga.
Learn more about TDK’s innovative advancements at https://www.tdk.com/en/index.html.
Resources:
- Qualcomm Robotics RB3 Development Kit. Accessed from https://invensense.tdk.com/technology/robotics/
- TDK IMU Product Page. Accessed from https://product.tdk.com/en/products/sensor/mortion-inertial/imu/index.html
- “Sensor solutions that enable advanced control of service robots”. Accessed from https://product.tdk.com/en/techlibrary/solutionguide/sensor-for-service-robots.html