Cybersecurity and the Supply Chain: Safeguarding PCBA Builds
Hackers can access sensitive data and disrupt device operations by activating embedded malware or hardware trojans in counterfeit components. How can you avoid these issues?
This article was first published on
www.macrofab.comCybersecurity & the Supply Chain: Safeguarding PCBA Builds

In today's hyper-connected world, the intersection of cybersecurity and the global supply chain has become increasingly crucial, particularly for electronics organizations. The growing reliance on digital technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) has given rise to new challenges, exposing vulnerabilities in cybersecurity measures and creating opportunities for cybercriminals.
In this blog post, we'll explore the current state of cyberattacks, the staggering financial and reputational costs of cybercrime, and the steps organizations can take to protect their Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) builds while fulfilling their ethical obligations to end users and the wider community.
The State of Cyberattacks

As we delve into the murky world of cyber threats, it's essential to understand the various attacks prevalent today. The cost of cybercrime is on the rise. With businesses becoming increasingly digital, the opportunities for cybercriminals are growing. In 2022, the estimated global cost of cybercrime was a staggering $600 billion, expected to rise in the coming years.
The digital world has observed a striking surge in ransomware assaults in recent years. These pernicious attacks not only freeze critical business functions, potentially leading to significant operational losses, but they can also inflict substantial financial penalties and tarnish an organization's reputation. Prominent cases such as the Colonial Pipeline incident in 2021 serve as stark reminders of the potential scale and real-world implications of these attacks.
The rapidly expanding ecosystem of the Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly falling under the crosshairs of cybercriminals. This interconnected network of devices, particularly integral and of interest to the electronics industry, often lacks stringent security protocols, making them prime targets for exploitation. Notably, the Mirai botnet attack of 2016, which commandeered IoT devices to launch distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, illustrates the inherent vulnerabilities of these systems.
Persistent threats from nation-state actors continue to menace government institutions and organizations, drawn by the cache of sensitive information they harbor. The U.S., with its vast digital infrastructure and wealth of data, remains a high-profile target, enduring an incessant barrage of cyberattacks. Examples of this include the SolarWinds hack of 2020, widely attributed to a nation-state actor, which infiltrated numerous U.S. government agencies.
How Cybercrime and PCBA Design Interconnect
PCBA design plays a significant role in determining the security and integrity of electronic devices, as it influences the effectiveness of security measures, exploitable vulnerabilities, and how resilient electronic devices are to cyber threats.
In this context, a well-executed PCBA design, integrating robust security practices, can help safeguard against cybercrime. Conversely, a poorly designed PCBA can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit, leading to data breaches, unauthorized access, and other malicious activities.
Here are some specific ways PCBA design can enhance or undermine cybersecurity:
- Device Vulnerabilities: PCBA design plays a crucial role in determining the security of electronic devices. If a PCBA is poorly designed, it may have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. For example, inadequate security measures, weak authentication mechanisms, or insufficient protection against tampering could make the device more susceptible to cyberattacks. Several modern DRAM devices were affected by a novel Rowhammer attack in 2021.
- Malware and Backdoors: Cybercriminals may target PCBA design to introduce malware or backdoors into electronic devices. By compromising the PCBA design process or the supply chain, attackers can inject malicious code into the firmware or hardware of the device, allowing them to gain unauthorized access, control the device remotely, or steal sensitive information.
- Data Breaches: PCBA design flaws can also contribute to data breaches. If a PCBA lacks proper encryption mechanisms or fails to implement secure communication protocols, cybercriminals may intercept or manipulate data transmitted by the device, leading to the compromise of sensitive information.
- Countermeasures: Conversely, PCBA designers need to incorporate cybersecurity measures into their designs to mitigate the risks of cybercrime. This includes implementing secure communication protocols, strong encryption algorithms, secure authentication mechanisms, and physical protection against tampering. By considering cybersecurity during the PCBA design process, designers aim to minimize vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of the device.
- Forensics and Investigation: In the aftermath of a cybercrime incident, PCBA design can play a role in forensic analysis and investigation. Experts may examine the PCBA design, firmware, or components to identify potential vulnerabilities, backdoors, or traces of tampering. This analysis can help in understanding the nature of the cyberattack, attributing it to specific actors, and taking appropriate measures to prevent future incidents. After the SolarWinds supply chain attack in 2020, cybersecurity experts investigated both the affected software and the hardware it interacted with.
The impact of PCBA design on cybersecurity cannot be overstated. A poorly designed or delivered product with design flaws or vulnerabilities not only risks user data and privacy but also puts individuals and organizations at risk of financial loss and reputational damage.
As such, it is imperative for companies to invest in robust PCBA design processes, incorporate best practices for security, and conduct thorough testing and evaluation to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
To avoid the financial repercussions of delivering a product leading to a cyber breach, companies should ensure they maintain continuous high standards for PCBA design and protection during manufacturing by working with a trusted manufacturing partner who takes security seriously. By prioritizing cybersecurity, companies can contribute to a safer digital landscape, bolster user trust, and mitigate the risks associated with cybercrime.
The Cost of Cybercrime
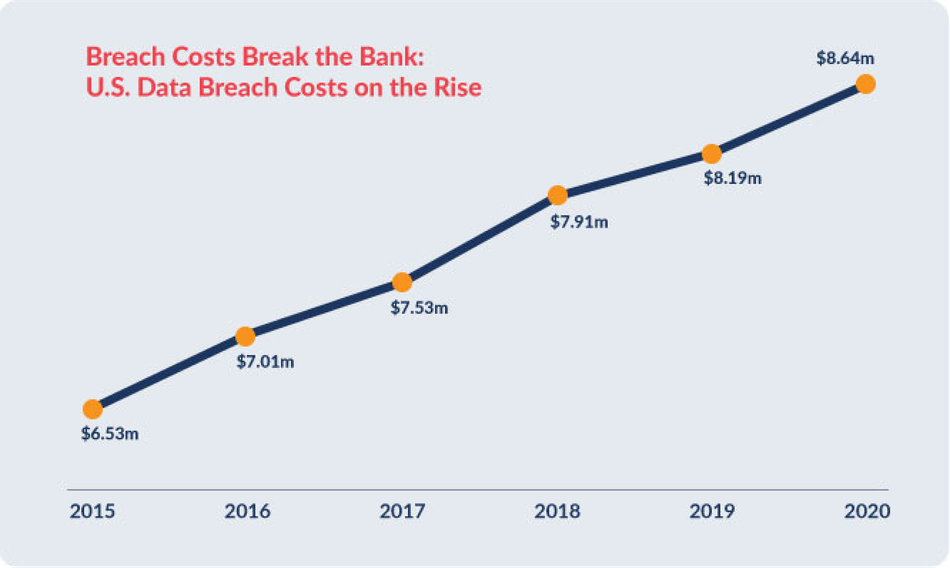
Cybercrime carries far-reaching financial implications. For example, in the U.S., the average cost of a data breach in 2022 was estimated to be $8.64 million. Moreover, the time it takes to identify and remediate a breach is also a significant factor in the overall cost. On average, it takes organizations 280 days to identify and contain a breach, during which the cybercriminals can cause substantial damage.
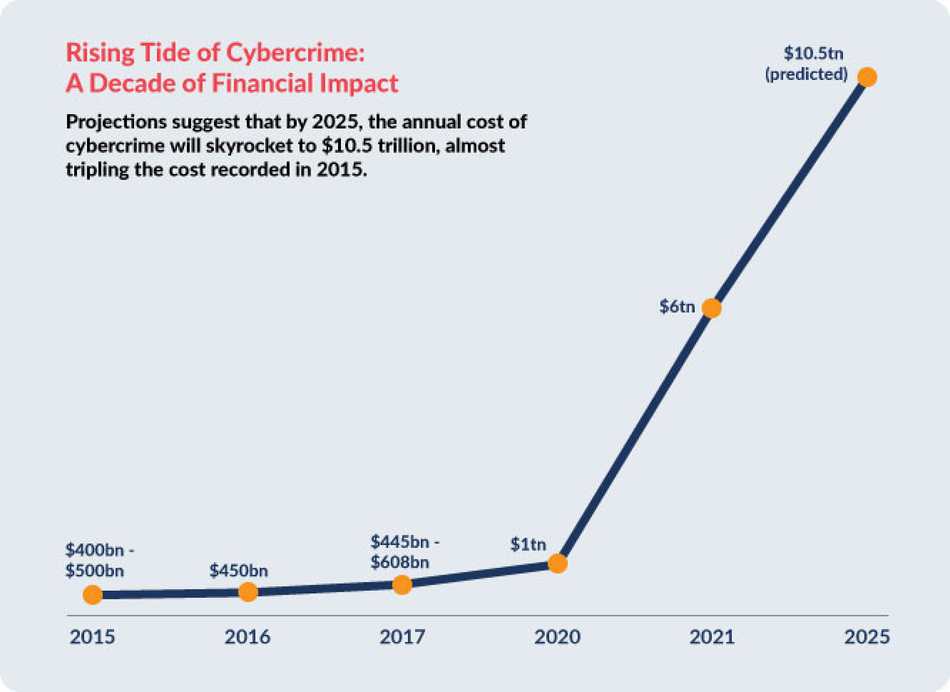
Source: Cybercrime Magazine
Projections suggest that by 2025, the annual cost of cybercrime will skyrocket to $10.5 trillion, almost tripling the cost recorded in 2015.
Source: Statista
Furthermore, reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and potential legal repercussions can have far-reaching effects hard to quantify but are just as damaging.
Protective Measures for Electronics Organizations Against Cyber Threats

The cost of cybercrime is expected to soar in the coming years. Global expenditure in the cybersecurity market is projected to rise by $5.7 trillion between 2023 and 2028, reaching a staggering $13.82 trillion by 2028. Electronics organizations are particularly vulnerable, as cyberattacks can lead to intellectual property theft, product counterfeiting, and fraud.
To address these challenges, manufacturers must adopt a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. This section outlines several data-driven steps manufacturers can take to protect themselves against cyber threats.
Uphold IP Confidentiality Throughout Manufacturing
For electronics organizations, ensuring the protection of intellectual property (IP) during the manufacturing process is of paramount importance. This is due to the potential of cyberattacks and theft. Here are some actionable steps to guarantee IP confidentiality throughout manufacturing:
- Secure File Sharing: Adopt secure practices for sharing design files with contract manufacturers (CMs). Measures could include file encryption, password protection, and the use of secure file transfer protocols. Access to design files should be strictly limited to necessary personnel.
- Trusted Partners: Maintain a strong relationship with CMs known for protecting sensitive information. Perform regular security audits to verify compliance and ensure they have robust cybersecurity defenses.
- Non-disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Establish NDAs with CMs and other partners who handle sensitive design files. These agreements should stipulate each party's responsibilities concerning IP protection and penalties for breaches.
- Design Obfuscation: Consider employing techniques that make unauthorized understanding or reverse-engineering of design files challenging. These could include splitting designs across multiple files or using proprietary file formats.
- Monitoring and Tracking: Consistently oversee and track the handling of design files throughout the manufacturing process. Implement a system that records access to sensitive files
- Manufacture in IP-strong locations: Manufacturing in countries with robust IP laws, like the USA and Mexico, further protects designs against cyber attacks.
- Employee training: Train employees on the importance of IP protection and the potential consequences of IP theft. Encourage a culture of cybersecurity awareness and vigilance within the organization. Ensure all manufacturing partners do the same.
By taking these proactive measures, electronics organizations can significantly reduce the risk of IP theft during manufacturing, helping maintain their competitive edge and protect their investments in research and development.
Mitigate Counterfeit Component Risks through Strategic Sourcing

A 2020 study by the Alliance for Gray Market and Counterfeit Abatement (AGMA) found that counterfeit components in the technology industry lead to an estimated loss of $28 billion in revenue annually. Ensuring components are sourced from reliable and verified suppliers can help mitigate this risk.
Not only can counterfeit components lead to system instability, failures, or unusual behaviors that can aid a cyberattack, but they can also allow embedded malware and hardware trojans to be activated once the PCBA they're attached to has been used. By doing so, hackers can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt the device's operations.
To mitigate these risks, companies should maintain the integrity of their supply chain by vetting suppliers carefully and by using secure hardware and software design practices to protect against threats.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the rapidly evolving landscape of cyber threats and the significant financial and reputational damages that cyberattacks can inflict necessitate proactive measures to safeguard businesses, particularly in the electronics industry. As cybercrime costs continue to rise, organizations must prioritize implementing robust cybersecurity strategies to protect their valuable assets and intellectual property.
By adopting various data-driven protective measures, such as detection and prevention tools, employee training, response planning, IP protection, and secure strategic sourcing, organizations can effectively mitigate cyber risks and create a more resilient and secure environment for their operations. Proactive investment in cybersecurity is essential for the survival of individual businesses and plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and security of the global supply chain.
Discover How MacroFab Can Keep Your IP Safe
PROTECT YOUR BUILDS WITH MACROFAB
