Bipedal robot
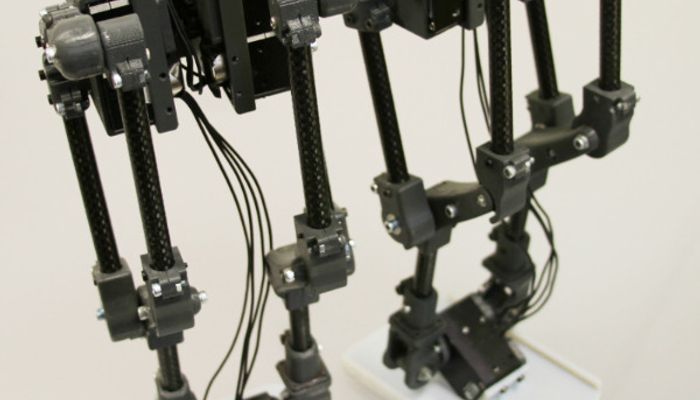
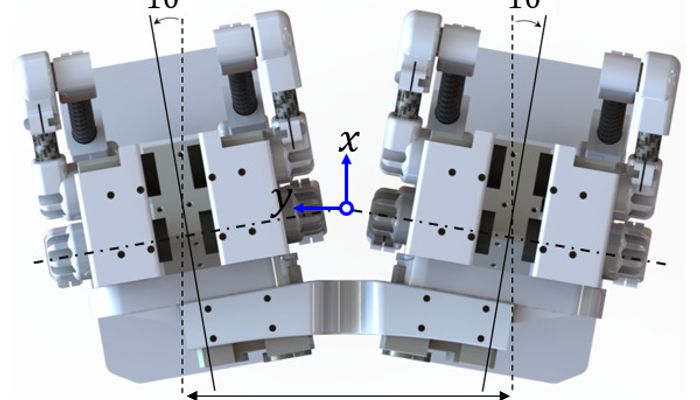
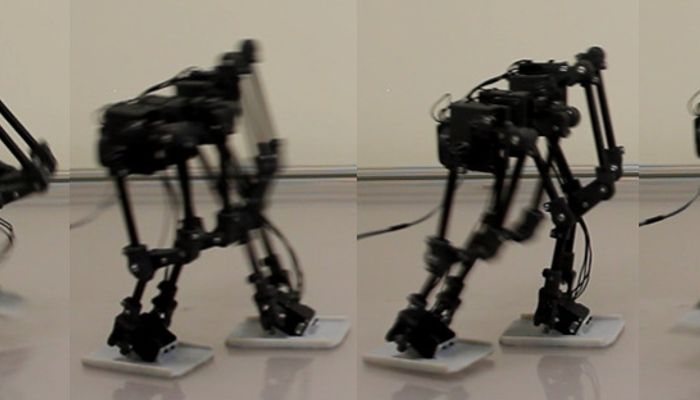
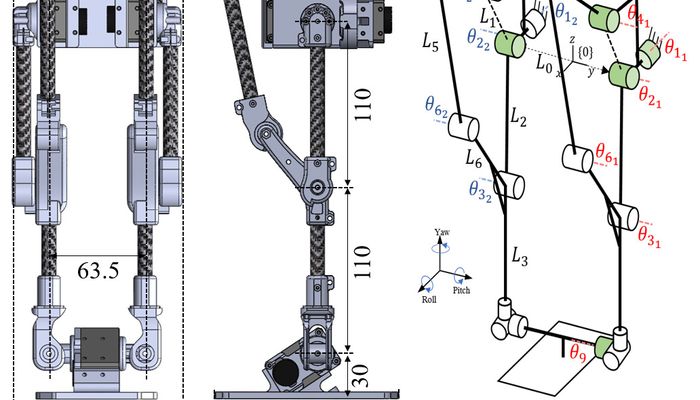
A bipedal robot using serial-parallel hybrid leg mechanism. The robot has a leg mechanism that achieves 6 DOF with a combined structure of serial and parallel mechanism. It is designed to have a light structural inertia and large workspace for agile bipedal locomotion. A new version of Hybrid Leg is fabricated with carbon fiber tubes and bearings to improve its structural rigidity and accuracy while supporting its weight. A pair of Hybrid Legs is assembled together for bipedal locomotion. In the assembly, we adopt a pelvis structure with an yaw angle offset to enlarge the feet workspace, inspired by the toe-out angle of the human feet.
Technical Specifications
| Degrees of freedom (DOF) | 6 |
| Weight | 1.9 |
| Servo's per leg | 6 |
| Center of mass | 38 |
| Manufacturing technique |
Overview
The robot has a leg mechanism that achieves 6 DOF with a combined structure of serial and parallel mechanism. It is designed to have a light structural inertia and large workspace for agile bipedal locomotion. A new version of Hybrid Leg is fabricated with carbon fiber tubes and bearings to improve its structural rigidity and accuracy while supporting its weight.
A pair of Hybrid Legs is assembled together for bipedal locomotion. In the assembly, we adopt a pelvis structure with an yaw angle offset to enlarge the feet workspace, inspired by the toe-out angle of the human feet.
The hardware design utilizes carbon fiber tubes and bearings to improve kinematic accuracy and dynamic characteristic. The linkages consist of a high modulus carbon fiber tube and 3D-printed bearing carriage tips mounted at each end of the tube.
References
The mechanical design of the single leg prototype and bipedal assembly is presented. Describes the results of performance evaluation including the workspace, maximum foot velocity, and trajectory tracking. Presents the experimental results of bipedal locomotion. Conclusions and future work are discu
Recommended Specs
Continue Reading
With the flexibility to deliver unmanned detection and rescue services, Jueying X20 is designed for the complex terrain of a post-earthquake landscape, the insides of vulnerable debris buildings, tunnel traffic accidents, and in toxic, hypoxia, and high-density smoke environments created by chemical pollution or disaster event.