What Is Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) Wireless Communication?
LPWA is an abbreviation for Low-Power Wide-Area. It is also referred to as Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN). LPWA is wireless communication technology that features low power consumption and wide-area and long-distance communication.
This article was first published on
article.murata.com1. What Is LPWA?
LPWA is an abbreviation for Low-Power Wide-Area. It is also referred to as Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN). LPWA is wireless communication technology that features low power consumption and wide-area and long-distance communication. Although the amount of communication data is small and it is slower than Wi-Fi and other networks, communication over 10 km is possible. The long-distance communication of small-size data is sought in the utilization of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine to Machine (M2M) in the smartification of factories, logistics, agriculture, housing, life infrastructure, and other facilities. Therefore, LPWA is attracting attention as the fundamental wireless communication technology behind IoT and M2M.
2. Two Features of LPWA
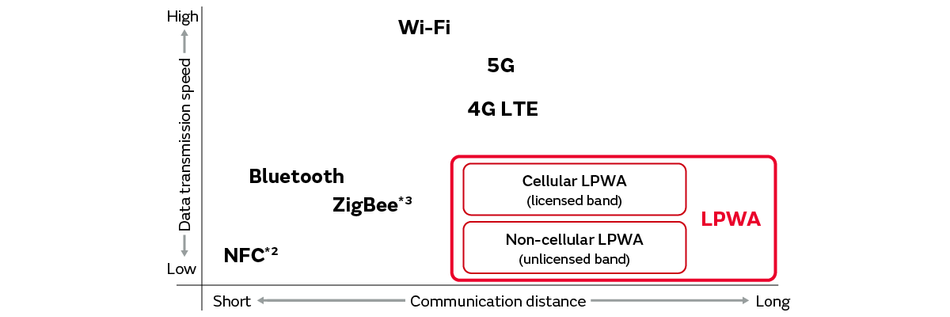
We explain here the differences between LPWA*1 and other wireless communication methods and, in particular, the major features of LPWA in terms of its low power consumption and long-distance communication. Fig. 1 shows the relationship between communication distance and communication speed (data transmission speed) in LPWA and other wireless communication methods. In addition to its longer communication distance than other communication methods, we can see that LPWA has a low data transmission speed; in other words, it is slow.
*1: LPWA is divided into cellular LPWA (licensed band) and non-cellular LPWA (unlicensed band). We explain these types and the various standards in “3. LPWA Types and Standards” below.
*2: Near Field Communication (NFC) is wireless communication technology with a maximum communication distance of about 10 cm. NFC has been adopted in contactless IC cards for public transportation and similar applications.
*3: ZigBee is short-distance wireless communication technology that makes it possible to directly connect between devices to build networks. It has a low speed (maximum of 250 kbps) and low power consumption. Accordingly, it has been adopted in IoT equipment (sensor data communication and remote control of home appliances, etc.).
2.1 Features of LPWA (1): Low Power Consumption
The communication speed is high from Mbps to Gbps in data communication using 4G LTE and 5G used in smartphones and other such terminals. Along with that, the power consumption required for communication also increases.
On the other hand, the size of the data required for the sensing and control of many of the devices used in IoT and M2M is small. Accordingly, IoT and M2M can be operated sufficiently with low-speed communication. Therefore, LPWA, which has been designed to be used in IoT and M2M, can keep power consumption low due to its low communication speed. In fact, the battery life of LPWA modules is 10 years or more. That means efficient operation is possible in various installation locations. For example, it is possible to dramatically reduce the frequency of battery replacement in IoT devices.
2.2 Features of LPWA (2): Long-distance Wireless Communication
When considering short-distance data communication from several meters to several hundred meters, the candidates are usually a type of Personal Area Network (PAN) called Bluetooth® or a type of wireless Local Area Network (LAN) called Wi-Fi. On the other hand, there are many cases in fields such as IoT and M2M, which require data communication to monitor and operate IoT devices that have been installed over a wide area, from several kilometers to dozens of kilometers. That means there is a need for wireless technology that enables longer-distance communication than wireless PAN or wireless LAN.
LPWA is a wireless communication technology designed to satisfy the requirement of long-distance communication as is needed in the IoT era. It mutually transmits small-size data over long distances including the sensor values output by IoT devices installed in distance places, data to identify the location of those devices, and control data sent to them.
3. LPWA Types and Standards
LPWA is divided into cellular LPWA and non-cellular LPWA*4. In addition, each of these has its own standards. There are differences in the specifications including the frequency bandwidth used, the communication distance, and the transmission speed.
*4: In Japan, cellular LPWA is sometimes called “cellular-based” or “licensed-based” LPWA, while non-cellular LPWA is sometimes called “non-cellular-based” or “unlicensed-based” LPWA.
3.1 LPWA Types: Cellular LPWA and Non-cellular LPWA
To start with, we will explain both cellular LPWA, which uses a frequency band requiring a radio station license (licensed band), and non-cellular LPWA using a frequency band not requiring a radio station license (unlicensed band).
Cellular LPWA (Licensed Band)
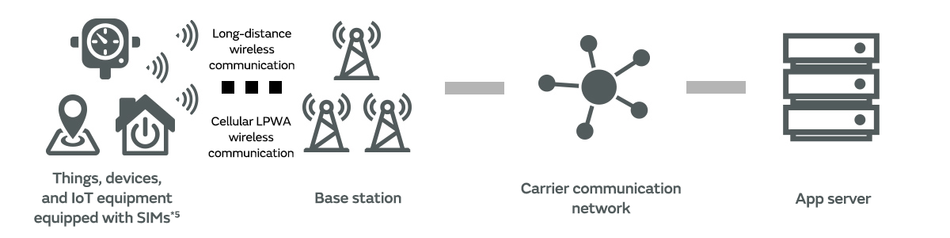
The base stations and communication networks of carriers are generally used in cellular LPWA, which requires a radio station license (Fig. 2). However, it is necessary to have an environment in which communication from IoT equipment equipped with LPWA modules to the base stations is stable. Accordingly, the areas between IoT equipment and base stations tend to be areas with a high density of people such as urban districts, residential districts, and industrial districts.
Non-cellular LPWA, which we talk about later, is selected in areas distant from urban districts such as mountainous regions and isolated islands where communication to base stations is difficult.
*5: A Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) is literally a module that identifies the subscriber. Equipping a SIM compatible with a carrier with which you have a contract in a device or module allows you to use the communication network of that carrier with cellular LPWA, which uses licensed bands requiring a license.
Examples of the utilization of cellular LPWA include data collection in electricity, gas, water, and other life infrastructure, and tracking of packages in international logistics with roaming*6 of the communication networks of carriers in each country.
*6: Roaming generally refers to a service that enables the use of a communication network of a local carrier affiliated with the carrier with which you have a contract outside the service provision area of your carrier. Such services provided internationally are also called “international roaming.”
Please see “4. LPWA Utilization Examples” in “What Is Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) Wireless Communication? - Utilization” for details of the examples.
Non-cellular LPWA (Unlicensed Band)
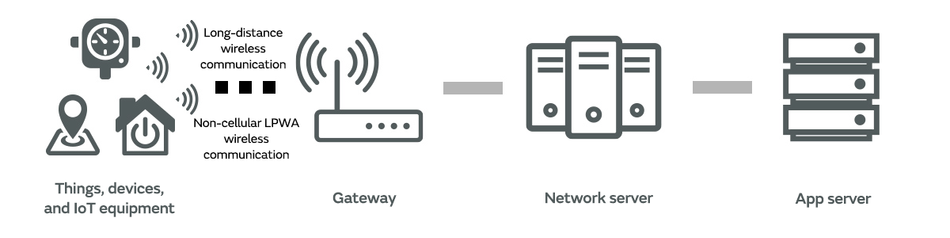
Non-cellular LPWA uses the 920 MHz band, which is a sub-GHz band that does not require a radio license in Japan. As shown in Fig. 3, it is possible to send data obtained through a gateway*7 from an LPWA module to a network server or app server without using the communication network of a carrier.
*7: Gateway: The communication protocol (regulations that define the procedures at the time of communication and data format, etc.) is determined to enable communication between equipment in wireless and wired communication. It is not possible to directly communicate between equipment or between networks with differing communication protocols. A gateway is a piece of equipment or software to solve this issue. It enables a relay connection by converting the protocols.
Examples of the utilization of non-cellular LPWA include long-distance communication applications that cannot be covered by cellular LPWA, such as communication in environments where it is difficult to connect to the base stations of carriers including mountainous regions and isolated islands, and communication in a private network.
Please see “4. LPWA Utilization Examples” in “What Is Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) Wireless Communication? - Utilization” for details of the examples.
3.2 Cellular LPWA and Non-cellular LPWA Standards
We explain here the standards and features of both cellular LPWA and non-cellular LPWA.
Cellular LPWA (Licensed Band) Standards
There are two standards for cellular LPWA that uses the base stations and communication networks of carriers: LTE Cat. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT. Both standards use free bandwidth in the LTE frequency band (700 MHz to 3.5 GHz). We give the features of both below.
- LTE Cat. M1 (LTE-M)
LTE Cat. M1 (LTE-M) is the abbreviation for LTE Category M1. It is also called LTE for Machine-type communication (LTE-M). The maximum speed is 1 Mbps for both uplinks and downlinks. The maximum communication distance is approximately 10 km. Communication is also possible while walking, riding a bicycle, driving a car, or otherwise moving. It is suitable for IoT devices that transmit location information while moving as applications. This includes, for instance, the monitoring of children and logistics cargo trackers.
- NB-IoT
NB-IoT is the abbreviation for Narrow Band IoT. Although the maximum speed is slow at 62.50 kbps for uplinks and 26.15 kbps for downlinks, it has a maximum communication distance of approximately 40 km. It is not suitable as an application for communication while moving. However, it is suitable, for example, for smart meters fixedly installed over a wide area and IoT devices that have crime prevention and alarm functions.
Please refer to Tab. 1 in the next section “3.3 Cellular LPWA and Non-cellular LPWA Specifications Comparison” for the differences in both standards.
Moreover, you can see the LPWA modules compatible with these two standards on the following page: “5. Murata Manufacturing’s LPWA Modules” in “What Is Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) Wireless Communication? - Utilization.”
Main Standards of Non-cellular LPWA (Unlicensed Band)
There are multiple standards for non-cellular LPWA including LoRaWAN as well as Sigfox, Wi-SUN, ZETA, and ELTRES. All these standards use the sub-GHz band. The communication speed of most of these standards is around 100 bps to 250 kbps. The communication distance varies greatly depending on the standard from about 2 km to 100 km. There is a tendency for the communication speed to be slower the longer the communication distance.
You can see the LPWA modules compatible with LoRaWAN on the following page: “5. Murata Manufacturing’s LPWA Modules” in “What Is Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) Wireless Communication? - Utilization.”
3.3 Cellular LPWA and Non-cellular LPWA Specifications Comparison
Tab. 1 shows the specifications using as an example the LTE CAT. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT cellular LPWA standards and the LoRaWAN non-cellular LPWA standard. This table also includes as a reference the specifications of LTE Cat. 1, which has a higher communication speed and communication cost than the current standards of LPWA. It mainly compares the necessity of a radio station license (or whether the environment allows stable communication with base stations), the communication distances, and the communication speeds to serve as a reference when choosing which standard to use.
Tab. 1: Specifications Comparison of the Main Standards of Cellular/Non-cellular LPWA and LTE (Reference) (as of June 2023)
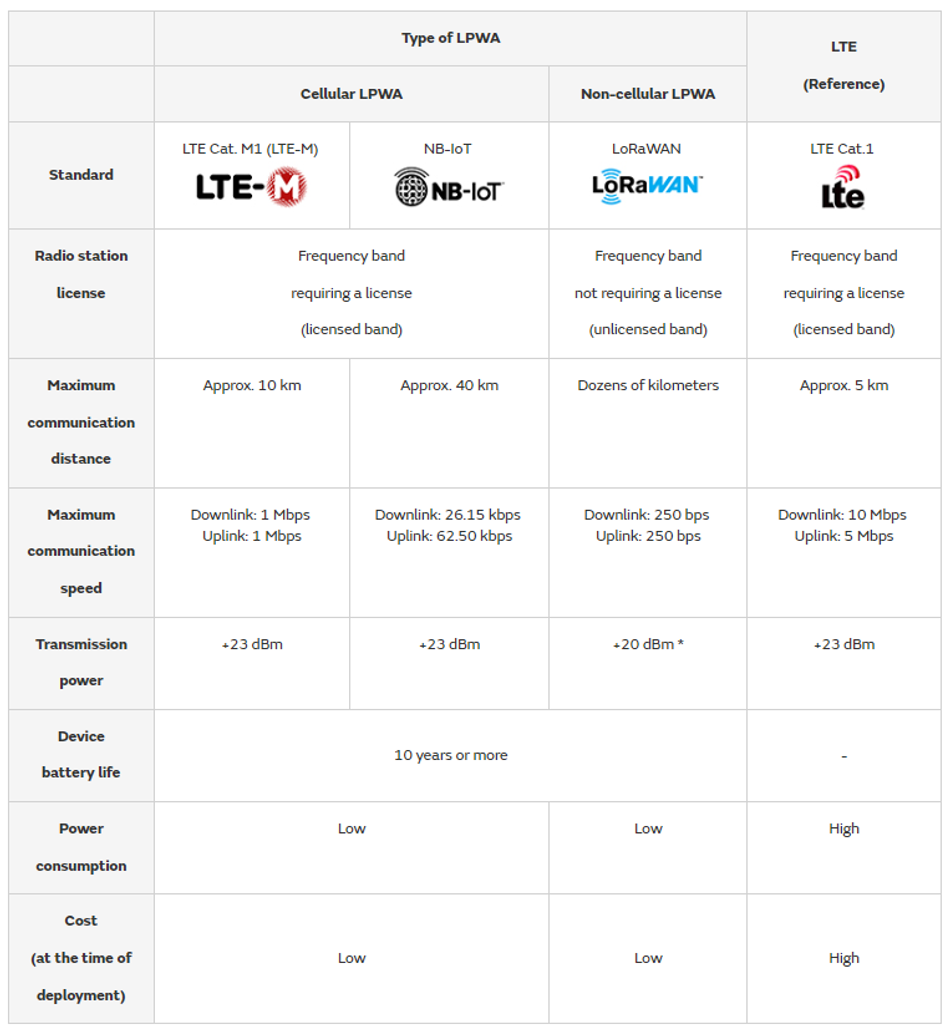
*+20 dBm is for the U.S. only. It is +14 dBm in the EU/Asia.
Column: Arrival of LPWA
There were cases in which wiring became the bottleneck to installation in the process of the IoT and M2M technologies spreading widely from the manufacturing industry to the home.
For example, the more complex wiring and increased man-hours at the time of setup changes become issues when connecting cables for power supply and communication to each IoT device that handles small-size data like general-purpose sensors in factories.
A desire emerged for battery drive and wireless communication to resolve those issues. However, when using Wi-Fi, for example, problems arise in factory facilities with large premises. Those problems include insufficient communication distance and a shortened battery life due to high-speed communication. Moreover, LTE used in mobile phones is also high-speed communication. Therefore, problems arise such as high usage costs due to the large power consumption in devices making it necessary to frequently charge them. (In fact, a standard called LTE Cat. 1 (reference: “3.3 Cellular LPWA and Non-cellular LPWA Specifications Comparison”) was initially used.) The amount of communication data in IoT/M2M devices such as general-purpose sensors in factories and control of electrical products in the home is small in the first place. That means it is not necessary to use high-speed communication.
This is also the same for the smartification of electricity, gas, water, and other life infrastructure installed in large numbers in a wide area. The size of the data communicated by smart meters is small. Therefore, there was an issue of how to realize low-speed, low-power consumption and long-distance wireless communication at low cost for that.
Accordingly, there was a desire for the specifications necessary for IoT/M2M applications; in other words, wireless technology capable of low-speed communication sufficient for a small amount of communication data, low-power consumption from that, and long-distance communication. LPWA was proposed as wireless technology to satisfy these specifications. Currently, LPWA standards are being provided by various companies and organizations. For example, the arrival of the LTE CAT. M1 (LTE-M), NB-IoT, and other standards we have introduced in this text has meant that LPWA has come to be widely utilized as a leading method of wireless communication in the IoT/M2M field.
4. LPWA Utilization Examples
We introduce here some examples of the applications LPWA is actually being utilized in. Using LPWA makes it possible to collect data sensed remotely in real time, control devices, and detect location.
4.1 Smartification of Life Infrastructure (Smart Meters) [Cellular LPWA]

Smart meters are becoming more widely used. These are devices that automatically collect meter data with LPWA long-distance wireless communication for the amount used of electricity, gas, water, and other services as the smartification of life infrastructure. The installation of smart meters has advantages for both operators and users. For example, operators can reduce the time, effort, and costs involved in meter readers actually going to meters to visually check the numerical values of the amount used on them. Meanwhile, users can grasp the amount they are using on a daily basis. Moreover, if, for example, an operator confirms that there is an electrical leakage, gas leakage, water leakage, or other malfunction from the meter data collected with LPWA, it is possible to take an emergency response such as cutting off the supply with remote control. Therefore, the safety of the living environment can be improved. The locations where LPWA is used in this case are mainly areas with residences, companies, and other buildings. Therefore, cellular base stations are plentiful. That means that cellular LPWA (licensed band) is used in many cases for automatic meter reading by smart meters.
4.2 Smartification of Houses and Facilities (Smart Homes and Smart Locks, Etc.) [Cellular LPWA / Non-cellular LPWA]

In addition to the aforementioned life infrastructure, the insides of buildings such as houses, offices, factories, and commercial facilities are also being made smarter. For instance, it has become possible to set up a highly convenient and comfortable living environment by integrating and controlling house locks (smart locks) and air conditioners, lighting equipment, and various other home appliances, that is, by realizing smart homes and connected homes. Moreover, it is possible to collectively manage the usage and locking situation of shared spaces and meeting rooms in factories, offices, and other facilities, freeing us from the complexity of managing the usage and locking situation.
LPWA is being considered and is becoming more widely used for the following reasons in the smartification of such facilities.
・The control signals and sensing data have a small size
・There is excellent cost-effectiveness in operation such as in terms of the cellular communication expenses
・Maintenance labor is low (the battery life is 10 years or more)
・It is possible to select cellular LPWA (licensed band) in regions where communication connections with the base stations of carriers are stable (regions where many people live and work) and non-cellular LPWA (unlicensed band) that enables communication using gateways even in regions where connections with base stations are not stable with cellular LPWA (mountainous regions, isolated islands, and regions distant from urban districts)
4.3 Tracking of People, Things, and Other (Wearable Devices/Trackers) [Cellular LPWA]

Small LPWA modules can also be equipped to small devices. For example, it is possible to acquire location information on people, animals, things, and other by equipping small LPWA modules to wearable devices and trackers. Therefore, location tracking technology using these devices is being widely utilized.
Let’s assume we will be using the cellular LPWA (licensed band). In that case, the location data transmitted from wearable devices and trackers is delivered to a data server via the communication network of a carrier from a cellular base station to enable tracking to be performed. It is possible to use wearable devices to watch over children and prevent pets from becoming lost with this technology. Moreover, packages in transport can be tracked in real time from a remote location. In addition, cellular LPWA also supports tracking in international logistics with roaming of the access point carriers in each country.
4.4 Environmental Monitoring and Smartification of Agriculture [Cellular LPWA / Non-cellular LPWA]

The introduction of LPWA with its features including long-distance communication and low-power consumption is expanding into fields such as environmental monitoring and smart agriculture. For instance, we can install various environmental measurement sensors (water temperature, water volume, soil and CO2 concentration, etc.) at monitoring points in mountainous regions, isolated islands, and areas far from urban centers. We can then collect the data acquired from those sensors if we use non-cellular LPWA (unlicensed band). This makes it possible to grasp in real time from a remote location the conditions at the monitoring points. Moreover, expansion from environmental sensing to smart agriculture (agri-tech) is also being considered based on this example.
It is possible to use cellular LPWA (licensed band) if the environment is located in a town or village capable of stable communication with base stations.
4.5 Use of Smart Payment Terminals Outdoors [Cellular LPWA]

When paying for goods or services using wireless communication (smart payment) outdoors, if, for example, Wi-Fi is used, the server is sometimes not able to receive the data because the strength of the signals reaching the gateway is low. Moreover, if we use methods of cellular mobile communication such as 4G LTE or 5G with a smartphone serving as the terminal, the burden of communication expenses may increase.
On the other hand, although it is the same cellular method as 4G LTE or 5G, if we use cellular LPWA (licensed band), we can send payment data in real time at a lower cost than mobile communication. Smart payment using LPWA is expected to be utilized in outdoor restaurants, mobile stores, sales of goods at outdoor events, taxis, and similar.
4.6 Remote Monitoring of Medical Equipment (CPAP Devices) [Cellular LPWA]

People who have been diagnosed with sleep apnea syndrome (SAS) in which breathing temporarily stops during sleep sometimes experience intense sleepiness, headaches, and other symptoms during the day. These symptoms may have a major impact on people’s lives and society. For example, an accident can be caused due to a driver falling asleep at the wheel of their car. Therefore, SAS requires treatment. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment is a leading method of treating SAS.
There are SAS patients who want to easily carry and use CPAP devices, which are usually used at home, on business trips, travel, and other such outings.
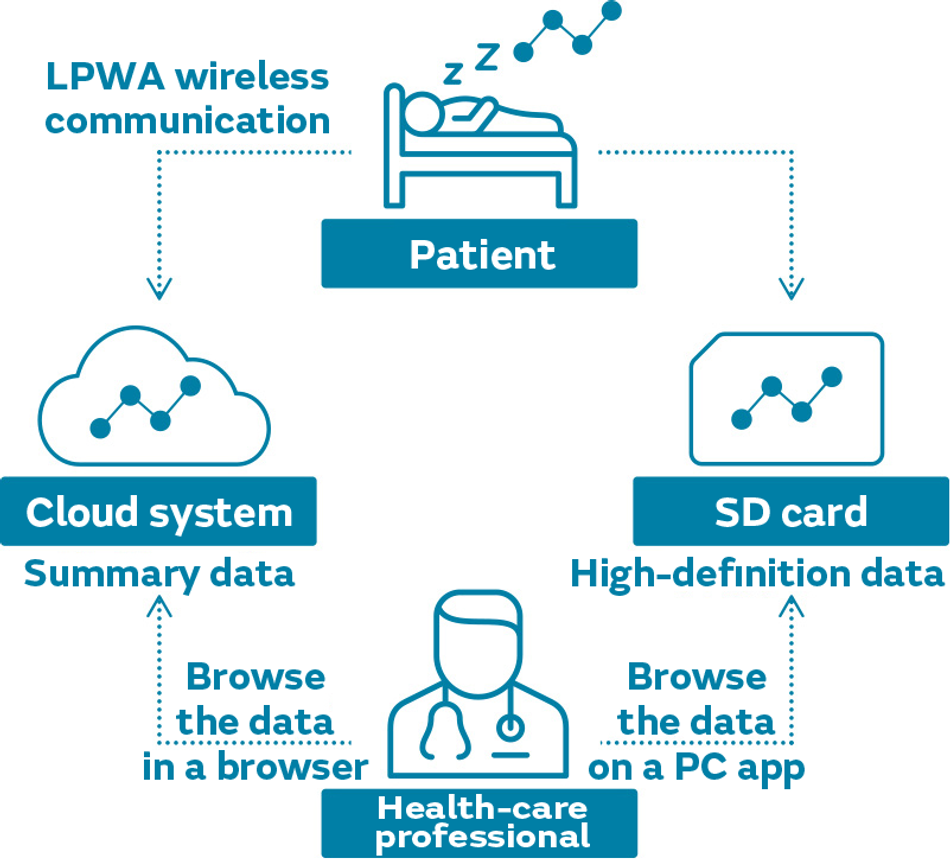
We have developed a small and thin CPAP device that is easy to carry around by adopting our small components, including blower components and cellular LPWA modules. We have started manufacturing and selling this product in Japan. This product comprises a base unit and a main unit that can be held in one hand. The main unit can be dismounted and carried to outing destinations. Furthermore, we have equipped our cellular LPWA module to the main unit. This has enabled long-distance wireless communication to carrier base stations, allowing the sleep data of patients to be transmitted to the cloud even at outing destinations. Health-care professionals can then remotely monitor this sleep data at any time.
5. Murata Manufacturing’s LPWA Modules
Murata Manufacturing manufactures small and low-power-consumption LPWA modules. We have a lineup of communication modules compliant with each of the LPWA standards used in various countries: LTE CAT. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT for cellular LPWA (licensed band) and LoRaWAN for non-cellular LPWA (unlicensed band).
5.1 Strengths of Murata Manufacturing’s LPWA Modules
The LPWA modules that Murata Manufacturing provides for diverse fields and applications in various places around the world have the following strengths and features.
・Small and High-quality
Our LPWA modules realize a 50% reduction in size compared to conventional products. We have achieved that by manufacturing the modules with advanced manufacturing technologies and quality control built up over many years using components we have developed and manufactured in-house and strong partnerships with market-leading IC manufacturers. It is also effective to equip these LPWA modules to wearable devices. Our modules are being used in diverse applications in various countries and regions around the world because they combine the world’s smallest-class compactness with stability and high reliability as well as offering a stable supply.
・Enhanced Support Structure
In addition to proposing LPWA modules suitable for applications, we have set up a support structure in line with our customer needs. This includes radio law certification in each country and connectivity verification. It also covers dealing with inquiries about cooperation with carriers in the use of the licensed band due to the introduction of cellular LPWA modules.
5.2 LPWA Module Lineup
Murata Manufacturing manufactures and sells cellular LPWA modules compatible with both LTE CAT. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT and non-cellular LPWA modules compatible with LoRaWAN. We have a lineup of communication modules compliant with each of the LPWA standards used in various countries.
Cellular LPWA Modules
We have a lineup of cellular LPWA modules compatible with both the licensed band standards of LTE CAT. M1 (LTE-M) suitable for communication while moving and NB-IoT suitable for communication in devices used after being fixed in place.
・Cellular LPWA Module Type 1SC (LBAD0XX1SC)

This is the world’s smallest in size LTE Cat. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT module with global certification. It supports GPS/GNSS, Open MCU, and iSIM. It is capable of providing MVNO network communication via eSIM in partnership with Truphone.
Type 1SC (LBAD0XX1SC)|LPWA Products
We also have available a Type 1SC evaluation kit to enable you to conduct operation, characteristics, and application tests before introducing multiple cellular LPWA modules.
・Cellular LPWA Module Type 1SE (LBAD0ZZ1SE)
This is an LTE Cat. M1 (LTE-M) and NB-IoT module. It complies with certification in Japan and supports Truphone eSIM.
Type 1SE (LBAD0ZZ1SE)|LPWA Products
You can obtain the STMicro Discovery Kit from one of our business partners, STMicroelectronics NV. This is an evaluation kit that allows you to confirm the operation and characteristics of Type1SE LPWA modules.
・Cellular LPWA Module Sample
We have available Type 1SC/1SE module samples. Please click here to contact us for details.
Non-cellular LPWA Modules
We have a lineup of LPWA modules compatible with LoRaWAN, which is widely supported because of its outstanding specifications in terms of the balance of communication speed and communication distance among the many non-cellular LPWA standards.
・Non-cellular LPWA Module Type ABZ (CMWX1ZZABZ)

This is a non-cellular LPWA module compatible with the LoRaWAN standard, which does not require a license. Having acquired radio law certification in major regions, this module operates in many regions and carrier networks around the world.
Type ABZ (CMWX1ZZABZ)|LPWA Products

If you have any questions based on this article that you would like to discuss with an expert at Murata, don't hesitate to reach out. There's an entire team ready to support you with your question.