Understanding the Fundamentals of PoleAttraction™ Technology
PoleAttraction™ is an advanced stage of electroadhesion technology, developed by Engimotion which promises to revolutionize industrial automation.
Electroadhesion, also known as electrostatic adhesion, is an electrically regulated mechanism, that creates attraction between two materials. Utilized in robotic handling, climbing, and active adhesion[1].
This term was coined by Danish scientists Johnsen and Rahbek in 1923, while working with polished lithographic stone and metal surfaces to describe the physical phenomenon of significant adhesion that occurred when the highly resistive stone was placed on top of a metal plate and a high voltage was applied between them[2]. When a conductor and a semiconductor are in contact and a voltage is applied across the two materials, the conventional Johnsen–Rahbek (J-R) effect explains the attractive force experienced between the two materials.
To date, a wide variety of other standard adhesion techniques have been used to stick objects or materials together temporarily. Chemical adhesion, synthetic gecko feet, suction cups, mechanical and magnetic gripper are some of these techniques. However, they are still not enough to cover all the challenges.
Electroadhesion mainly takes its place where the standard solution creates damage and marks on the product or fails to stick it effectively and efficiently during the process.
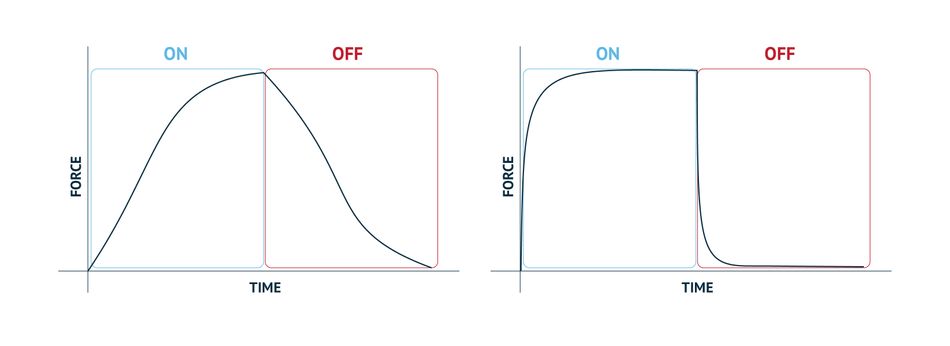
Although this technology has improved over the years, two major problems remain. It is extremely difficult to adjust and eliminate the attractive force created, in a fast and controlled way. These points assume special importance when applied in industrial applications.
PoleAttraction™, an Engimotion development and the ultimate evolution of electroadhesion, intends to solve these challenges. Especially focused on non-conductive materials, it promises a fast and controlled delivery of the handled part at the delivery point, as well as handling of product stacks, with the defined number of layers, reliably.
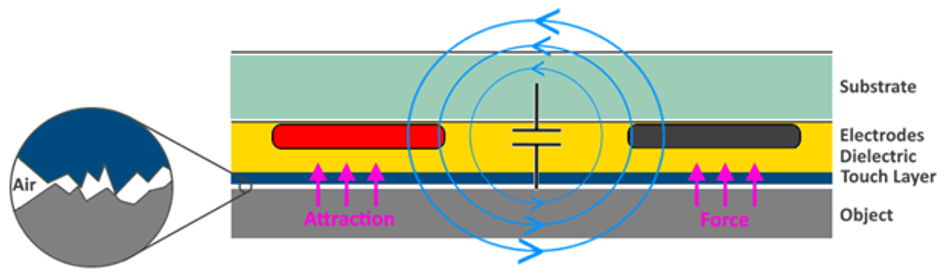
PoleAttraction™ consists of an advanced electronic controller and a set of attraction pads. The controller is responsible for energizing each pad, generating a magnetic field that will polarize it and the non-conductive part or surface in contact, creating an attractive force between them[3], according the defined thresholds and orders received through the existent interfaces.
The pad is based on a capacitor model, where the part to be handled is included, and normally depending on the application, it can have various sizes, shapes, and levels of rigidity[4]. PoleAttraction™ uses a proprietary design that ensures effective attraction with over 90% non-conductive materials and surfaces.
Each PoleAttraction™ pad needs a specific combination of certified materials, applied through a very demanding and controlled manufacturing process, to ensure, beyond the good functioning, a fast and controlled attraction response.
Nonetheless, to achieve really interesting and viable performance results, the PoleAttraction™ controller was developed with an integrated closed loop control, empowered by artificial intelligence, which manages the amount of attraction with the part or surface in real-time.
Advantages of PoleAttraction™ Over Other Existing Adhesion
PoleAttraction™ has a number of advantages over other standard adhesion techniques, such as pneumatic, mechanical, magnetic, and bioinspired, even if combined.
The following are some of the main advantages that make PoleAttraction™ so interesting for certain areas, products, and applications:
- Delicate and Contamination free: By using suspension or soft pads, PoleAttraction™ endows the ability to handle delicate and valuable objects efficiently and safely, without creating damage, marks or even stains.
- Adaptability: PoleAttraction™ empowers equipment to be independent of the material structure of the part to handled. So, porous and flexible parts are no longer a problem.
- Versatility: The same PoleAttraction™ system can handle different materials or surfaces, with varying shapes and dimensions, single layer or multilayer.
- Robustness: Even when PoleAttraction™ faces harsh situations such as rough surfaces, wet materials, dusty settings, low pressures and temperature conditions, the equipped system will maintain the task success level, with no wear.
- Low Consumption: Despite the fact that a high voltage needs to be supplied, PoleAttraction™ endows systems with low energy consumption, because only a very small current (mA range) will travels through the pad.
- Low weight and compact: PoleAttraction™ can be easily applied in a system using materials and structures that are mechanically simple and lightweight, reducing system complexity.
- High forces: PoleAttraction™ is very efficient when comparing the attraction force generated per contact area (up to 1.1N per 10mm^2), keeping the rest of the advantages unchanged.
- Fast response: One device empowered with PoleAttraction™ will be very independent of the part to be handled, achieving minimum pick and place waiting time of 0.2 seconds.
- Silent: A device equipped with PoleAttraction™ will work without creating any additional noise, due to the fact that the generated sound will be out of hearing range.
- Detection: PoleAttraction™ enable the system to have real-time feedback on the presence of part or surface. This feature offers the possibility of a closed loop control.
Applications of PoleAttraction™ in the Real World
PoleAttraction™ can help in a wide range of applications, in different areas and equipment. As a disruptive solution that offers new capabilities, the most demanding situations are those where standards adhesion solutions fail to effectivity and efficiently solve the challenge. However, the recent focus on electrical efficiency opened the door to a wide range of applications, where standard adhesion solutions has been applied.
In the next points we will present some particularly advantageous applications of PoleAttraction™ technology:
- End of arm tooling: It is the most important component in robotic solutions, the one that interacts directly with parts and components, whose functioning can be influenced by the environment. PoleAttraction™ is often used in EOAT solutions, mainly due to its soft touch, adaptability, versatility, and robustness, providing effective and more efficient solutions. Beyond that, other advantages such as fast response, energy efficiency, integrated closed-loop control, low weight, and noise, are in line with the latest requirements and needs of robotic and automation solutions.
- Cleanroom: Cleanroom is one of the most demanding environments where zero contamination is mandatory. PoleAttraction™ as standard is 100% compliant with all requirements, keeping contact with sterilized parts, medical equipment, or even pharmaceutical products possible.
- High incline conveyor: When transporting certain products, the conveyor system can only be tilted to a certain degree. The material will slip, turn or fall when the angle exceeds this limit. PoleAttraction™ mainly due to its high force and compact volume can be used in the conveyor system to solve this limitation. Since the material is grasped when it is driven, the angle may be significantly higher.
- Biomedical: PoleAttraction™ enables biomedical devices to function like a clutch, to replicate exoskeleton actuation such us the ankle. Its low weight, consumption and wear make it a very suitable solution.
- Climbing robots: A wide variety of technologies have been tested and implemented in climbing robots, such as magnetic grippers, suction cups, gecko feet, etc. PoleAttraction™, due to its low weight, compact volume, robustness and low consumption provides additional arguments for this type of systems.
Conclusion
Several major applications have been presented since the inception of electroadhesion, enabling technical improvements ranging from robotic gripping and climbing to active adhesion and biomedical applications. It has been determined that an increase in electroadhesion research is both foreseeable and necessary. To that purpose, this article provides a presentation and overview of the new and disruptive PoleAttraction™ approach, including how it works, its benefits, and its applications.
With these in place, the industrial community has at its disposal a new technology capable of being applied in more sectors and applications, improving the efficiency of its processes. Some existing limitations are now solved with PoleAttraction™, increasing the quality of products, processes, and working conditions.
While it is unclear how near scientists and companies are to developing one efficient electroadhesive technology, one thing is certain: Engimotion’s PoleAttraction™ has arrived.
About the sponsor: Engimotion
Engimotion is a Portuguese start-up based in Porto with an aim of making the cutting-edge world of robotics accessible to SME’s.
References
- Guo, J., Jinsong, L., and Rossiter, J. (2019). Electroadhesion Technologies for Robotics: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Transactions on Robotics PP(99):1-15. DOI:10.1109/TRO.2019.2956869
- Johnsen, A., and Rahbek, K. (1923). A physical phenomenon and its applications to telegraphy, telephony, etc. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 61, 713–725. doi: 10.1049/jiee-1.1923.0092
- Alpha Lab Inc (2018). Common static electricity problems and remedies: a series of brief articles. Available at: https://www.alphalabinc.com/common-static-problems/ (Accessed January 4, 2022).
- Cao, C., Sun, X., Fang, Y., and Qin, Q. (2016). Theoretical model and design of electroadhesive pad with interdigitated electrodes. Materials and Design 89:485-491 DOI:10.1016/j.matdes.2015.09.162