Inside-the-Box Connectivity Solutions by Molex for Modern Automotive Electronics
Inside-the-box connectors enable reliable power and signal transmission within automotive modules. Molex offers tailored solutions that combine electrical performance, mechanical durability, and manufacturing efficiency to meet the diverse demands of modern vehicle electronics.

Executive Summary
The shift toward smarter, more feature-rich vehicles has accelerated the integration of electronic modules across the cabin and body. From steering wheel controls and head-up displays to lighting, mirrors, seat systems, and power conversion units, each module depends on precise, reliable inside the-box connectivity to deliver its intended performance.
Operating within controlled environments but still subject to vibration, heat, and space constraints, these connectors must meet stringent requirements for electrical performance, mechanical durability, miniaturization, and cost efficiency. The right design choices can significantly influence module reliability, assembly efficiency, and overall vehicle quality.
Molex offers a comprehensive portfolio of wire-to-board, board-to-board, flat flexible cable (FFC), and flexible printed circuit (FPC) solutions engineered to meet these demands. With global manufacturing capabilities and localized engineering support, Molex enables OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to shorten development cycles, streamline production, and deliver dependable, cost-effective connectivity for next-generation automotive electronics.
Introduction
Modern vehicles, whether powered by internal combustion engines or electric drivetrains, rely on a complex network of electronic modules to deliver functionality, comfort, and safety. The electronics content of today’s vehicles already accounts for an estimated 35-40% of total vehicle cost and is projected to exceed 50% by 2030.[1] Premium models can contain more than 100 electronic control units (ECUs), each with multiple internal interconnects.[2]
From steering wheel controls and head-up displays to lighting assemblies, mirror systems, seat modules, and power conversion units, these systems depend on reliable connectivity solutions to transmit power and signals efficiently. Electrified vehicles add even more module complexity, incorporating high-voltage power electronics and advanced infotainment platforms that demand compact, reliable connectors.
As automotive electronics evolve toward higher integration, reduced weight, and greater functionality, inside-the-box connectors must balance electrical capability, miniaturization, assembly efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This whitepaper examines the key design considerations for these interconnects and explores their application across multiple in-cabin and module-level systems. It also highlights how the broad automotive portfolio from Molex addresses these requirements, offering tailored solutions that streamline design, support high-volume manufacturing, and ensure dependable operation throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
Understanding Inside-the-Box Connectivity
“Inside-the-box” connectivity refers to connectors, cables, and interconnects located within enclosed modules or devices inside the vehicle. Unlike external harness systems, these connections are housed in controlled environments, such as steering wheel hubs, lighting housings, head-up display (HUD) assemblies, mirror modules, seat controllers, and power conversion units, where they are protected from direct exposure to moisture, road debris, and extreme thermal cycling.
These connectors typically:
- Link printed circuit boards, sensors, actuators, and subassemblies within the same module
- Handle a mix of low-power signal lines and mid-power delivery for components like LEDs, motors, or heaters
- Operate in compact spaces that demand miniatur ized, robust, and easy-to-assemble designs
While not subject to the full rigor of safety critical standards, inside-the-box connectors must still deliver consistent electrical performance, mechanical reliability, and cost efficiency. In high-volume automotive production, their design impacts functionality, manufacturing efficiency, and total system cost.
Design Considerations for Inside-the-Box Connectors
Selecting the right connector for in-module automotive applications requires balancing multiple engineering and production priorities. The following factors guide optimal design and product selection for reliable, scalable, and cost-effective connectivity:
Electrical Requirements
Inside-the-box connectors must meet the specific current and voltage needs of their target application, which can range from low-power signal lines to mid-power delivery for actuators, lighting, or heating elements. Signal integrity is critical, especially in high-speed data transmission for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), driver monitoring systems (DMS), or infotainment modules. Low contact resistance, stable impedance, and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) mitigation features contribute to consistent performance over the vehicle’s lifetime.
Mechanical Performance
Even within enclosed modules, connectors are subject to vibration, shock, and thermal cycling during vehicle operation. Mechanical robustness ensures connectors maintain contact retention and resist fretting corrosion over many mating cycles. Compact designs and low-profile form factors are often required to fit within space-constrained enclosures while maintaining ease of access for assembly and servicing.
Thermal Performance
Although ambient temperatures inside modules are generally lower than under-hood environments, heat generated by electronics can still push connectors toward their thermal limits. High-temperature materials, typically rated to 105 °C or above, are essential for applications near LED drivers, heating elements, or motor controllers.
Ease of Assembly
In high-volume automotive manufacturing, connectors must be quick and intuitive to assemble, with features such as polarization, keyed mating, tactile/audible engagement, and tool-less latching. Consistency in assembly reduces the risk of production defects and speeds up module integration.
Compliance and Reliability
The United States Council for Automotive Research (USCAR) develops connector performance specifications widely adopted across the automotive industry, covering requirements such as vibration, durability, and electrical performance. LV214 is a European standard (from German OEMs) that specifies rigorous testing for automotive connectors, especially for high-reliability and safety critical applications.
While these standards may not be mandatory for inside-the-box applications, many OEMs still expect compliance with automotive-grade specifications for materials, flammability, and long-term performance. Testing for durability, vibration resistance, and electrical continuity remains a critical step in product validation.
Cost and Scalability
Inside-the-box connectors are deployed in large volumes across vehicle models, making cost efficiency a major consideration. Solutions that combine performance with minimal tooling requirements, simplified manufacturing steps, and compatibility across multiple platforms can significantly reduce total cost of ownership.
Taken together, these design factors form the foundation for selecting the right interconnect solution. In the following sections, we examine how these considerations apply across key automotive modules, and how Molex products are engineered to address them.
Molex Automotive Connector Portfolio Overview
Molex offers one of the industry’s most comprehensive portfolios of automotive-grade connectors, addressing the full spectrum of inside-the-box connectivity needs. This breadth allows OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to select optimal solutions for performance, packaging, and cost targets, while leveraging proven automotive reliability.
Molex power solutions deliver robust, high-current and mixed-signal connectivity for automotive modules, combining advanced connector systems, cable assemblies, and busbars engineered for durability, efficiency, and ease of integration.
Table 1: Molex power solutions
 |  |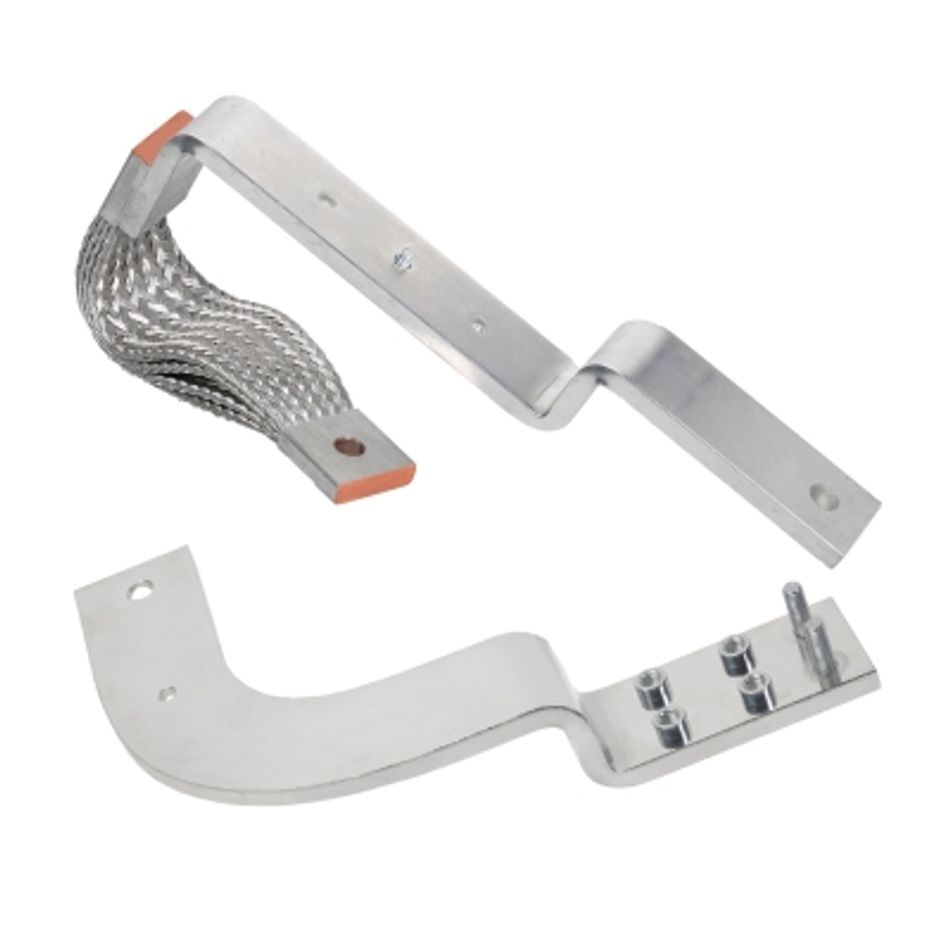  | 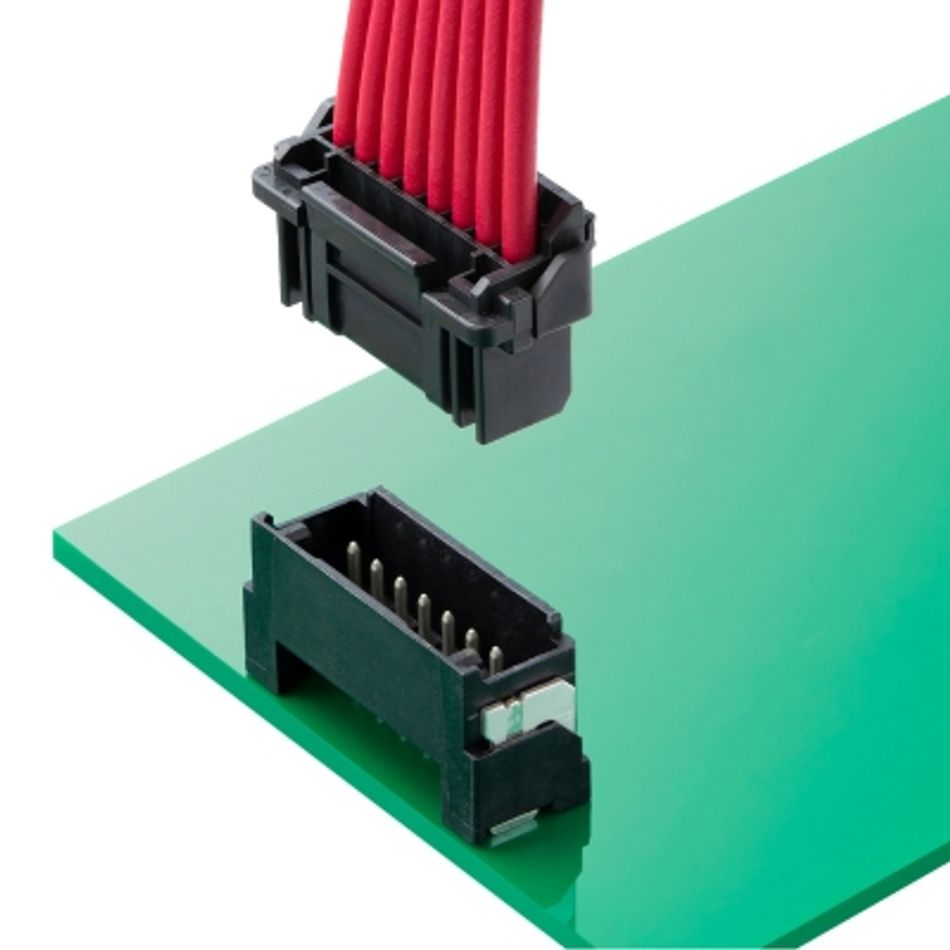 |
| HIGH POWER CONNECTORS | CABLE ASSEMBLIES | BUSBARS | WIRE-TO-WIRE & WIRE-TO-BOARD |
| •EXTreme board-to-board connectors •COEUR socket technology (CST) •Busbars | • Complex cable assembly • Discrete wire assembly • Sealed cable assembly • Over-molded cable assembly • High-power cable assembly • NTC sensor cables • Ribbon cable assembly | • Rigid • Flexible • Laminated • Hybrid • Including COEUR socket technology • Powder coated | • More than 90 product families • Application tooling excellence • 0.80mm to 2.00mm signal portfolio • Low power > 2.0mm including: fit families Pin and socket Custom headers RAST |
Complementing its power products, Molex micro solutions provide compact, fine-pitch, and high speed interconnects that enable reliable signal, data, and low-power delivery in space-constrained in-module designs.
Table 2: Molex micro solutions
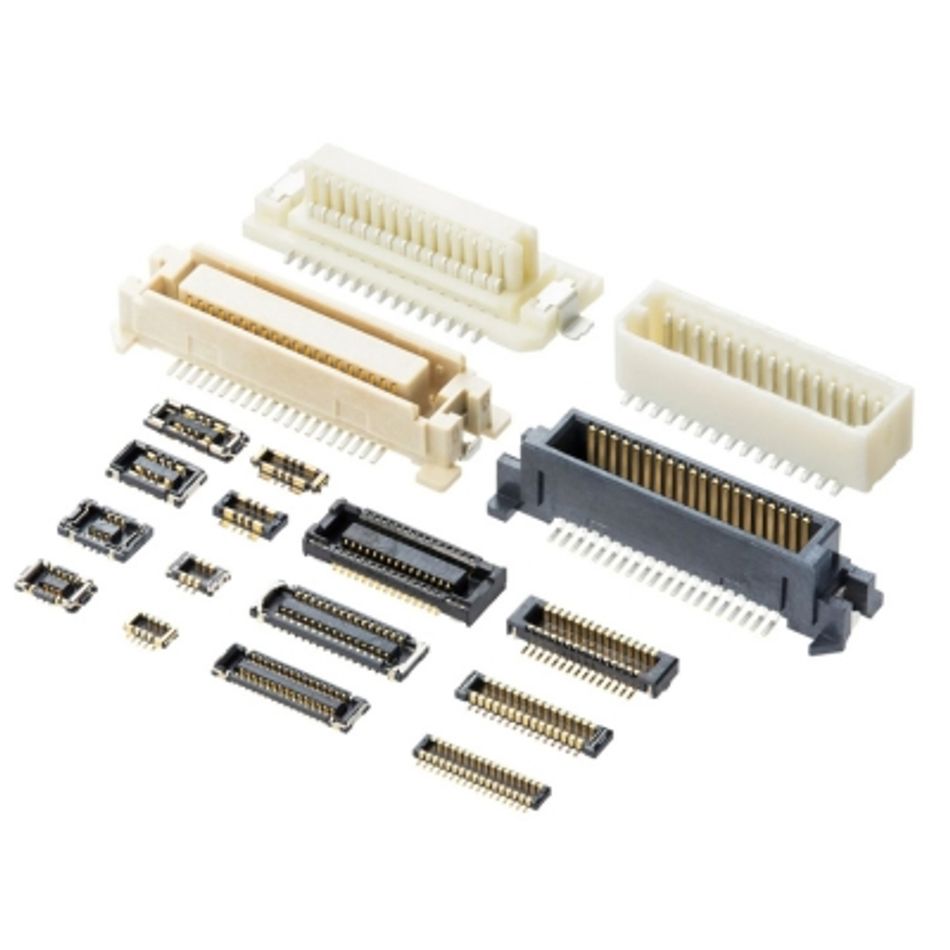 | 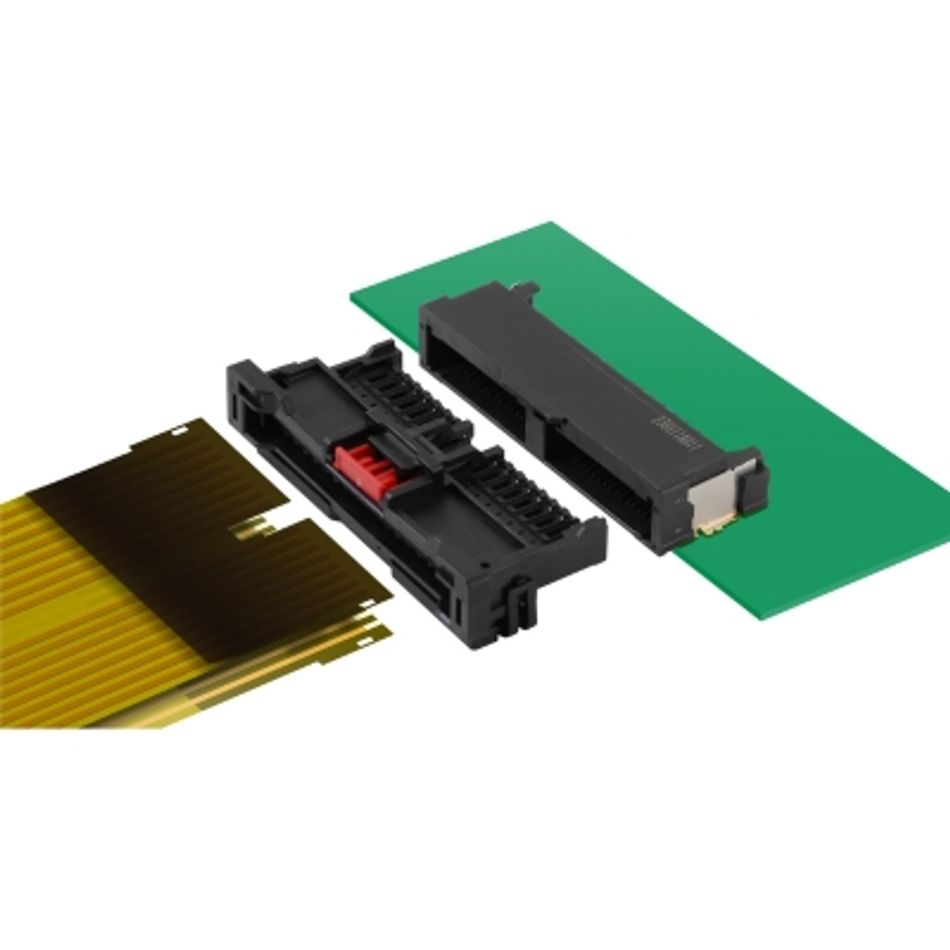 |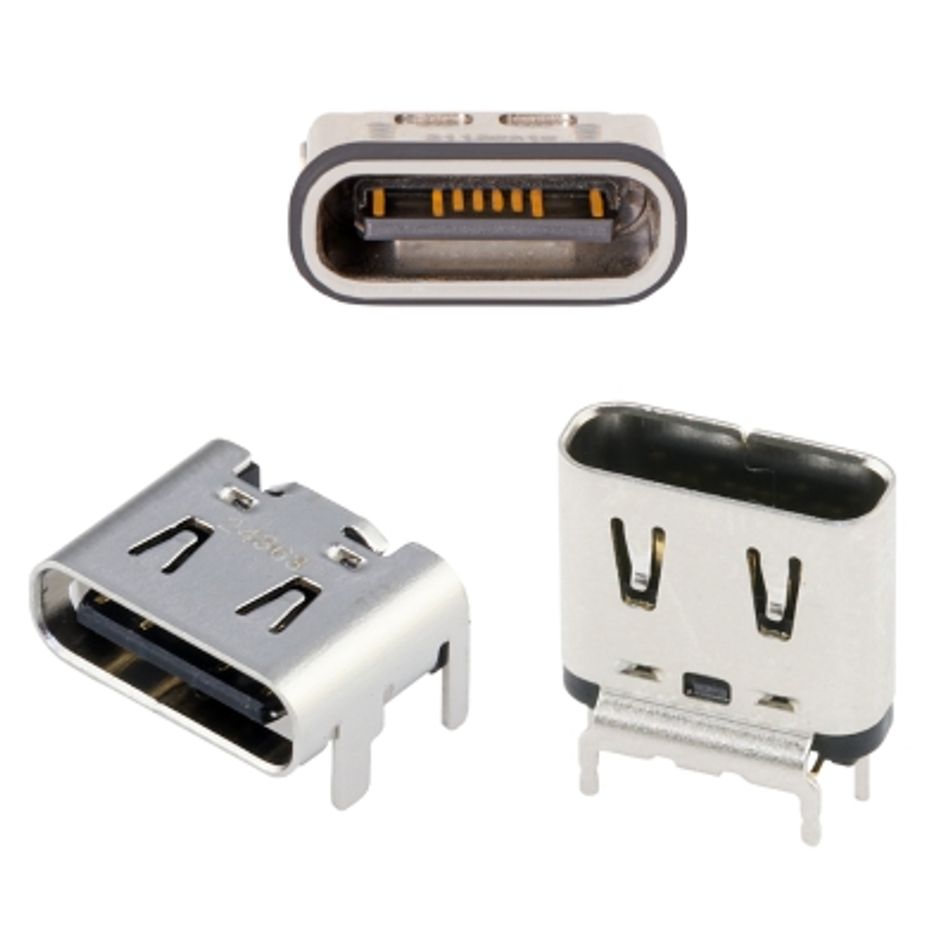  |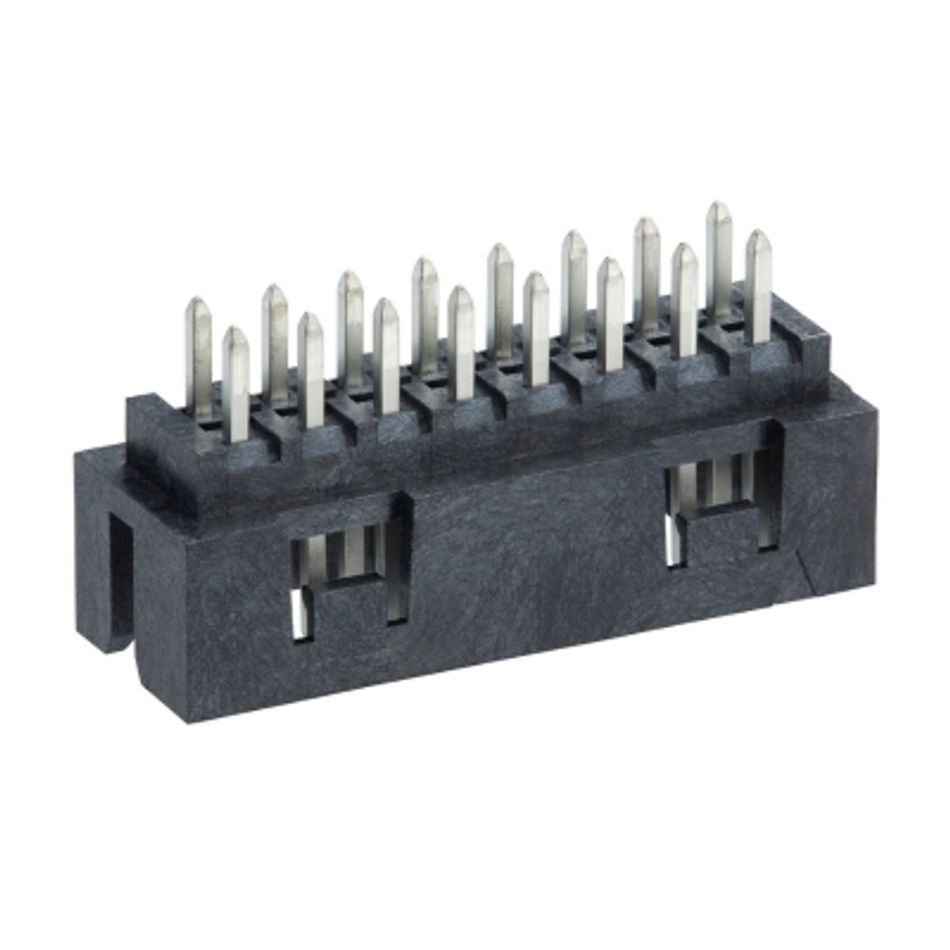  |
| BOARD-TO-BOARD CONNECTORS | FPC-FFC (FLAT CABLE) CONNECTORS | I/O CONNECTORS | CUSTOM PIN HEADERS |
| • ZN Stack • Float Stack • 0.635 floating • FSB • Promoted off-the-shelf | • Flexi-Latch • Flexi-Latch+ • FD19/FD4P • One-Touch • Promoted off-the-shelf | • USBC • USBA • HDMI | • Various |
These solutions serve as the building blocks for diverse in-module applications, from steering wheels and HUDs to lighting, mirrors, seat systems, and power conversion units, ensuring optimized electrical performance, mechanical fit, and ease of assembly across platforms.
Inside-the-Box Applications and Molex Solutions
Inside-the-box connectors are used across a wide range of automotive modules, each with distinct electrical, mechanical, and packaging requirements. From driver controls to comfort systems and power electronics, these interconnects enable reliable communication between PCBs, sensors, actuators, and control units within confined spaces. The sections below highlight key in-module applications, explaining their unique connectivity demands and how Molex tailors solutions to meet them.
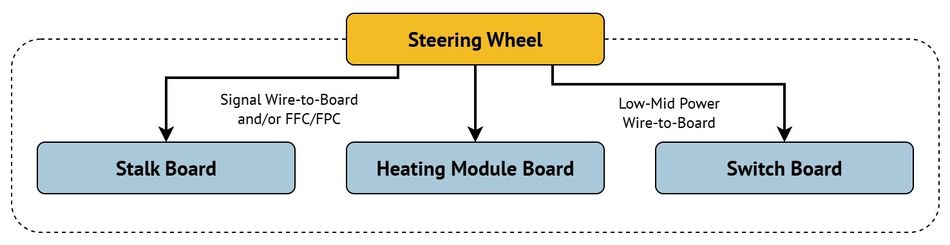
Steering Wheel Modules
Modern steering wheels integrate multiple electronic functions, transforming them into multifunctional control hubs. Typical features include:
- Stalk controls for turn signals, headlights, and wipers
- Switch assemblies for infotainment, cruise control, and voice activation
- Hands-off detection (HOD) sensors to meet UN R79 and Level 2 autonomous driving requirements
- Heating elements for driver comfort
These elements are housed within a compact space, requiring connectors that can handle both signal and low- to mid-power delivery while withstanding vibration from regular steering operation. The architecture often links stalk boards, switch boards, and heating module boards via a mix of wire-to board and FPC/FFC interconnects.
Table 3: Molex interconnect solutions for steering wheel modules
Product | Type/Pitch | Placement (Module/Board) | Key Features |
Wire-to-board, 1.25mm | Stalk board, switch board | High-reliability signal connector, compact footprint | |
Wire-to-board, 1.00mm | Stalk board, switch board | Wide header variations, space-saving | |
FFC/FPC Connector, 0.5–1.0mm | Switch board | Easy-On, design flexibility for flat cables | |
Wire-to-board, >2.0mm | Switch board | High temperature tolerance, robust design | |
Wire-to-board (Low to Mid Power) | Various, 2.50mm-3.00mm | Heating module board | Handles higher current, robust |
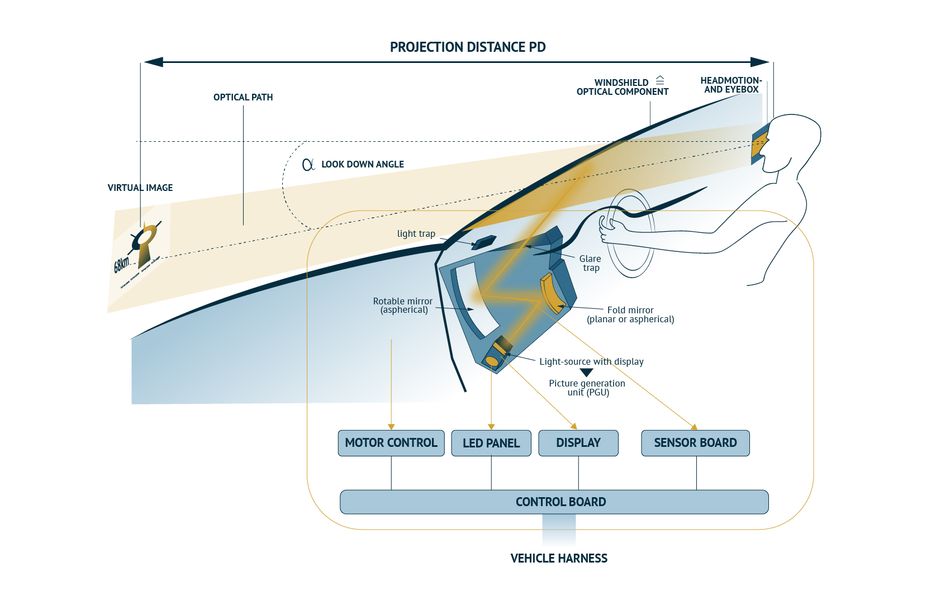
Head-Up Displays (W-HUD/AR-HUD)
Head-up displays project critical driving information, such as speed, navigation, and ADAS alerts, directly into the driver’s line of sight. Windshield HUDs (W-HUD) use 2D projection, while augmented reality HUDs (AR-HUD) overlay 3D graphics aligned with the real world for enhanced situational awareness.
These systems combine optical projection units, LED display panels, sensor boards, and control electronics in a compact assembly. Connectors must preserve high-speed signal integrity between display controllers and panels, provide reliable low-to-mid power delivery, and fit within tight mechanical envelopes. Thermal performance is also key, as LED drivers and imaging modules generate localized heat.
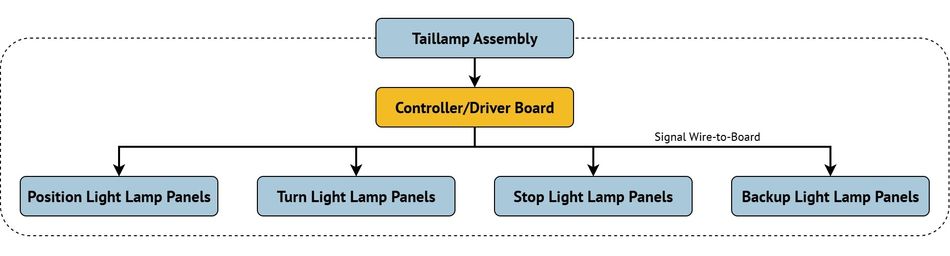
Lighting Systems
Automotive lighting has transitioned to advanced LED-based designs, improving efficiency, brightness, and styling flexibility. Whether in headlamps, taillamps, or interior modules, inside-the-box connectors must provide stable power and signal performance within compact, heat-intensive assemblies.
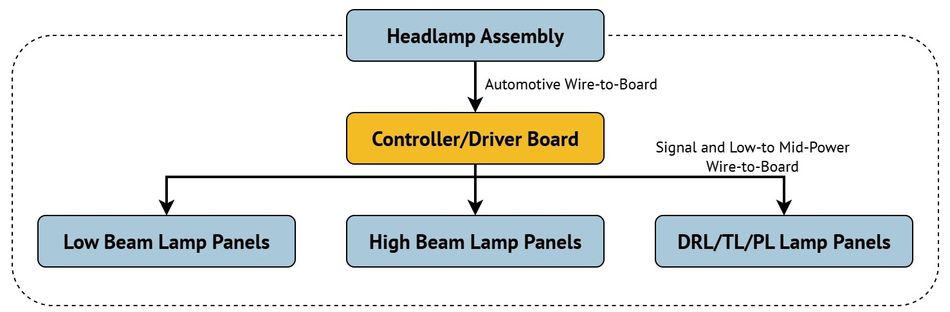
In headlamps, connectors handle both high-current delivery (3.0 A-8.0A) for low and high beams, and low-current signal lines for control. Slim taillamp assemblies demand low-profile solutions to fit narrow housings while supporting multiple functions such as stop lights, turn indicators, and rear fog lamps.
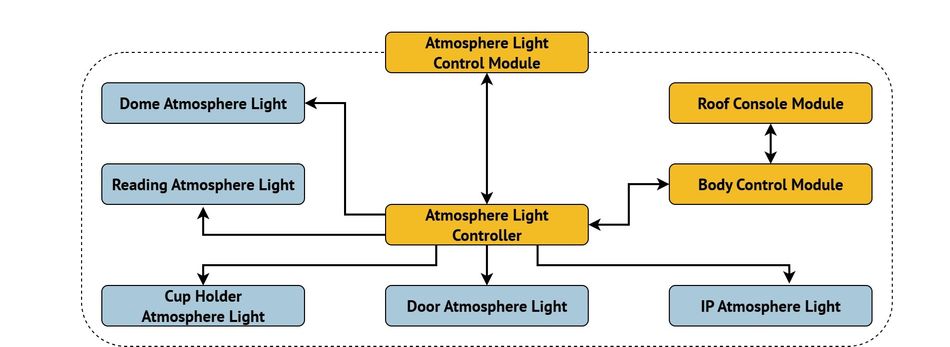
Interior lighting modules like roof consoles, dome lights, reading lamps, and ambient lighting are increasingly integrated with comfort and personalization features. These systems often employ RGB LEDs, light guides, and programmable control modules to enable dynamic color effects and brightness adjustment.
Connectors in these modules must combine compact form factors with secure retention, vibration resistance, and easy assembly to support high-volume manufacturing. In ambient lighting applications, FFC and fine-pitch board-to-board connectors help route signals and power through confined cabin spaces, while maintaining aesthetic design freedom for OEMs.
Table 4: Molex interconnect solutions for automotive lighting assemblies
Product | Type/Pitch | Placement (Module/Board) | Key Features |
Automotive Wire-to-board | Headlamp assembly | Durability, high temperature resistance | |
Wire-to-board, 3.00mm | Control/Driver board (headlamp) | High temperature, robust, mid-power capability | |
Wire-to-board, 1.25/2.00mm | Control/Driver board (headlamp) | High reliability, compact connector | |
Wire-to-board, 1.50mm | Control/Driver board (Headlamp) | Reliable signal connector, low profile | |
Wire-to-board, 1.00/1.50/2.00/ 3.00mm | Control/Driver board (taillamp), lamp panels | Ultra-low height, supports high current | |
One-piece direct solder | Control/Driver board (taillamp) | Simple integration, space-saving |
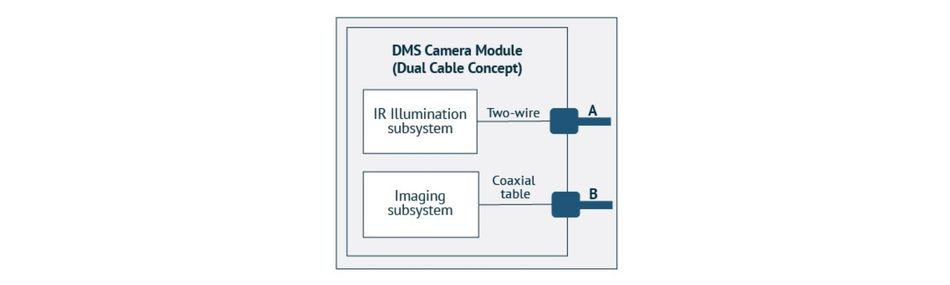
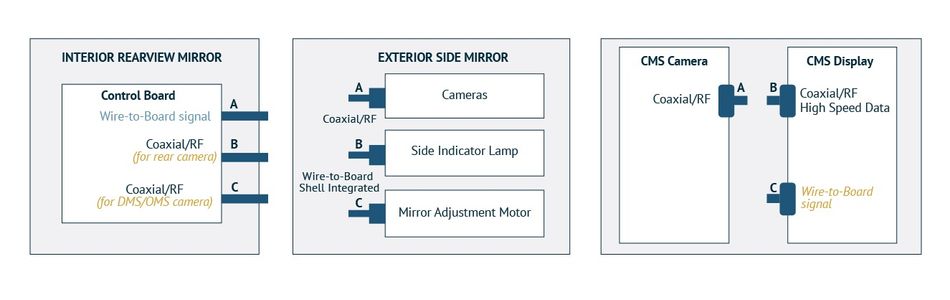
Mirror and Driver Monitoring System (DMS)
Modern mirror assemblies have evolved into multifunctional sensor platforms. Exterior side mirrors integrate cameras, indicators, and motorized adjustment, while interior rearview mirrors can host displays, driver monitoring cameras, and advanced sensing modules. DMS tracks driver attention and alertness, playing a key role in meeting safety regulations and enabling higher levels of autonomy.
These modules must handle high-speed data from cameras, provide power to motors and indicators, and remain securely mounted in compact housings that are exposed to vibration.
Connectors must support coaxial data lines alongside low voltage signal and mid-power circuits, while maintaining automotive-grade durability.
By offering coaxial and signal/power connectors optimized for vibration resistance and compact assembly, Molex enables the reliable performance of camera-based safety systems and motorized mirror functions throughout the vehicle’s lifespan.
Table 5: Molex interconnect solutions for interior lighting modules, mirrors, and DMS
Product | Type/Pitch | Placement (module/board) | Key features |
FAKRA /HSD | Coaxial/RF connector | DMS camera module (imaging subsystem), camera and display in camera monitoring system, Rear view/side mirrors | High-speed data transmission, automotive-grade, secure locking |
Wire-to-board, 1.25mm | Interior rearview mirror (control board) | High-reliability, compact connector | |
Wire-to-board, 1.00mm | Interior rearview mirror (control board, DMS/OMS camera) | Wide header variations, flexible signal interface | |
Wire-to-board (shell integrated) | Custom integration | Exterior side mirror (side indicator lamp, adjustment motor) | Robust design, supports compact mirror integration |
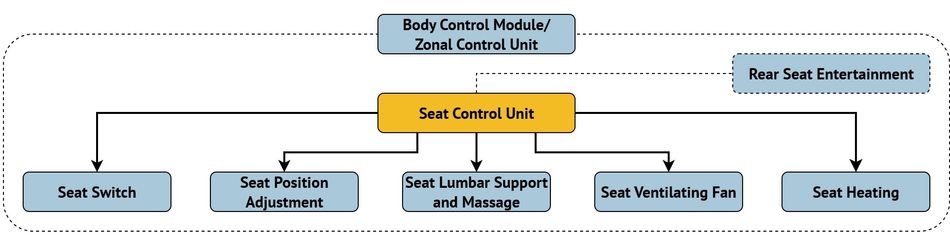
Seat Modules
Automotive seats have become complex electromechanical systems, integrating comfort, safety, and infotainment features. Beyond basic adjustment, modern seat modules can include heating, ventilation, lumbar support, massage functions, and rear-seat entertainment connectivity. Each
subsystem relies on reliable inside-the-box connections for both power delivery and signal control. Seat modules involve a variety of connectivity requirements, such as:
- Adjustment motors for height, tilt, and position require mid-power connectors that can handle frequent operation cycles.
- Heating and ventilation systems demand connectors with high-temperature tolerance and stable contact performance over time.
- Control units manage user inputs, sensor data, and actuator commands, requiring high-reliability signal connections.
- Optional features like massage units, entertainment interfaces, and zonal control integration add further complexity.
By leveraging a mix of high-power, compact, and robust connector families, Molex enables seat designers to combine comfort, safety, and entertainment functions without compromising reliability or ease of assembly
Table 6: Molex interconnect solutions for seat modules
Product | Type/Pitch | Placement (module/board) | Key features |
Stac64 | Wire-to-board | Seat control unit | Automotive grade, high circuit capacity |
stAK50h | Wire-to-board | Seat control unit | Automotive grade, robust design |
Wire-to-board, compact | Rear seat entertainment | Automotive grade, supports High Speed Data (HSD) interface | |
FFC/FPC connector, 0.50–1.00mm | General seat electronics | Easy-On, design flexibility | |
One-Touch | FFC/FPC connector, 0.50mm | General seat electronics | Easy-On, reliable cable retention |
Board-to-board, 0.635mm | General seat electronics | Floating/non-floating option, compact stacking |
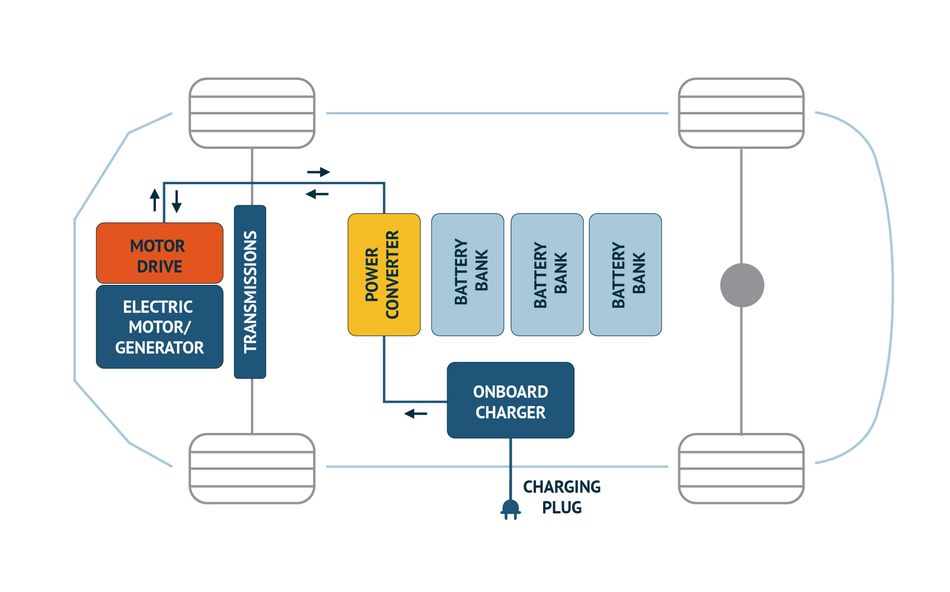
Power Conversion Systems (PCS)
The PCS serves as a critical interface between a vehicle’s battery management system (BMS) and its AC/DC power sources. In electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids, PCS units perform both AC-to DC conversion for charging and DC-to-AC conversion for propulsion, while also managing DC/DC conversion for auxiliary systems.
PCS assemblies house multiple boards for power electronics, control circuitry, and thermal management systems. Inside-the-box connectors must handle:
- High-reliability power delivery for inverters, converters, and charging modules
- Signal transmission for monitoring and control between boards and the BMS
- Space-constrained layouts where low-profile, vibration-resistant connectors are essential
- High-temperature tolerance to operate in proximity to power semiconductors and heat sinks
By combining compact form factors, high current-handling capability, and proven automotive-grade reliability, Molex interconnect solutions support the performance and long-term durability of PCS units in electrified vehicles.
Global Manufacturing and Supply Capability
Delivering reliable inside-the-box connectivity at automotive scale requires advanced product engineering and a robust global supply and manufacturing network. Molex operates a strategically distributed footprint of production facilities, engineering centers, and logistics hubs to support automotive customers worldwide.
Manufacturing plants across North America, Europe, and Asia ensure that high-volume programs benefit from regional sourcing, reduced lead times, and consistent quality standards. Key locations including facilities in Germany, Poland, China, Japan, Mexico, and the United States, are equipped to produce automotive-grade connectors with rigorous process control and end-of-line testing.
In addition to production capacity, Molex regional engineering and application support teams collaborate closely with OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to optimize connector selection, customization, and integration. This localized expertise accelerates design cycles, supports compliance with regional requirements, and helps quickly resolve challenges during program development and production ramp-up.
Through this combination of global reach and localized service, Molex ensures dependable supply continuity, technical support, and quality assurance—all critical factors for the fast-paced, high-stakes automotive industry.
Conclusion
Inside-the-box connectors are essential to the reliable operation of modern automotive electronics, enabling seamless communication and power delivery within modules such as steering wheel controls, HUDs, lighting systems, mirrors and DMS, seat assemblies, and power conversion units. While shielded from the harshest external conditions, these connectors must still meet demanding requirements for electrical performance, mechanical durability, compactness, and cost efficiency.
Molex addresses these challenges with a broad, automotive-grade portfolio designed for high reliability, ease of assembly, and optimized fit for space-constrained applications. Supported by a global manufacturing footprint and localized engineering expertise, Molex ensures consistent quality, supply chain resilience, and tailored solutions for diverse automotive programs.
By engaging Molex early in the design process, OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers can accelerate development, reduce integration risk, and achieve long-term performance across a wide range of in cabin and module-level applications.
Learn more about Molex at TTI.com.
References
[1] P Martin. Automotive Electronics Cost as a Percentage of Total Car Cost Worldwide from 1970 to 2030. Statista; 2023 Jan 6 . Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/277931/automotive-electronics-cost-as-a-share-of-total-car-costworldwide/
[2] Go Digit. What is an ECU in a car?: Digit Insurance; Available from: https://www.godigit.com/motor-insurance/car-insurance/car-parts/ecu-in-car