Modular Power Distribution Units for EVs: A Fast and Scalable Approach by Littelfuse
Modular high-voltage PDU architectures enable scalable power distribution using standardized components. This approach reduces tooling requirements, supports platform reuse, improves serviceability, and accelerates integration in EV systems.
Executive Summary
The growing adoption of EVs, electrified commercial fleets, and battery-powered systems is driving demand for safe, efficient, and adaptable high-voltage power distribution units (PDUs). Yet, traditional approaches to PDU design often introduce unnecessary complexity, time, and cost, especially when custom solutions must be developed from scratch for every new platform.
Littelfuse, in partnership with TTI, offers a transformative approach through modular, vehicle-rated power distribution components. These ready-to-integrate building blocks eliminate the need for tooling, reduce time-to-market, and simplify system design across a broad voltage range (48V-1kV). Unlike conventional industrial-grade parts retrofitted for automotive use, Littelfuse components are purpose-built for harsh environments, ensuring long-term reliability and scalability.
This whitepaper explores the challenges in current PDU design workflows, details the modular strategy offered by Littelfuse, and explains how OEMs and Tier 1s can reduce both engineering overhead and manufacturing risk by adopting this approach.
Introduction
As vehicle electrification advances, the electrical systems inside modern electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more sophisticated and demanding. At the center of these high-voltage systems is the Power Distribution Unit (PDU), a critical component that routes power from the battery to traction inverters, electric compressors, heating systems, and auxiliary loads.
PDUs do more than distribute current. They also integrate essential protective and control functions such as fuses, relays, and contactors, while supporting diagnostic and serviceability requirements. As voltage levels climb from 48V in mild hybrids to 800V or more in full EVs, PDUs must balance electrical precision with thermal stability, packaging efficiency, and mechanical durability.
Despite their growing importance, the methods used to design PDUs have not evolved at the same pace. Most systems are still built using custom enclosures, hand-made busbars, and adapted industrial components. These legacy approaches are time-consuming to develop, expensive to prototype and tool, and difficult to scale across multiple vehicle platforms.
This whitepaper explores the design constraints of traditional PDUs, introduces the modular approach in detail, and highlights how this architecture enables faster development, improved platform flexibility, and greater long-term value for EV manufacturers.
Market Pressures and Evolving Requirements
High-voltage EV systems now span a wide range of architectures, from 48 V mild to 800-1000 V full electric drivetrains. Current demands can exceed 500 A in traction applications, requiring precise current handling, thermal stability, and efficient power routing.
As of 2025, many leading global automakers have announced targets to electrify at least 50% of their vehicle portfolios by 2030.[1] This shift has accelerated platform diversification and design complexity. EV programs now span multiple platforms and model lines, demanding flexible electrical architectures that can accommodate varying voltage levels, current ratings, and packaging constraints.
At the same time, product cycles have compressed. Development timelines that once spanned four to five years are now closer to 24-30 months for many EV programs.[2] Within these tighter schedules, any delays in PDU design caused by custom tooling, last-minute layout changes, or component incompatibility, can delay validation by 8 to 12 weeks and inflate development costs. Similar trends and design shifts are also being seen outside the traditional passenger car market, including trucks, tractors, material handlers, and powersports vehicles. A similar trend can be seen in the Agriculture market with pressures on bringing electrification to market, as well as decreasing the time to market for new models.
Given these pressures, OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers increasingly require power distribution systems that are flexible, pre-validated, and quickly configurable to support diverse platforms and late-stage design changes.
Challenges of Custom PDU Design
Designing a custom PDU from the ground up for each vehicle platform presents multiple challenges that extend development timelines and drive up costs. Key examples include:
Lack of Standardized Components
Each application comes with its own requirements - voltage levels, current ratings, mounting constraints, and environmental conditions. Because there are few off-the-shelf, vehicle-rated components that meet these exact needs, teams are often forced to pursue custom solutions. This leads to:
Fragmented designs across platforms
Limited reusability of components
Reinventing the wheel for each project
High Tooling and Prototyping Costs
Custom molded enclosures and proprietary fuse holders require dedicated tooling, which comes with high upfront cost and long fabrication lead times. Iterative changes due to late-stage design shifts can reset tooling cycles, compounding the problem.
Inflexible Layouts
Traditional molded PDUs are rigid by nature. Once a layout is set, making even minor changes like adding a fuse, adjusting current capacity, or rerouting busbars, can require a full redesign. This lack of flexibility limits a designer’s ability to respond to evolving platform requirements or component availability.
Vehicle-Grade Reliability Is Hard to Guarantee
Many high-voltage components are adapted from industrial applications, which are not always suitable for the harsh vibration, thermal cycling, and packaging demands of on-road vehicles. Achieving compliance with automotive standards requires extra validation steps or redesigns.
Production Scale Inefficiency
Even if a custom PDU design is successful, it may only be produced in small quantities for niche vehicle models. This drives up the cost per unit and limits economies of scale, especially painful when the design can’t be reused elsewhere.
Together, these challenges contribute to increased project risk, slower time-to-market, and higher total cost of ownership.
Rethinking PDU Architecture with Littelfuse: The Modular Advantage
To overcome the inefficiencies of traditional custom-built PDUs, Littelfuse introduces a modular approach tailored for high-voltage EV systems. This strategy redefines how engineers design, assemble, and deploy power distribution by replacing inflexible, bespoke designs with pre-engineered, drop-in modules that are both standardized and scalable.
Built for Automotive from the Start
Unlike retrofitted industrial components, Littelfuse’s modular PDU elements are designed specifically for vehicle environments. They meet stringent reliability and safety standards, withstand harsh operating conditions, and are ready for immediate integration into EV architectures.
Pre-Engineered Building Blocks
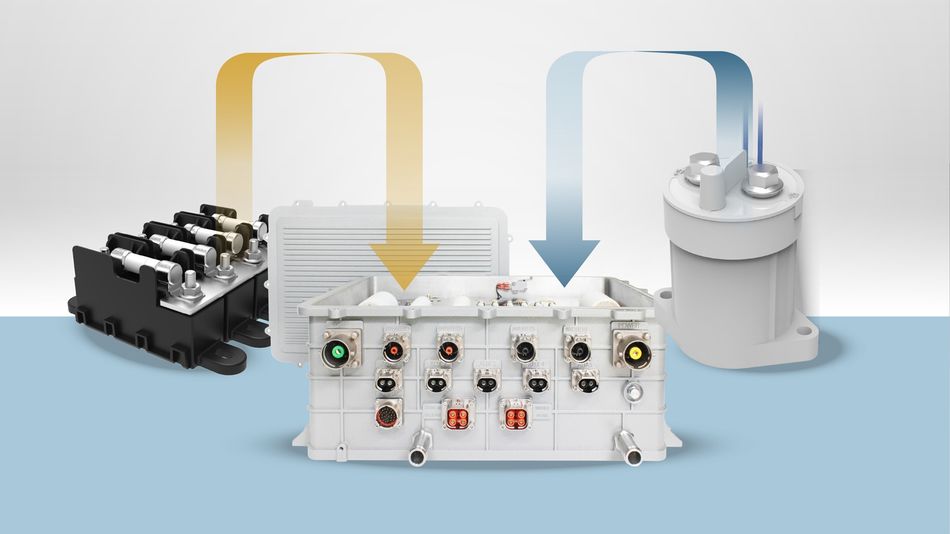
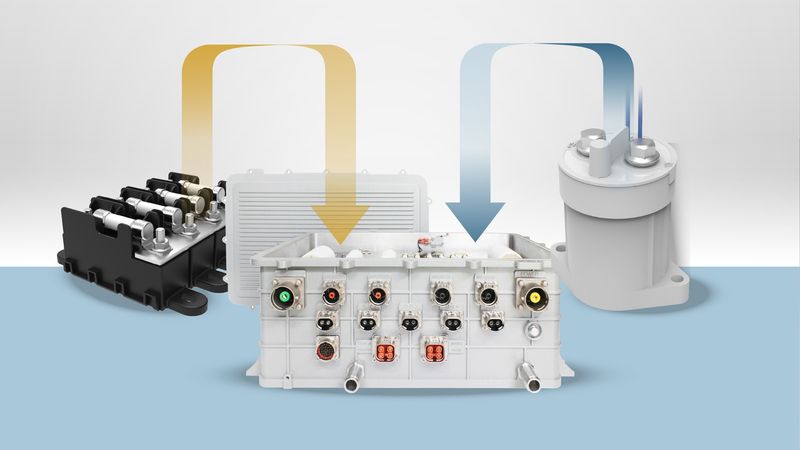
These modules include contactors, high-voltage fuse holders, relay bases, busbars, current sensors, and housing elements that can be configured in various combinations. Whether the requirement is for 48V auxiliary power or 800V traction systems, the same modular base can accommodate different current paths, voltage levels, and fuse types.
Plug-and-Play Flexibility
Designers can select, arrange, and modify components with minimal layout constraints. New application needs like increasing the fuse count, changing form factors, or integrating connectors, can be addressed without restarting the design from scratch.
Tooling-Free Enclosure Design
By avoiding custom molding, teams eliminate the costs and delays associated with hard tooling. The modular assemblies can be installed in off-the-shelf enclosures or lightweight sheet-metal housings, further reducing time-to-market.
Simplified Assembly and Distribution
Assemblies can be pre-loaded by distributors and delivered as kits or subassemblies to manufacturing lines. This reduces the workload on OEMs and ensures consistency and traceability across vehicle platforms. A direct benefit is improved inventory management, enabled by distributors supplying only the volumes required for each build.
Support for Prototyping and Low-Volume Builds
Because these modules are stocked and distributed via TTI, they are available in low quantities for prototyping and limited production runs. This enables agile development without the long lead times or cost penalties typical of custom systems.
Key Elements of the Modular Approach
Littelfuse’s modular power distribution strategy is anchored by a suite of vehicle-grade components designed for flexibility, scalability, and real-world automotive reliability. These elements can be combined in countless configurations to suit the electrical and mechanical needs of diverse EV platforms. The following components form the foundation of this architecture, each contributing to a modular PDU system.
High-Voltage Fuse Holders
Littelfuse offers a range of fuse holders designed for 48V to 1000V systems. These are built to accommodate varying fuse sizes, mounting orientations, and thermal performance requirements. Key benefits include:
Secure mechanical retention
Easy fuse replacement
High vibration resistance
Support for bolt-down fuses of numerous ratings and capabilities
Modular Mounting and Busbar Integration
Modular fuse and relay bases allow for direct integration of custom or pre-formed busbars. This reduces the need for complex wiring harnesses, enhances current handling, and streamlines layout within the enclosure. Features include:
Snap-fit assembly options
Busbar-compatible terminals
Stackable and scalable layouts
Contactors
In high-voltage systems, contactors play a critical role in safely switching current on and off during normal operation, startup, or fault conditions. Littelfuse offers compact, vehicle-grade contactors that can be seamlessly integrated into modular PDU designs.
These contactors are designed for high current loads and are validated for harsh automotive environments, with support for thermal, mechanical, and electrical robustness. Their standardized mounting patterns and signal leads allow easy drop-in integration into the enclosure alongside fuse holders, relays, and busbars.
Using modular standard footprint contactors reduces the need for external disconnect mechanisms and simplifies the overall system layout.
Standardized Interfaces
Connectors, fasteners, and mounting patterns are standardized across modules to enable rapid configuration and straightforward mechanical integration. These uniform interface dimensions simplify both initial design and future adaptation, allowing engineers to reconfigure or upgrade systems without altering the base enclosure or harness layout.
High-current terminals feature consistent bolt patterns and thread sizes, while signal connectors are designed to align with automotive sealing and vibration standards. This enables drop-in replacement of modules across vehicle variants, reduces validation burden, and improves serviceability in the field.
By maintaining mechanical and electrical consistency across the ecosystem, modular PDUs support scalable platform strategies and long-term maintainability.
Compact, Serviceable Assemblies
Each modular component is engineered for accessibility and maintainability, enabling field technicians to isolate, inspect, and replace individual units without disturbing surrounding circuits or wiring. Unlike monolithic PDUs that often require full disassembly for basic service tasks, the modular design allows direct access to fuses, contactors, or terminals through top-mounted fasteners or quick-release features.
Modules are thermally and electrically isolated within the housing, which minimizes the risk of collateral damage during repair or replacement. Consistent torque specs across mounting points further reduce the margin for installation error in high-voltage environments.
This service-friendly design is especially valuable for fleet operators and commercial vehicle OEMs, where downtime is costly, and accessibility is essential for field diagnostics, preventive maintenance, and warranty support.
Demo: Flexible Array Assembly with Sliding Terminal Bases
Littelfuse’s modular PDU ecosystem is engineered for maximum flexibility with minimal part count. A single system consisting of just seven components, including M6 and M8 fuse bases, a universal cover, and four common busbars, can be configured into hundreds of distinct layouts to accommodate a wide range of fuse types and voltages.
A core part of this system is the sliding terminal base, a patented design that supports multiple fuse lengths and terminal spacings. For instance, a single M6 holder can accommodate:
MEGA® fuses rated at 32V, 70V, and 120V
MIDI® fuses rated at 32V, 70V, and 120V
Both M6 and M8 terminal spacing
The snap-in design allows technicians to adjust fuse spacing without the need for special tools or custom tooling. Modules can be quickly snapped together in dovetail fashion, enabling array configurations that mix and match fuse types and ratings on a shared busbar.
This flexibility simplifies procurement and inventory management while enabling OEMs and integrators to create tailored power distribution arrays without redesigning or revalidating entire systems. In addition, visual and mechanical differentiation between fuse types enhances assembly accuracy, reducing the risk of misplacement or mismatch in the field.
Traditional vs. Modular PDU Design
A direct comparison between conventional custom-built PDUs and the Littelfuse modular approach highlights the significant improvements achievable in design:
Factor | Traditional Custom PDU | Modular PDU by Littelfuse |
Tooling Requirements | Requires custom-molded enclosures and busbars | No tooling required; uses validated, off-the-shelf modules |
Time-to-Market | 6-12 months or more | As little as 2-3 weeks |
Design Flexibility | Fixed layouts; difficult to change mid-cycle | Easily reconfigurable for late-stage design changes |
Platform Reusability | Unique designs per vehicle | Shared modular base supports multiple vehicle platforms |
Component Validation | Often adapted from industrial parts; additional testing needed | Automotive-grade, pre-validated components |
Cost at Low Volumes | High unit cost due to limited production runs | Cost-effective even for prototyping and specialty builds |
Manufacturing Complexity | Multi-vendor coordination, custom parts, and manual assembly | Pre-loaded assemblies, simplified sourcing and integration |
Serviceability | Requires disassembly for minor repairs | Accessible, replaceable components for easier field service |
Scalability | Limited reuse; high variation between models | Standardized modules scale across models and production volumes |
Table 1: Comparative overview of key design and operational differences between traditional custom PDUs and Littelfuse’s modular PDU architecture.
This side-by-side comparison makes it clear: modular PDUs offer a more agile, scalable, and production-friendly path forward for EV manufacturers seeking to keep pace with rapidly changing market demands.
Market-Ready Offerings by Littelfuse and TTI
Littelfuse, in partnership with TTI, has developed a portfolio of readily available, automotive-grade components that serve as the foundation for modular PDU design. These products are designed not just for concept validation, but for full-scale deployment across vehicle platforms.
Pre-Engineered Modules
The modular ecosystem includes:
High-voltage fuse holderss
Configurable busbars and terminals
Mounting brackets compatible with common enclosures
Stocked and Distributed by TTI
Through its global partnership with TTI, Littelfuse ensures that these modules are:
In-stock and available in low or high quantities
Shippable quickly, enabling rapid prototyping or field trials
Packaged as kits or subassemblies, reducing integration time on customer lines
This logistics model removes one of the biggest pain points for design teams - waiting weeks or months for long-lead custom components.
Backed by Application Support
Littelfuse offers technical support and documentation to guide customers through selection, layout, and integration. This ensures that both new and experienced teams can take full advantage of the modular ecosystem, without a steep learning curve.
By combining robust, validated hardware with distributor-backed availability and engineering support, Littelfuse makes it easier than ever to bring modular PDUs into real-world EV programs.
Conclusion
The transition to electrified mobility has exposed the limitations of traditional power distribution design, long lead times, high tooling costs, and inflexible layouts that struggle to adapt to evolving platform needs. Littelfuse offers a smarter path forward through modular, automotive-grade solutions built specifically for high-voltage systems.
By adopting this modular approach, OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers can reduce development cycles, eliminate unnecessary engineering overhead, and accelerate time-to-market, all without compromising on safety, performance, or reliability. Whether it’s a low-volume specialty vehicle or a scalable EV platform, Littelfuse’s components provide the flexibility and durability needed to meet modern demands.
Learn more about Littelfuse modular solutions at TTI.
References
[1] Editorial Board EVBoosters. The electrification targets of light-duty vehicles by 2030. EVBoosters. Available from: https://evboosters.com/ev-charging-news/the-electrification-targets-of-light-duty-vehicles-by-2030/
[2] Morley C. Innovation and Development of Electric Vehicle Powertrain Technology: An Analysis. Jabil. Available from: https://www.jabil.com/blog/automotive-industry-trends-point-to-shorter-product-development-cycles.html