Complex 3D Electronic Shapes with Particle-Free Inks
Molecular particle free inks can offer extreme formability and stretchability, allowing the design and production of 3D shaped and/or in-mold electronics parts with extreme curvatures and complex shapes.
Arnold Kell and Julie Ferrigno showcased some unique properties of these inks- together with unique IME possibilities- at a TechBlick conference in May 2021. Some unique feetures are:
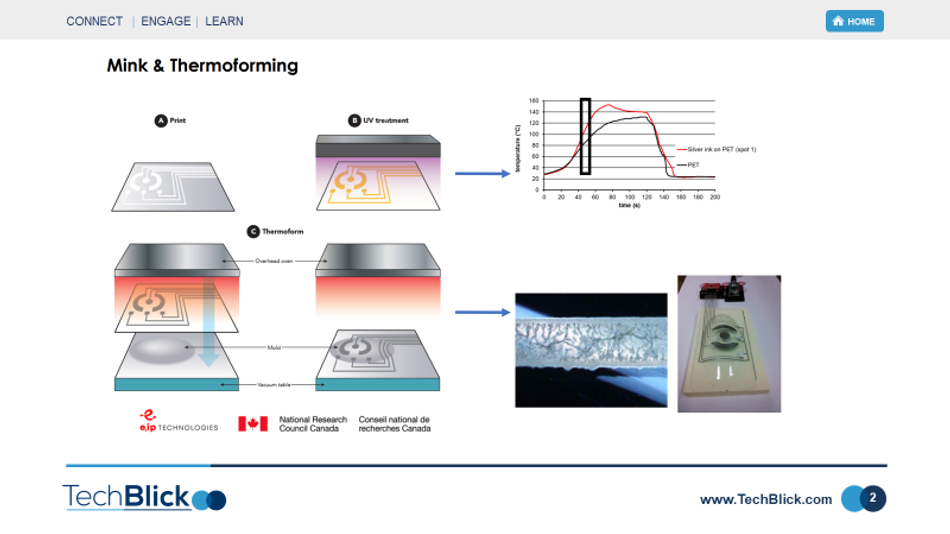
1- UV sintering: you can see in the slide below how the transparent clear molecular inks can be UV sintered (x5 times faster than thermal cure). At first, the clear inks absorb very little UV light. However, as Ag particles begin to percipitate out, the absorption grows. The higher absorption in turn raise the temperature, accelerating the sintering and resulting in higher UV absorption. This process continues until the ink is fully sintered and then self stops because then the particles reflect the light back like a mirror.
2- Partial sintering compatible with InMold Electronics: as part of the IME process, a thermoforming step is required. In this step, the substrate temperature is raised in a controlled fashion to soften the material, allowing it to be 3D formed. In the proposed scheme, the printed molecular inks are first only partially cured by UV light. The full sintering then takes place in-situ by the elevated temperature of the 3D thermoforming process. This is an interesting approach because it enables faster curing and also allows one to sinter molecular inks on low-T substrates like PC.
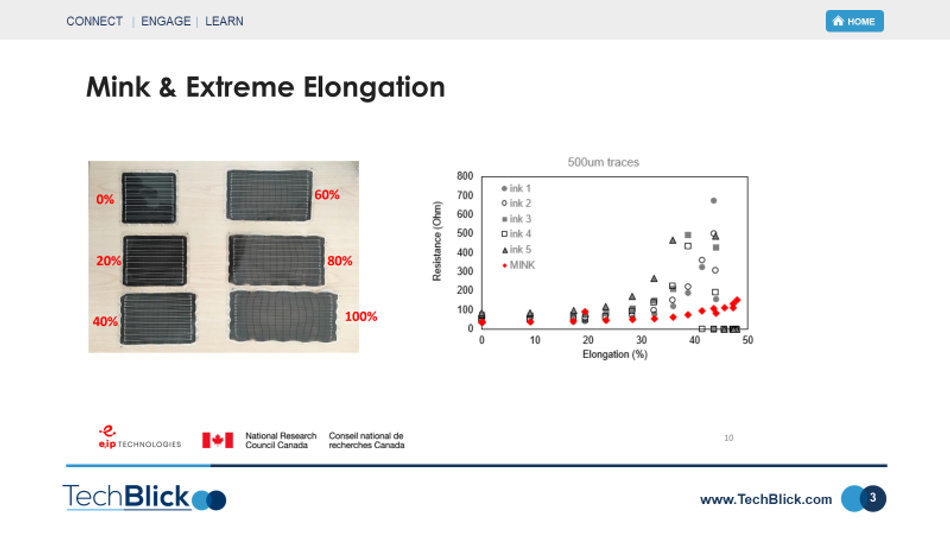
3- Extreme formability: The 3rd slide belows shows comparision of these molecular inks with other standard inks. It shows that these inks can be stretched upto 50% with comparatively little change in resistance. This can be because these printed lines are very thin, and are thus able to follow the contours of the stretched substrate far better than a thicker particle-filled ink/paste
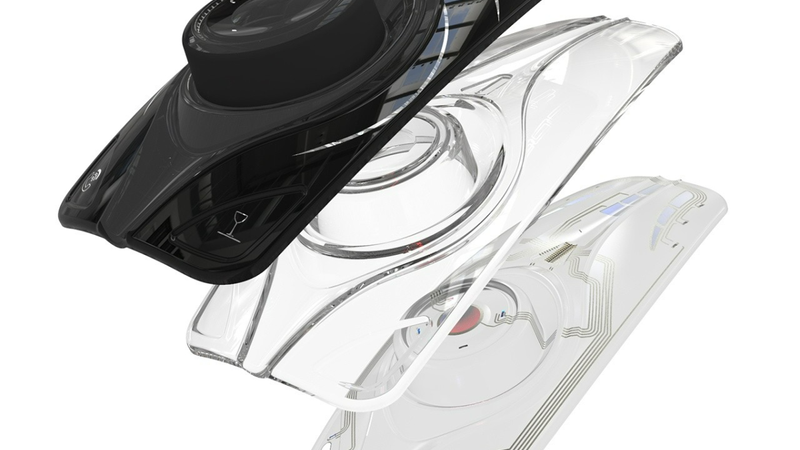
4- Unique shaped: The shapes enabled by IME are often limited by the formability of the inks. These inks can liberate the designer from such limitation, allowing the design and production of complex shapes with extreme curvatures. Here, an award-winning example is showcased by Julie, showing steep curves (see the controlled knob).
To learn more about additive electronics visit www.TechBlick.com
E2IP TECHNOLOGIES
National Research Council Canada / Conseil national de recherches Canada
Ilira Qamirani
Patrick R. L. Malenfant
Chantal Paquet