Case Study: Embedded Artificial Intelligence Unleashes Smart Shopping
Understand how embedded AI is changing the way we shop

Image credit: Amazon
The concept of smart shopping has been in the works since the internet first entered the retail scene—shaking up the shopping experience and making eCommerce[1] mainstream. Retail is changing and evolving, and several advanced computer technologies are beginning to influence the way we shop not only online, but in brick-and-mortar stores too.
‘Smart shopping’ can refer to multiple things from data-backed advertising campaigns and price comparison websites to contactless shopping in retail stores. In all cases, its end goal is the same—to make shopping easier, faster, and cheaper.
The focus of this article is hardware-enabled smart shopping—particularly how retail businesses can apply Artificial Intelligence-powered microprocessors to checkout systems and devices to improve the shopping experience for customers and sellers.
A short introduction to embedded Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the capacity of machines, computers, software, and other devices to simulate the human problem-solving approach and decision-making process by mimicking human intelligence, learning, and actions[2].
In essence, AI is a comprehensive tool that uses biologically-similar technology to receive, combine and evaluate data while applying the processed information to accomplish tasks and make better decisions. These biologically similar tools include computer vision and neural network technology—concepts that are central themes in this article.
Embedded AI is a type of Artificial Intelligence system that implements Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) to software in hardware systems. While general-purpose AI uses cloud technology to analyze data and make predictions, embedded AI relies on specialized hardware systems—microprocessors—for its operations[3].
Software used in embedded AI can be developed to give both predictive and reactive results based on collected and evaluated data. Therefore, you can run AI models and then utilize the findings to accomplish a job or action using the embedded system.
For engineers applying embedded AI to real-life scenarios goes beyond having a working knowledge of AI software and learning models[4]. It requires knowledge of how complex AI algorithms integrate with physical hardware.
So, developing solutions with the technology involves a thorough understanding of electronics, sensors, and modern, near-real-time signal processing algorithms for audio, motion, video, and other information—since embedded AI is as much hardware as it is software.
Smart Registers Enabled By Embedded AI Processors
Smart cash registers are context-aware electronic devices that perform the functions of regular registers through autonomous processing and by connecting to suitable devices and networks. Smart cash registers include everything from wifi-enabled devices to cash registers that allow users to sync electronic wallets via QR code, but the smart registers in this article utilize microprocessors powered by Artificial Intelligence, computer vision, and Deep Learning technologies to detect, recognize and categorize objects in real-time.
Smart payment systems are becoming more ubiquitous — owing in part to checkout-free shopping sites like Amazon Go[5] as well as advancements in consumer payment technology like Walmart Pay[6]. However, smart cash registers have the potential to improve shopping for everyone in the value chain by making in-person shopping faster and more personal.
The future of smart shopping
Cash registers are typical of retail businesses, and they are crucial devices in the commerce industry. Sellers rely on them for cash storage and sales tracking to enable transactions and facilitate the checkout process—regardless of the size of the business.
Renesas Electronics Corporation, a Japan-based semiconductor manufacturing company, has developed a range of Embedded AI processors that have the potential to dramatically change the smart retail scene by encouraging faster checkout times and frictionless shopping.
In this case study, we explore how the Renesas’ RZ/V Embedded AI processors can be applied to smart cash registers using computer vision and Neural Network technology—allowing retail businesses to detect objects in real-time creating frictionless shopping experiences.
Renesas’ RZ/V2M AI Object Detection System
Let’s examine how embedded microprocessors can be applied in smart shopping.
The RZ/V2M AI Object Detection System is a part of the RZ/V series of embedded AI processors from Renesas. The equipment consists of an AI-dedicated hardware accelerator and image signal processor (ISP) suitable for a range of computer vision applications in industrial and commercial settings.
It also includes a Renesas RZ/V2M board equipped with Renesas’ AI-MPU, DC-DC converter, and Low Dropout (LDO) regulator for heat and power efficiency.
The entire setup is contained in a board kit that can interface with other hardware systems using USB 3.1, Gigabit Ethernet, HDMI, as well as several other digital transmission connections. Retailers can easily link this embedded AI system to their cash registers. The resulting AI-driven object recognition smart cash register system is used to detect items placed on a conveyor belt in order to process payment in real-time.
This case study involves a pool of 20 everyday retail items like fruits, bread, and bottles—commodities you’d find in a typical grocery store. And the embedded AI system functions just like a regular cashier would, recognizing, cataloging, and checking out the items on the conveyor belt—albeit faster and more efficiently.
However, the system needs to be taught how to recognize these items using a neural network. Therefore, we would have taught the AI to recognize these objects using Tiny-YOLOv2[7] as an object detection model. However, similar AI frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow would suffice.
The system has an inference time of 29 milliseconds (34fps)—impressive speeds for AI-powered image recognition systems. The smart cash register successfully detects the object's name, position, and the AI Accelerator (DRP-AI) processing time.
Renesas’ Embedded AI technology successfully detects and recognizes all the items moving on the conveyor belt in real-time. It also allows multi-case detection, recognizing multiple objects simultaneously and in real-time. Therefore, the smart cash register can count items and successfully issue receipts without human intervention.
The technology also allows for packaging case detection, successfully recognizing wrapped items like bread and bottled items like milk. This aspect is particularly critical, as several objects are wrapped in clear plastic before being displayed in grocery stores.
In the next section, we dive into the technical details, exploring how Renesas’ Embedded AI technology works, the data flow, and the importance of each component that powers the smart cash register.
Operation Overview
The core of the smart cash register is Renesas’ AI-MPU RZ/V2M microprocessor—handling image processing and recognition. However, the AI relies on pre-trained frameworks, and the scenario in this article uses open-source Artificial Intelligence software to produce results.
Renesas’ RZ/V2M AI Objection System uses Computer Vision AI by running input images through a convolution system[8]. The convolution system works by first separating input images (usually by cropping or resizing) into smaller images and classifying these grouped pixels via weighed values. These weighed values are referred to as pixel density—the number of pixels in each group.
Afterward, a suitable Activation Function[9] (which improves accuracy) converts the aggregate into an output, and passes this result through the convolution system a few more times until we achieve recognition. The time it takes for the system to recognize an object depends on the embedded AI system and the efficiency of the learning model, but the system in this article infers results in 29 milliseconds (34fps).
In summary, the input image is pre-processed (usually cropped or resized), processed, and a result is inferred.
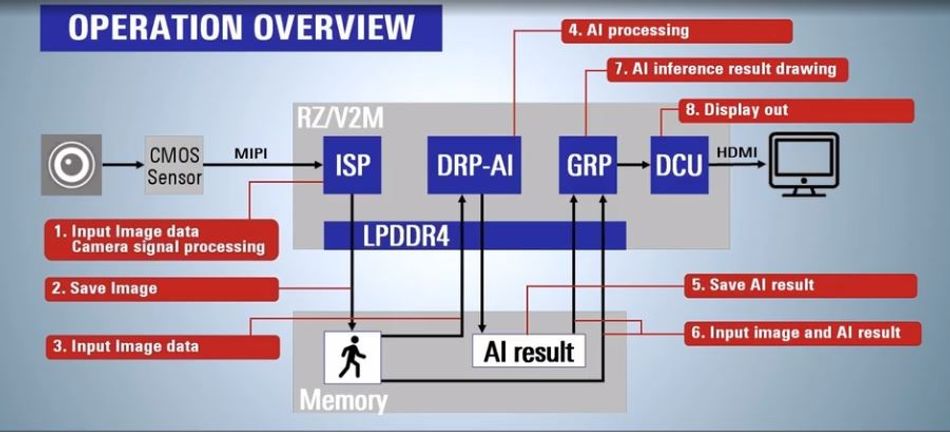
The overall data flow for the operation is straightforward, and the setup in the case study described is shown below:
The image below provides a graphical representation of how the operation works in a Renesas Embedded AI system for a cash register using Renesas’ RZ/V2M AI Microprocessors:
In the diagram above, input data moves from the Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)[10] image sensor through the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI)[11] to the embedded system. Afterward, the input images are sent to the Input Image data Camera signal processing (ISP) to improve and correct the quality of images received from the CMOS sensor.
The image is saved in the Double Data Rate (DDR)[12] memory—1200kb is typically sufficient for the entire operation—and then the stored image is passed to Renesas’ AI Accelerator, the DRP-AI[13]. The DRP-AI—which consists of AI-MAC (multiply-accumulate processor) and DRP (reconfigurable processor)—performs inference using AI models that have been loaded into the memory in advance.
Then, the AI inference results are stored in the DDR memory before being sent, alongside the corrected image data processed by the ISP, to a 2D graphics engine. The graphics engine handles the AI inference result drawing and combining image data with AI inference results.
Finally, the Display Control Unit (DCU) outputs the processed image data to a monitor via High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI).
A retailer could design their own neural network models to accommodate their business needs if open-source frameworks like Tiny-YOLOv2 are unsuitable. These frameworks—technically called proprietary AI Model Development Environments—can be trained and connected to Renesas’ AI microprocessor. However, there’s also the choice to modify open-source models for use in any environment.
Summary
AI-driven microprocessor units—particularly Vision AI-powered technology like those offered by Renesas—have the potential to deliver a low-cost, highly efficient, frictionless shopping experience. After all, in light of recent incidents like the Covid-19 pandemic, more businesses are starting to see the positive impacts of computer technology on the retail landscape.
Embedded AI technologies like Renesas’ RZ/V microprocessors described in this article could improve safety, save time, and ensure customer satisfaction. You can learn more about how Renesas is making strides in Vision AI development and learn how to set up your own Artificial Intelligence microprocessor unit here.
About the sponsor: Renesas
At Renesas we continuously strive to drive innovation with a comprehensive portfolio of microcontrollers, analog and power devices. Our mission is to develop a safer, healthier, greener, and smarter world by providing intelligence to our four focus growth segments: Automotive, Industrial, Infrastructure, and IoT that are all vital to our daily lives, meaning our products and solutions are embedded everywhere.
References
1. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8588224
2. https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/what-is-artificial-intelligence
3. https://info.support.huawei.com/info-finder/encyclopedia/en/EAI.html
4. https://www.fierceelectronics.com/electronics/what-embedded-ai
6. https://www.walmart.com/cp/walmart-pay/3205993
7. https://gallery.azure.ai/Model/Tiny-YOLOv2
8. https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/convolutional-neural-networks
10. https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/CMOS-sensor
11. https://www.e-consystems.com/blog/camera/technology/what-is-a-mipi-camera-how-does-mipi-camera-work/
12. https://www.microcontrollertips.com/understanding-ddr-sdram-faq/
13.https://www.renesas.com/solution/technologies/ai-accelerator-drp-ai
14. https://www.forbes.com/sites/honeywell/2021/01/29/why-the-future-of-retail-is-frictionless/
15. https://www.renesas.com/video/rzv2m-ai-object-detection-demo-cash-register