The Critical Role of Precision Gears in Robotics
Precision gears drive the performance of robotic systems. Find out how choosing the right gear design enables higher accuracy and long-term durability.
Introduction
From manufacturing lines and medical devices to packaging and transport systems, robots play a vital role in various sectors that affect our lives. These robots rely on robust mechanical systems to achieve quick, accurate, and reliable movement. Among the essential components of these systems are the gearboxes, which provide the precise torque and positioning required for robotic applications.
This article explores the importance of precision gears in robotics and explains how to choose the right gear for each application. It also explains how global leader Nabtesco is driving innovation through advanced gear designs tailored for high-performance robots.
The Role of Precision Gears in Robotics
Robots need precision gears to withstand rapid motion, sudden acceleration, and heavy loads. These gears must work smoothly and reliably, even after millions of cycles. To ensure this, these components have to meet strict performance standards. They need high torsional and moment rigidity to maintain stability during complex tasks. They also have to withstand shock loads and sudden force changes without losing accuracy.
Since robots are compact machines, space is another challenge. Gears need to be small and lightweight without sacrificing strength or precision. That’s why precision gears are the preferred choice owing to their high efficiency and minimal backlash.
Nabtesco's Robotic Gears
For robotics applications, Nabtesco offers specialised sets of the RV-N solid-shaft and RV-C hollow-shaft series, designed for 6-axis robots.
Their unique design delivers power transmission without compromising on rigidity and transmission precision. The cycloid stage, consisting of two offset cams, also makes the gearboxes insensitive to shock loads and enables high-acceleration torque.
A special feature of the RV-C series is the large hollow shaft with a diameter of up to 138 mm for the feedthrough of power cables and supply lines. Instead of remaining rigid, the shaft is designed to rotate at the output speed. The advantage is that the drive shaft position can be determined directly by a sensor on the hollow shaft.
You can find more information about the RV-C series here and the RV-N series here!
Choosing the Right Gears
Gears are used in many different robotic applications, but not all gears suit every task. Gears that perform well in a high-speed pick-and-place operation might not meet the precision requirements of a welding or painting robot. Therefore, when selecting gears for robots, it is important to conduct a detailed analysis of the specific requirements.
It is ideal to begin with the key parameters of robots. The most important factor is the payload, which defines the maximum weight the manipulator can carry. Other critical parameters include rated torque, speed, acceleration, overshoot, positioning accuracy, and repeatability. It is also important to determine whether a hollow shaft is needed to accommodate cables and hoses.
Key Technical Considerations
Positioning Accuracy and Repeatability
Positioning accuracy indicates the precision with which a desired position can be reached. Repeatability describes the degree of precision when a position is approached repeatedly with the same speed and acceleration. Nabtesco’s precision gears feature very low backlash, typically 0.1–0.2 arcmin. This high precision ensures reliable performance even during continuous, high-speed operations.
Backlash, Hysteresis Loss, and Lost Motion
Backlash and hysteresis loss refer to the slight twist that can occur at a gearbox's output shaft when the input shaft is fixed. These factors help measure the precision of a gearbox. Hysteresis loss is the angular tolerance between the input and output shafts at 0 Nm torque, which is the sum of backlash and friction. Crucial factors affecting backlash are the gearbox design and the precision of the manufacturing process. Lost motion describes torsional rigidity at low torques.
Rated Torque and Acceleration Torque
To perform operations, robot arms constantly move, speeding up or slowing down. To ensure smooth operations, they need acceleration torque, along with rated torque and emergency stop torque. It is important to note that the acceleration time and the life of the gearbox are directly related. In Nabtesco solutions, both parameters are balanced. The gears are built to support fast acceleration while providing durability and resistance to shock loads.
Gear Reduction Ratio
Servo motors generally drive the robot axes. However, their specific speeds and rated torque often don’t match the requirements of a robotic system. Gears step in to ensure the required torques and speeds are achieved. A higher reduction ratio increases the average and maximum torque at the gearbox output shaft and reduces the average and maximum speed of the servo motor.
Implementation in a 6-Axis Articulated Robot
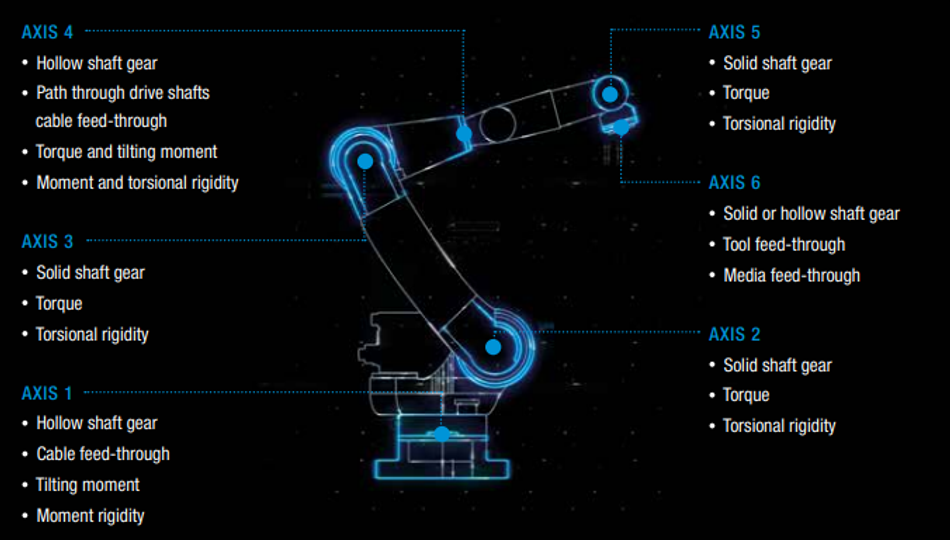
The six-axis articulated arm robot is the most common type in the industry. It belongs to the class of serial kinematics with three vertical and three horizontal rotary axes. The axes 1–3 position the robot’s base, while axes 4–6 orient the tool or effector. Let’s break down the technical considerations that influence the choice of the gearbox for each axis:
Main Axes (Axes 1 to 3)
The main axes give the robot its structural strength and stability. Their gearboxes must therefore be both robust and precise.
Axis 1 (Base)
Gears here are usually hollow shaft designs. This design is practical as it allows power and data cables to pass through the gearbox.
Axes 2 and 3
These axes use solid shaft gears. Without the need for cable or hose feed-throughs, engineers can achieve a smaller, more efficient design. High torque and excellent torsional rigidity are top priorities for the main axes.
Hand Axes (Axes 4 to 6)
The hand axes drive the end-effector of the robot. They require a lightweight, compact design, as every extra kilogram in these axes can affect performance.
Axis 4 (Connecting Link)
Hollow shaft gears are often used. This design reduces weight while providing strong torque and high moment rigidity.
Axes 5 and 6 (Final Joints)
These gears focus on compactness. Depending on the application, they may use either solid or hollow shaft designs. The design here is key to maintaining fast, precise movements while minimising wasted space.
This structured approach ensures that each axis gets a tailored solution. The gears are chosen based on load requirements, motion dynamics, and available space. By matching gear designs to each axis, engineers can optimize performance across the entire system.
Most Commonly Implemented Gears in Robotics?
There are two types of gears on the market: cycloidal gears and strain wave gears. The optimal type depends on the requirements of the application. If high positioning accuracy or rigidity are important requirements, for example, cycloidal gears deliver better performance across the board. With rated torques from 100 to 28,000 Nm, they also offer a larger performance range. Strain wave gears are ideal in low-torque applications, especially where high performance is needed in compact spaces.
Conclusion
Precision gears are the backbone of modern robotics, enabling the seamless interaction between power, motion, and control. Whether it's executing movements with pinpoint accuracy or operating reliably over millions of cycles, the right gearbox makes all the difference.
As illustrated by the example of a six-axis robot, it's clear that gear selection depends on the unique requirements of each axis. That’s where Nabtesco stands out. The company's RV-N and RV-C series gearboxes are explicitly designed for robotic applications, combining high torque capacity, extreme torsional rigidity, and low backlash. For more information, Nabtesco offers different white papers.
By matching the right gears to each robotic task, Nabtesco helps robots perform better, last longer, and work more reliably across a wide range of industries.