Context-Aware Industry: Bridging Consumer-Grade Intelligence into Industrial Environments
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) has moved from niche industrial RTLS to mainstream, with easier deployment via enterprise access points and standards. Discover how UWB is transforming asset tracking, logistics, and manufacturing with cost-effective, sub-meter accuracy.
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) recently gained mainstream visibility through its use in consumer applications like secure vehicle access and gesture-based controls. But long before that, UWB’s first high-value applications were in industrial Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), where it delivered mature, field-proven solutions for years. Industries such as manufacturing and logistics have relied on UWB’s fine-ranging capabilities to track assets and personnel with sub-meter accuracy, even in complex, RF-dense environments.
What’s different today is not the technology itself, but how deployable it has become. Thanks to the integration of UWB into enterprise access points (EAPs) and the emergence of multi-vendor standards, industrial infrastructure that once required specialized hardware can now be deployed more quickly and cost-effectively. Reducing installation complexity and upfront investment opens the door for broader RTLS adoption that extends well beyond high-value assets to everyday tools, mobile equipment, pallets, and people. Once the fixed infrastructure is in place, the incremental cost of tracking more things drops significantly, maximizing ROI.
At the same time, factories, warehouses, and logistics hubs are increasingly complex, high-throughput spaces. Here, UWB’s technical strengths of sub-meter precision, low latency, and non-line-of-sight performance in dense, metallic, multipath environments offer a substantial edge over legacy technologies like RFID or Bluetooth Low Energy.
In this context, UWB has become a foundational technology for what’s emerging as the “context-aware” industry. In this paradigm, physical environments go beyond reporting status to actually inferring behavior, detecting movement, and responding dynamically. Whether identifying the exact location of a tool or rerouting mobile robots based on real-time congestion, context-aware systems rely on spatial intelligence to make smarter decisions. With UWB, these systems introduce predictive optimization and consumer-grade intelligence to industrial scale.
Application 1: Worker Safety and Geofencing
Worker safety is one of the most compelling applications for UWB in industrial environments, as real-time awareness can make the difference between a safe operation and a serious incident.
To this end, UWB-powered Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) offer sub-meter accuracy that allows facilities to track the live position of personnel in complex, fast-moving environments. Whereas legacy systems rely on fixed zones or low-resolution proximity sensors, UWB provides a dynamic map of worker movement, regardless of obstructions or in non-line-of-sight conditions. By providing such a detailed spatial understanding, UWB guarantees that every individual’s location is visible and actionable.
This positional awareness powers geofencing systems that monitor and intervene for worker safety. UWB geofences are live digital boundaries that automatically trigger alerts when workers approach high-risk zones or dangerous equipment. In environments with autonomous mobile robots or forklifts, UWB location data can be used to automatically slow or reroute machines, or shut down operations if a worker enters a restricted area.
A real-world example of this architecture comes from Hyundai’s Gwangju Global Motors facility. There, Geoplan’s G-Pixel tags – built on Qorvo’s ultra-low power UWB and connectivity SoCs – are mounted on vehicles to communicate process status across the assembly line. The same tags can be used to unlock personnel tracking and dynamic safety enforcement in vehicles and wearables.
Incorporating UWB into personal protective equipment (PPE) adds another layer of intelligence to the equation. Tags embedded into hard hats, vests, or ID badges can trigger real-time alerts if someone enters a no-go zone, falls, or becomes immobile. These smart PPE systems support automated compliance monitoring and incident detection to minimize response times in emergencies and help facilities be more proactive in their approach to safety.
Application 2: Asset and Tool Tracking
Visibility is non-negotiable in industrial envrionments, yet it remains difficult to achieve. Modern factories are metallic, rife with obstructions, and full of RF devices competing for signal path. Where the standard operating environment is interference prone, traditional technologies like BLE and passive RFID are not viable. UWB, on the otherhand, offers a compelling alternative. With sub-meter accuracy and refresh rates as fast as 333 milliseconds, it performs reliably in the dense RF environments and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) conditions that have become the norm in complex factory floors and storage facilities.
By embedding UWB tags in assets and integrating them with inventory and maintenance systems, manufacturers can gain true visibility into the location and status of tools, parts, and vehicles. Meanwhile, improvements in tracking, utilization, availability, and predictive maintenance allow operators to realize benefits like fewer lost tools and better-informed decisions across operations.
Volkswagen Slovakia provides a strong case study of UWB in action. Working with CEIT and Qorvo, the factory deployed a UWB-based RTLS across its Bratislava facility in just six months. The system tracked both assets and fleets with 99.98% reliability, even in reflective and metallic production zones. With live visibility into travel distances, idle times, and utilization rates, VW was able to optimize fleet routes and identify inefficiencies.
The impact was substantial: warehouse layout efficiency improved by 20% without physical expansion, and fleet travel distances were reduced by 10%. UWB tags used in the system offer over a year of battery life, and the resultant reduction in maintenance requirements notably lowered the company’s total cost of ownership.
With the infrastructure in place, VW is now exploring new applications such as worker and visitor tracking and part-level traceability. Because UWB systems are highly scalable, expanding use cases will require minimal changes to their physical infrastructure.
Application 3: Production Line and Warehouse Optimization
Production environments rely on the continuous movement of assets to keep operations flowing. Any disruption or inefficiency in that movement can impact output, delivery schedules, and ultimately, profitability. With live spatial awareness enabled by UWB, task coordination becomes far more efficient.
For example, UWB data can inform congestion-aware routing for mobile fleets, reassign AMRs based on queue density, or optimize shift-based workflows depending on floor utilization. With this level of transparency, layout changes can be guided by real-world movement data rather than assumptions, helping teams continuously fine-tune production and logistics.
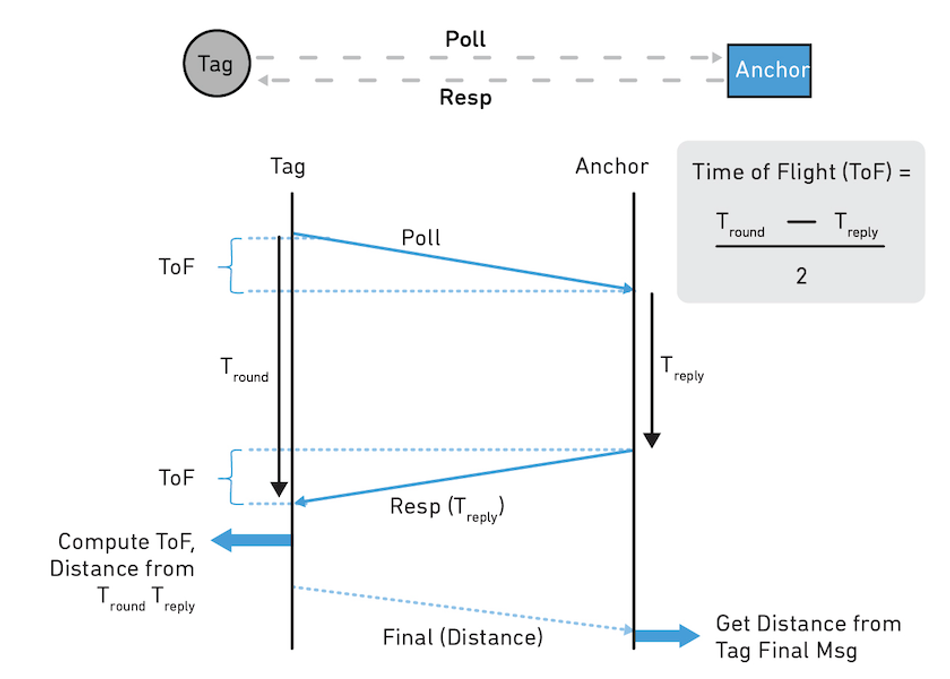
UWB’s underlying architecture offers technical advantages as well. With UWB, time-of-flight ranging techniques like Two-way ranging (TWR) and time difference of arrival (TDoA) can be employed to significantly minimize signal degradation caused by reflections in cluttered or metallic environments. As a result, compared to other RTLS options, UWB systems require fewer homing anchors to cover large areas and, therefore, make deployment both scalable and cost-effective.
Budweiser Budvar Brewery demonstrated this approach when it replaced a legacy RFID system with UWB-based RTLS to address warehouse complexity and SKU diversity. The brewery achieved a 19% improvement in both uptime and warehouse space utilization. Forklift movements and inventory were tracked with 30 cm accuracy, and the location data was integrated into the company’s ERP system to support analytics and planning.
What’s more, the system was installed and integrated within months, showing how UWB affords quick wins while laying the groundwork for long-term optimization. As operations shift from reactive to predictive, UWB provides a path for leaner, more agile production lines.
System Integration and Network Considerations
UWB needs to integrate smoothly with the broader enterprise infrastructure if it’s ever to truly deliver on the promise of real-time spatial intelligence. Increasingly, that’s exactly what’s happening. For example, major network providers like Cisco and Juniper are embedding UWB into their enterprise Wi-Fi access points to achieve native positioning capabilities without dedicated UWB gateways or standalone anchors. With tighter integration, companies are reducing deployment complexity and lowering the barrier to adoption in large-scale industrial environments.
“Qorvo has brought together all partners across the RTLS ecosystem to make it easier and faster for customers to deploy real-time location solutions, and to get more return from their investment.” says Shadi Hawawini, Director of Ecosystem Development at Qorvo
Equally important is UWB’s ability to coexist with other key IoT protocols. Industrial and enterprise systems often run a mix of Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Thread, and now Matter. Qorvo’s solution to this complexity is its ConcurrentConnect technology, which allows multiple protocols to operate simultaneously on separate channels, with no noticeable latency or interference. This means that a single SoC can handle multiple connectivity layers in parallel in a way that is simple and doesn’t sacrifice responsiveness.
Additionally, ConcurrentConnect offers exceptional performance under load. In environments with dense wireless traffic and real-time control demands, channel contention can cause delays or failures. Qorvo’s architecture isolates protocols at the hardware level so that location services, sensor data, and command/control traffic all maintain their integrity.
ConcurrentConnect also offers Antenna Diversity, which improves receiver sensitivity by 8-12 dB to maintain reliable connectivity in environments filled with RF interference, reflections, and multipath fading. Where competitors rely on external switches or software-based selection, Qorvo implements fast, hardware-based antenna selection based on signal-to-noise ratio. This approach boosts performance in noisy environments and reduces energy consumption by up to 18% by minimizing retries.
By embedding UWB into existing infrastructure and supporting true multiprotocol operation, Qorvo makes it possible to build robust, context-aware systems that are ready to scale without forcing trade-offs between interoperability and real-time responsiveness.
Conclusion: UWB as a Core Enabler of Industry 4.0
UWB is a mature, field-proven solution that is already impacting industrial environments. With the ability to deliver high precision, real-time spatial awareness, UWB is unlocking a new generation of context-aware systems. In such environments, adopting UWB translates directly into real-world advantages, including increased safety, smarter workflows, higher asset utilization, and leaner operations..
Qorvo’s comprehensive portfolio combines fine-ranging, radar-based sensing, and secure connectivity into a unified platform. Meanwhile, its UWB-enabled SoCs, such as the QM35825, support low-power, AI-enhanced applications that blend location awareness with contextual decision-making. And with native support for RTLS, Matter, Zigbee, Thread, and BLE, Qorvo’s ConcurrentConnect technology guarantees that these systems operate cohesively in multi-protocol environments.
Want to learn more about Qorvo’s UWB solutions? Discover UWB.