The Rise of Generative AI and Enhanced Phishing Schemes
Generative AI has opened up an entirely new world of cybersecurity threats.
In recent years, the rise of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been nothing short of revolutionary. This technology, capable of producing content that closely mimics human output, has paved the way for innovations across various fields. From writing convincingly real emails to creating impressive images, generative AI's capabilities are vast and transformative.
However, as with any technological advancement, there are two sides to the story. The same capabilities that offer numerous benefits also pose significant risks, particularly concerning cybersecurity. Specifically, one of the most concerning developments has been the enhancement of phishing schemes, making them more sophisticated and challenging to detect than ever before. This article explores the rise of generative AI, how it's changing the phishing landscape, and best practices to avoid becoming a victim.
The Evolution of Generative AI
Generative AI is marked by its ability to learn from a vast dataset of existing digital content and generate new, unique outputs that can pass for human-created. This process involves complex algorithms and neural network models that analyze patterns, styles, and structures within the data they're fed. As a result, generative AI can produce a wide range of outputs, including textual content, images, music, and even synthetic voices. Its applications are far-reaching, offering potential benefits in areas such as content creation, entertainment, education, and beyond. [1]
However, the power of generative AI extends beyond positive use cases. Its very capabilities, particularly in mimicking human communication styles and generating personalized content, have opened new avenues for cybercriminals. These advancements have led to a new generation of phishing attacks that are significantly more difficult to identify and combat.
The Transformation of Phishing Tactics
Phishing schemes have long been a staple in the arsenal of cybercriminals. Traditionally, these attacks involved sending generic, often poorly written emails, attempting to lure recipients into divulging sensitive information or downloading malicious software. While effective to a degree, these attempts were easier to spot and avoid due to their lack of personalization and sophistication. [2]
Enter generative AI, and the landscape of phishing has changed dramatically. With the ability to analyze and replicate communication styles, generative AI enables cybercriminals to craft highly convincing and personalized messages. These messages can mimic the tone, style, and even specific phrases used by individuals or organizations, making them far more likely to deceive recipients.
Understanding AI-Enhanced Phishing
The core threat of AI-enhanced phishing is its personalization and realism. Generative AI can create emails, text messages, or social media messages that look and sound like they're from a trusted source, such as a colleague, friend, or a reputable organization. This level of personalization is achieved by analyzing publicly available data or previously breached information to tailor attacks to individual targets. [3]
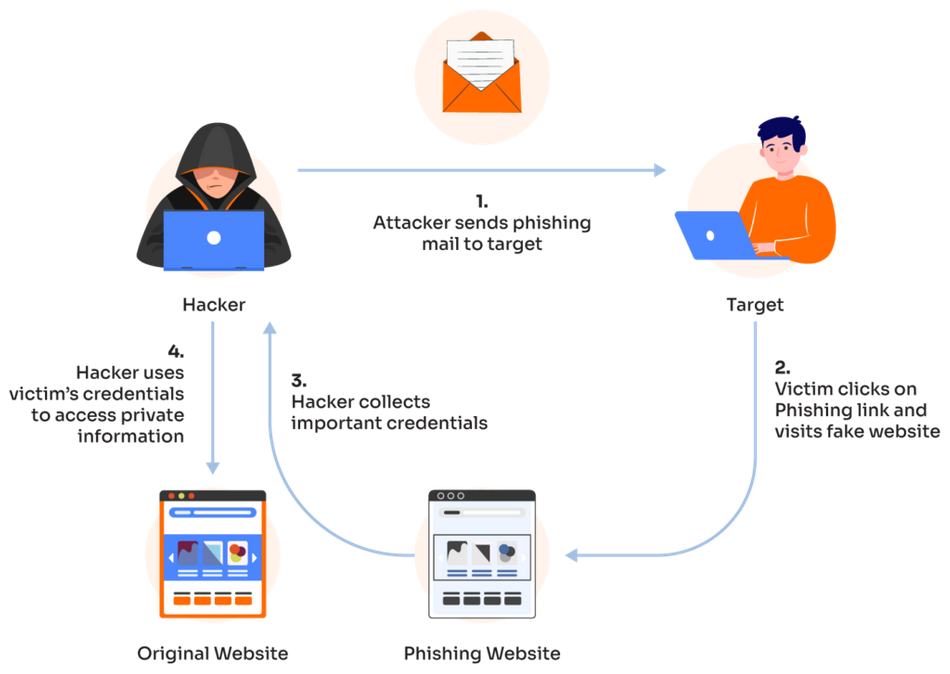
Phishing attacks begin with tricking users out of their important credentials. Image credit: Vailmail
For instance, a generative AI-powered phishing email might reference recent transactions, use language that matches the supposed sender's usual tone, or mimic the layout and design of legitimate correspondence. With such attention to detail, these fraudulent messages are incredibly persuasive, increasing the likelihood that recipients will comply with their requests, whether that involves providing passwords, financial information, or other sensitive data.
The Signs of AI-Generated Phishing Attacks
Despite their sophistication, AI-generated phishing attacks are not foolproof. There are still telltale signs that can help discerning individuals identify them. These include slight inconsistencies in language or format, unusual requests, or links to websites that, upon closer inspection, have subtle differences from legitimate addresses. Moreover, these messages might lack the personal touch or in-depth knowledge that genuine communications from friends or colleagues would have, relying instead on information that could be publicly accessed or inferred.
Strategies for Personal and Organizational Protection
Naturally, the advancement of AI-enhanced phishing schemes necessitates stronger defensive measures, both at personal and organizational levels. Awareness is the first step; understanding that no one is immune to these attacks is crucial. From there, adopting a multi-layered approach to security can significantly mitigate risks. [4]
For individuals:
Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Communications: Always approach unexpected requests for information or action with caution, even if they appear to come from known contacts or organizations.
Verify Independently: If a message asks for sensitive information or to perform a specific action, verify its authenticity through an independent channel. For example, if you receive an email from your bank asking for personal details, contact the bank directly using a phone number from their official website.
Use Advanced Security Features: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible. This adds an extra verification step that can protect your accounts even if your password is compromised.
Regularly Update Software: Ensure that your operating system, applications, and anti-virus software are up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
For organizations:
Conduct Regular Training: Employees should be regularly trained on the latest cybersecurity threats and how to recognize phishing attempts. Simulated phishing exercises can be particularly effective.
Implement Strict Information Handling Policies: Limit the amount of personal and sensitive information that can be shared or accessed based on job roles.
Adopt Advanced Security Technologies: Utilize email filtering, intrusion detection systems, and AI-based security solutions that can identify and block phishing attempts.
Establish Clear Reporting Procedures: Employees should know how to report suspected phishing attempts promptly, allowing IT security teams to respond quickly.
The Role of Continuous Education
As generative AI continues to evolve, so too will the tactics used by cybercriminals. For this reason, staying informed about the latest developments in AI and cybersecurity is essential. For individuals, this means staying abreast of the latest security advice and best practices. For organizations, it involves regular training sessions and updates on cybersecurity trends and threats. [5]
Awareness campaigns, workshops, and online courses can play significant roles in educating the public and employees about the dangers of AI-enhanced phishing schemes and how to protect against them. Knowledge is power, and in the context of cybersecurity, it's also the best defense.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
The dual-use nature of generative AI in cybersecurity presents a continuous game of cat and mouse between cybercriminals and defenders. As AI technologies become more sophisticated, so too do the tools and strategies to combat malicious use. Future developments in AI could offer more robust detection mechanisms, identifying and neutralizing phishing attempts before they reach their intended targets. Similarly, advancements in natural language processing could enable more effective filtering of phishing content, while machine learning models might predict and block new phishing tactics.[6]
However, as technology advances, the complexity and novelty of phishing attacks will likely increase as well. A proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity, emphasizing technological solutions and human vigilance and education, will be necessary to combat these advances.
Conclusion
The rise of generative AI has brought with it an era of enhanced phishing schemes, presenting new challenges in the realm of cybersecurity. While these sophisticated attacks pose significant risks, the combination of advanced security measures, continuous education, and heightened awareness provides a formidable defense. As we navigate this evolving landscape, staying informed, cautious, and prepared is essential for protecting personal and organizational integrity in the digital age. Through collective effort and the strategic application of technology, we can mitigate the threats posed by AI-enhanced phishing and secure our digital future.
References
https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/definition/generative-AI
https://consumer.ftc.gov/articles/how-recognize-and-avoid-phishing-scams
https://www.cisa.gov/secure-our-world/teach-employees-avoid-phishing
https://sennovate.com/the-role-of-artificial-intelligence-in-detecting-phishing-attacks/